Welcome to Chapter 23 of our comprehensive guide on women’s health. In this chapter, we will discuss the gynecologic examination and prenatal care, two crucial aspects of women’s healthcare. Understanding these topics is essential for both healthcare professionals and women seeking to take charge of their own reproductive health.
The gynecologic examination is a regular check-up that focuses on a woman’s reproductive organs. This examination allows healthcare providers to assess any potential issues, such as infections, abnormalities, or reproductive health disorders. By conducting a thorough examination, healthcare professionals can detect conditions early on and provide appropriate treatment, improving overall health outcomes.
Prenatal care, on the other hand, is specifically tailored for pregnant women. This type of care emphasizes the health and well-being of both mother and baby throughout the entire pregnancy journey. Regular prenatal visits and screenings help monitor the development of the fetus, detect any potential complications, and provide necessary interventions or support.
Join us as we delve into the details of the gynecologic examination and prenatal care. We will explore the various components of these examinations, their importance, and how they contribute to maintaining women’s reproductive health and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Let’s empower ourselves with knowledge and take proactive steps towards our well-being.
Chapter 23: The Gynecologic Examination and Prenatal Care
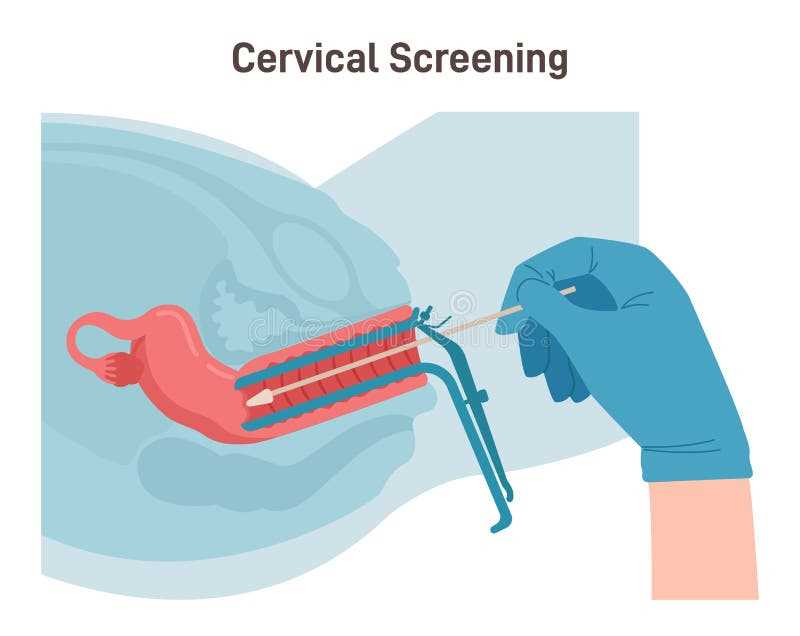
The gynecologic examination is a crucial aspect of women’s healthcare, allowing healthcare providers to assess and monitor their reproductive health. In Chapter 23, we delve into the various components of the gynecologic examination, including the pelvic examination and Pap smear. These procedures enable healthcare providers to detect any abnormalities or diseases, such as cervical cancer or sexually transmitted infections.
During the gynecologic examination, healthcare providers also discuss prenatal care with their patients. Prenatal care is vital for ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. This chapter explores the importance of prenatal care, covering topics such as frequency of visits, necessary screenings, and preventive measures. Through early detection and intervention, healthcare providers can mitigate risks and promote a healthy pregnancy.
The pelvic examination: The gynecologic examination typically begins with a pelvic examination, during which the healthcare provider examines the external and internal reproductive organs. This includes visual inspection, palpation, and assessment of the cervix, uterus, and ovaries. The pelvic examination allows for the evaluation of any abnormalities, such as cysts or tumors, and helps identify potential reproductive health concerns.
The Pap smear: Another important component of the gynecologic examination is the Pap smear, also known as cervical cytology. This screening test involves collecting cells from the cervix to detect abnormal changes or signs of cervical cancer. The results of the Pap smear can guide further diagnostic procedures or interventions to ensure early detection and treatment, if necessary.
