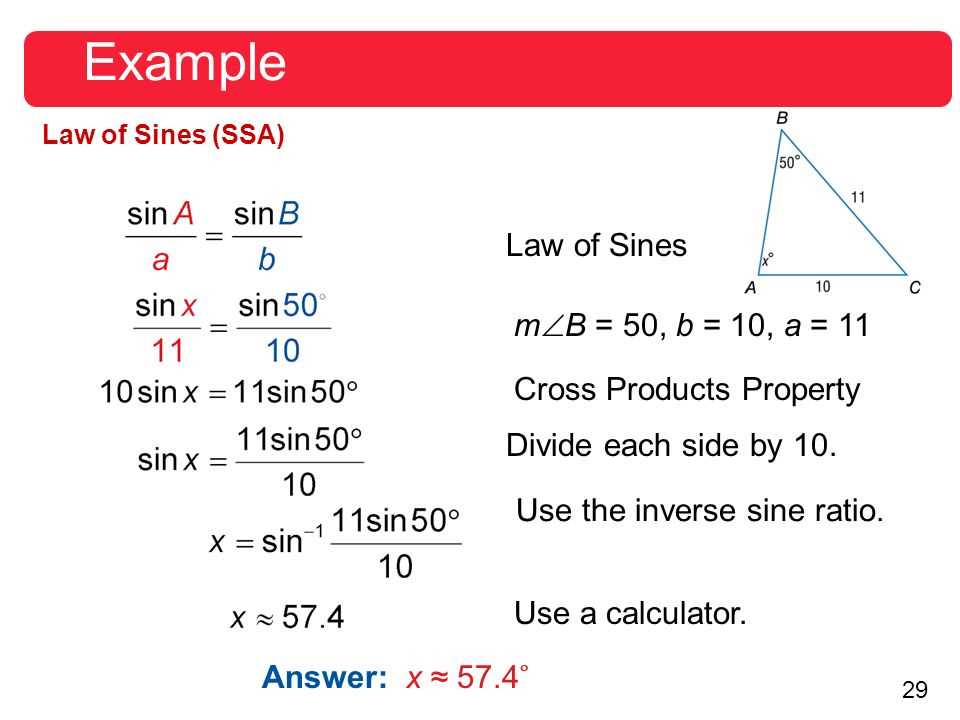
In mathematics, the law of sines is a fundamental relationship that relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the sines of its angles. It is a useful tool for solving trigonometric problems involving triangles, especially when only limited information is given.
The law of sines states that the ratio of the length of each side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. In other words, if we denote the lengths of the sides of a triangle as a, b, and c, and the angles opposite those sides as A, B, and C, respectively, then:
a / sin A = b / sin B = c / sin C
This relationship allows us to find missing side lengths or angles in a triangle when we have enough information. For example, if we know the lengths of two sides of a triangle and the measure of the angle opposite one of those sides, we can use the law of sines to find the measure of the other two angles.
Overall, the law of sines is a powerful tool in trigonometry that can be used to solve a wide range of problems involving triangles. Whether you’re working on a geometry homework assignment or trying to solve real-life applications of trigonometry, understanding and applying the law of sines can help you find the answers you need.
What is the Law of Sines and how does it work?
The Law of Sines is a fundamental concept in trigonometry that relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the sines of its angles. It states that the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of the angle opposite that side is constant for all three sides of the triangle. This law is particularly useful when solving triangles that are not right triangles.
To understand how the Law of Sines works, let’s consider a triangle with sides a, b, and c, and angles A, B, and C. According to the Law of Sines, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of the opposite angle is constant, so we have the following equations:
- a / sin(A) = b / sin(B) = c / sin(C)
These equations allow us to find the lengths of unknown sides or angles of a triangle when we have enough information. For example, if we know the lengths of two sides and the measure of the included angle, we can use the Law of Sines to find the length of the remaining side or the measures of the other two angles.
To use the Law of Sines, we can rearrange the equation to solve for a side or an angle. For example, to find the length of side a when we know the length of side b and the measures of angles A and B, we can use the equation:
- a = (b * sin(A)) / sin(B)
The Law of Sines is a powerful tool that allows us to solve a wide range of problems involving non-right triangles. It is especially useful in navigation, surveying, and engineering, where triangles are commonly encountered and their dimensions need to be determined.