- Benefits of prenatal care: Prenatal care plays a critical role in promoting a healthy pregnancy and minimizing potential risks and complications. Regular visits to healthcare providers allow for the monitoring of the mother’s health, identification of any existing medical conditions, and addressing any concerns or questions.
- Frequency of visits: The frequency of prenatal care visits may vary depending on the patient’s health status and the stage of pregnancy. Healthcare providers typically recommend monthly visits during the first and second trimesters, and more frequent visits as the pregnancy progresses. These visits allow for the monitoring of the baby’s growth and development, as well as the mother’s blood pressure, weight, and overall well-being.
- Screenings and preventive measures: Prenatal care visits also involve various screenings and preventive measures to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the baby. These may include blood tests, ultrasounds, genetic screenings, and vaccinations. Additionally, healthcare providers provide guidance on prenatal nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle modifications to promote a healthy pregnancy.
In conclusion, Chapter 23 explores the gynecologic examination and prenatal care, highlighting the importance of these aspects in women’s healthcare. By conducting thorough gynecologic examinations and providing comprehensive prenatal care, healthcare providers can contribute to the early detection of reproductive health issues, ensure a healthy pregnancy, and ultimately improve the overall well-being of women.
The Importance of Regular Gynecologic Examinations
Regular gynecologic examinations are an essential part of women’s overall health and wellness. These examinations, also known as well-woman exams, provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to assess and monitor a woman’s reproductive health, including the prevention, detection, and treatment of various gynecologic conditions.
Gynecologic examinations typically include a discussion of the patient’s medical history, a physical examination, and various tests and screenings, such as cervical cancer screening (Pap test), breast examination, pelvic examination, and sexually transmitted infection (STI) testing. These examinations allow healthcare providers to identify any potential issues or abnormalities early on, which can lead to more effective interventions and better health outcomes.
One of the main reasons why regular gynecologic examinations are important is the early detection of gynecologic cancers, such as cervical, ovarian, and uterine cancers. Cervical cancer, for example, is highly preventable and can be detected early through routine Pap tests. When detected early, the chances of successful treatment and survival increase significantly.
In addition to cancer prevention and early detection, regular gynecologic examinations also play a crucial role in monitoring and managing various reproductive health concerns, such as menstrual irregularities, hormonal imbalances, pelvic pain, and sexually transmitted infections. By addressing these issues promptly, healthcare providers can help improve women’s quality of life and overall well-being.
Furthermore, regular gynecologic examinations provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to educate women about contraception, family planning, and prenatal care. By discussing these topics during examinations, healthcare providers can empower women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health and take necessary steps to prevent unplanned pregnancies or ensure a healthy pregnancy.
In conclusion, regular gynecologic examinations are essential for maintaining women’s reproductive health and preventing and detecting various gynecologic conditions. These examinations enable healthcare providers to address any concerns or abnormalities early on, leading to better outcomes and improved overall well-being for women.
Preparing for a Gynecologic Examination
Before undergoing a gynecologic examination, it is important for women to be mentally and physically prepared. This involves taking certain steps to ensure their comfort and ease during the examination. Wearing comfortable clothing, such as a loose-fitting dress or skirt, can make the experience more pleasant. It is also recommended to use the restroom before the examination, as a full bladder can interfere with certain tests.
In addition to physical comfort, it is crucial for women to mentally prepare themselves for the examination. Some women may feel anxious or embarrassed about the procedure, but it is important to remember that gynecologic examinations are routine medical procedures performed by professionals who prioritize patient comfort and privacy.
During the examination, the gynecologist will ask the patient about her medical history, including any medications or allergies. It is important for women to be honest and open about their medical history, as this information can affect the course of the examination. The gynecologist will also explain each step of the examination and may ask for consent before performing certain procedures or tests.
In conclusion, being mentally and physically prepared for a gynecologic examination is key to ensuring a comfortable and successful experience. Women should prioritize their own comfort by wearing appropriate clothing and using the restroom beforehand. It is also important to be mentally prepared and honest about one’s medical history. By following these steps, women can approach the examination with confidence and ease.
The Components of a Gynecologic Examination
A gynecologic examination is an essential part of women’s healthcare, allowing healthcare providers to assess reproductive health, detect any abnormalities, and provide necessary care and treatment. It typically consists of various components, each serving a specific purpose.
Medical History: Before conducting the examination, the healthcare provider will usually begin by asking the patient about her medical history, including any previous gynecologic issues, surgeries, pregnancies, or chronic conditions. This information helps establish a baseline and provides important context for the examination.
External Examination: The healthcare provider will then perform an external examination, which involves visually inspecting the external genitalia for any signs of infection, irritation, or abnormalities. This includes checking the vulva, pubic hair, and surrounding skin.
Pap Smear: A crucial part of the gynecologic examination is the Pap smear, which involves collecting cells from the cervix to screen for abnormal changes that may indicate cervical cancer or other cervical abnormalities. This test is recommended for women starting at the age of 21, or earlier if there are specific risk factors.
Bimanual Examination: The bimanual examination involves the insertion of two fingers into the vagina while the other hand is placed on the lower abdomen. This allows the healthcare provider to assess the size, shape, and position of the uterus and ovaries, as well as check for any abnormalities or signs of tenderness.
Speculum Examination: The speculum examination involves the insertion of a speculum into the vagina to visualize the cervix and vagina. This allows for a closer assessment of the cervix, such as checking for any polyps, ulcers, or abnormal discharge. It also provides the opportunity to collect additional samples for further testing if necessary.
Breast Examination: While not directly related to the gynecologic examination, a breast examination is often performed as part of overall women’s health assessment. This involves visual inspection and palpation of the breasts and surrounding areas to check for any lumps, changes in size or shape, or other abnormalities that may indicate breast disease.
Overall, a gynecologic examination is a comprehensive assessment of a woman’s reproductive health that aims to detect any abnormalities, provide preventive care, and ensure early intervention and treatment when necessary. It is important for women to undergo regular gynecologic examinations as recommended by their healthcare providers to maintain optimal health and well-being.
Understanding Prenatal Care
During pregnancy, regular prenatal care is essential to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. Prenatal care includes a series of medical check-ups and screenings that are designed to monitor the progress of the pregnancy, identify any potential complications, and provide necessary interventions or treatments.
Antenatal visits: Prenatal care typically begins with the first antenatal visit, which is usually scheduled around 8-10 weeks of gestation. These visits are usually scheduled monthly during the first and second trimesters, and then more frequently during the third trimester. At each visit, the healthcare provider will assess the mother’s overall health, measure her blood pressure, check her weight gain, and monitor the growth and development of the fetus.
- Screenings and tests: Throughout the pregnancy, various screenings and tests may be conducted to detect any potential complications or genetic abnormalities. These may include blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound scans, and genetic screenings. These screenings and tests help identify any potential risks or complications and allow for appropriate intervention or treatment.
- Prenatal education and counseling: Prenatal care also involves providing education and counseling to the mother and her partner about nutrition, exercise, and general prenatal care. This includes information about healthy eating habits, the importance of staying active, managing stress, and preparing for childbirth. It also allows the mother to discuss any concerns or questions she may have with the healthcare provider.
- Preparing for childbirth: As the pregnancy progresses, prenatal care also focuses on preparing the mother for childbirth. This may involve discussing different birthing options, creating a birth plan, and attending childbirth classes. It also includes discussions about pain management during labor and delivery, and potential interventions that may be necessary.
Overall, prenatal care plays a crucial role in promoting a healthy pregnancy and reducing the risk of complications. By attending regular antenatal visits, undergoing necessary screenings and tests, and receiving education and counseling, the mother can make informed decisions about her health and the well-being of her baby. It is important for expectant mothers to actively participate in their prenatal care and communicate any concerns or questions they may have with their healthcare provider.
Why Prenatal Care is Essential for Pregnant Women

Prenatal care is an essential aspect of a healthy pregnancy. It involves regular medical check-ups, screenings, and education to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby. This care is important for detecting and managing any potential complications or health issues that may arise during pregnancy.
One of the main reasons why prenatal care is essential is that it allows healthcare professionals to monitor the development and growth of the baby closely. Regular check-ups and ultrasounds help determine if the baby is growing properly and if there are any abnormalities or concerns that need attention. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Prenatal care also plays a crucial role in identifying and managing any health conditions or risks that the mother may have. Through screenings and tests, healthcare providers can identify conditions such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and infections, among others. Timely detection and appropriate management of these conditions can help prevent complications and ensure a healthier pregnancy.
In addition to medical monitoring, prenatal care also provides important educational and support resources for pregnant women. It includes information on proper nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle choices that can promote a healthy pregnancy. Pregnant women also receive guidance on preparing for labor and delivery, breastfeeding, and postpartum care. All these aspects contribute to ensuring the overall well-being of the mother and her baby.
Overall, prenatal care is essential for pregnant women as it not only allows for close monitoring of the baby’s development but also helps identify and manage any health risks or complications. Education and support provided during prenatal care further contribute to a healthy pregnancy and a positive birth experience. Every pregnant woman should prioritize and take advantage of prenatal care to ensure the best possible outcomes for both herself and her baby.
What to Expect During Prenatal Care Visits
During prenatal care visits, pregnant women can expect to receive a variety of medical evaluations, screenings, and treatments to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. These visits play a crucial role in monitoring the progress of the pregnancy and identifying any potential complications early on.
The typical prenatal care schedule:
- First trimester (weeks 1-12): Monthly visits
- Second trimester (weeks 13-26): Bi-monthly visits
- Third trimester (weeks 27-40): Weekly visits
At each prenatal care visit, the healthcare provider will perform various checks and tests, including measuring blood pressure, monitoring weight gain, and measuring the size of the uterus. They will also listen to the baby’s heartbeat, assess the baby’s position, and check for any signs of swelling or other discomforts.
Additionally, prenatal care visits may involve various screenings and tests, such as blood tests to check for infections or genetic disorders, urine tests to monitor kidney function and detect any signs of gestational diabetes or preeclampsia, and ultrasounds to monitor fetal development and detect any abnormalities.
Throughout prenatal care, healthcare providers also provide education and counseling to pregnant women on various topics, including proper nutrition, exercise, and the importance of prenatal vitamins. They may also discuss the mother’s emotional well-being and provide resources for support.
In conclusion, prenatal care visits are essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and a safe delivery. By regularly monitoring the progress of the pregnancy, identifying any potential complications, and providing necessary education and support, healthcare providers can help expectant mothers have a positive prenatal experience and increase the likelihood of a successful outcome for both the mother and the baby.
Q&A:
What is prenatal care?
Prenatal care is the medical care and support provided to pregnant women to monitor and ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby.
How often should I have prenatal care visits?
Typically, prenatal care visits are scheduled once a month for the first 28 weeks of pregnancy, then every two weeks until 36 weeks, and finally every week until delivery.
What happens during prenatal care visits?
During prenatal care visits, the healthcare provider will check the mother’s blood pressure, weight, and urine for any signs of complications. They will also measure the size of the uterus, listen to the baby’s heartbeat, and may perform additional tests or ultrasounds as needed.
What kind of tests are done during prenatal care visits?
Some common tests done during prenatal care visits include blood tests to check for conditions such as anemia or gestational diabetes, urine tests to detect urinary tract infections or preeclampsia, and ultrasounds to monitor the baby’s growth and development.
Why is prenatal care important?
Prenatal care is important because it allows healthcare providers to monitor the mother’s and baby’s health, identify and address any potential complications or issues early on, and provide education and support for a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Regular prenatal care has been shown to improve pregnancy outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.