Understanding the Law of Sines and its application in mathematics
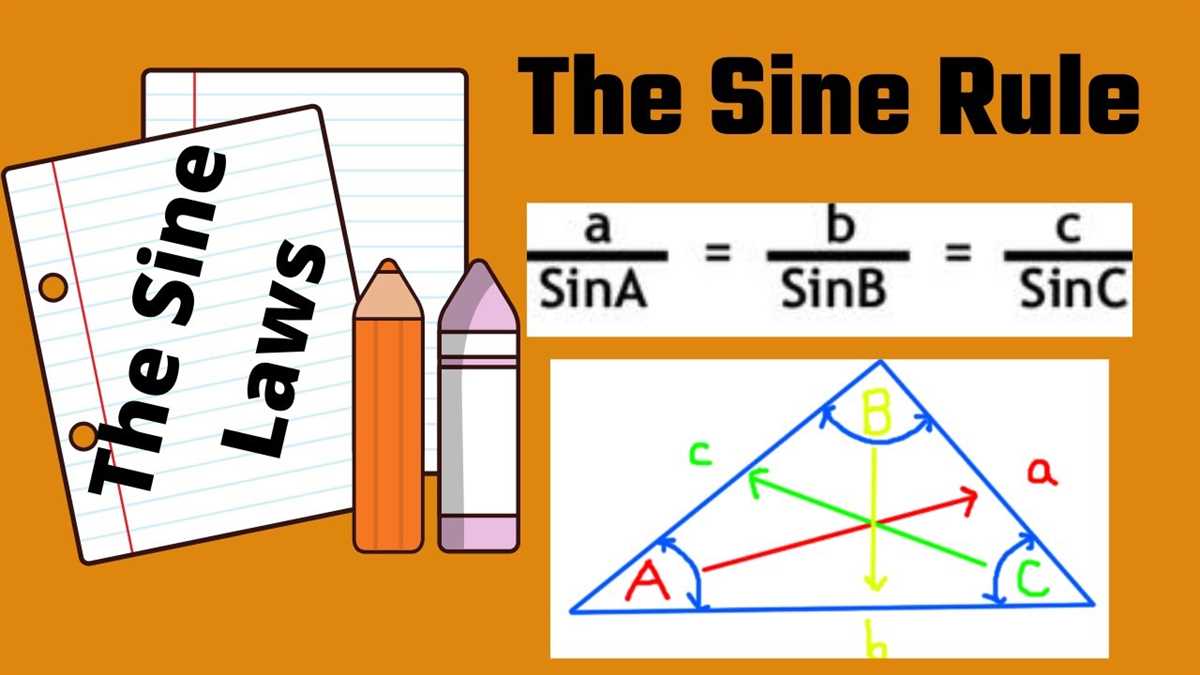
The Law of Sines is an important concept in trigonometry that helps us solve triangles when we have information about the lengths of sides and angles. This law is particularly useful when dealing with non-right triangles, also known as oblique triangles. By understanding the Law of Sines and its application in mathematics, we can solve various real-world problems involving triangles.
The Law of Sines states that the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. In mathematical terms, this can be expressed as:
a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) = c/sin(C)
where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and A, B, and C are the measures of the angles opposite to those sides, respectively.
Using the Law of Sines, we can solve for unknown side lengths or angle measures in a triangle. For example, if we know the lengths of two sides and the measure of an angle opposite to one of those sides, we can use the Law of Sines to find the measure of the other angle or the length of the remaining side.
Furthermore, the Law of Sines can be used to solve real-world problems involving triangles, such as determining the height of a mountain or the distance between two points. By applying trigonometric principles and utilizing the Law of Sines, mathematicians, engineers, and surveyors are able to accurately calculate and navigate various spatial and geometric scenarios.
Overall, understanding the Law of Sines and its application in mathematics allows us to effectively solve triangles and tackle real-world problems involving spatial measurements. By utilizing this fundamental trigonometric concept, we can enhance our problem-solving skills and gain a deeper understanding of the relationships between angles and sides in triangles.
How to solve for missing angles using the Law of Sines?
The Law of Sines is a trigonometric rule that relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the measures of its angles. It is especially useful when dealing with non-right triangles. According to the Law of Sines, the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of its opposite angle is a constant value.
To solve for missing angles using the Law of Sines, you need to have at least two angle-side pairs of information. Once you have this, you can set up and solve an equation using the Law of Sines. Here’s how:
- Identify the known angle-side pairs in the triangle. Let’s say we have an angle A and its opposite side a, and an angle B and its opposite side b.
- Write the Law of Sines equation using the known angles and sides: a/sin(A) = b/sin(B).
- Solve the equation for the missing angle by isolating it on one side of the equation. For example, if we are solving for angle A, we can rewrite the equation as sin(A) = a/sin(B) * b.
- Use a calculator to find the value of the missing angle by taking the inverse sine (sin^-1) of both sides of the equation. This will give you the measure of the angle in degrees.
By following these steps, you can use the Law of Sines to solve for missing angles in a triangle. It is important to note that the Law of Sines may have multiple solutions for an angle, depending on the given information. In such cases, be sure to consider the appropriate angle range and choose the solution that is relevant to your problem.
Step-by-step guide on using the Law of Sines to find unknown angles
The Law of Sines is a trigonometric formula that relates the sides of a triangle to the sines of its opposite angles. It can be used to find unknown angles in a triangle when the lengths of at least two sides and the measure of one angle are known. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use the Law of Sines:
Step 1: Determine which sides and angles of the triangle are known and which side or angle you are trying to find. Label the triangle with the given values.
Step 2: Use the Law of Sines formula, which is given by: sin(A)/a = sin(B)/b = sin(C)/c. Here, A, B, and C represent the angles of the triangle, and a, b, and c represent the lengths of the sides opposite these angles.
Step 3: Substitute the known values into the formula. If you are trying to find an angle, use the sine ratio to find its value. If you are trying to find the length of a side, rearrange the formula to solve for the unknown side length.
Step 4: Solve for the unknown angle or side length using algebraic manipulation or a calculator if necessary.
Step 5: Verify your answer by checking if the sum of the angles in the triangle is 180 degrees. If the sum is not 180 degrees, check your calculations and try again.
By following these steps, you can successfully use the Law of Sines to find unknown angles in a triangle. Remember to pay attention to the units of measurement and use appropriate trigonometric ratios to calculate the values accurately.
How to solve for missing side lengths using the Law of Sines?
The Law of Sines is a trigonometric formula that relates the sides of a triangle to its angles. It states that the ratio of the length of a side of a triangle to the sine of the opposite angle is constant. This means that if we know the lengths of two sides and the measure of the included angle, we can use the Law of Sines to find the length of the remaining side.
To solve for a missing side length using the Law of Sines, follow these steps:
- Identify the known side lengths and angles of the triangle.
- Use the Law of Sines formula: sin(A)/a = sin(B)/b = sin(C)/c, where A, B, and C are the angles of the triangle, and a, b, and c are the respective side lengths.
- Determine which angle and side lengths you have and which one you want to find.
- If you have the measure of an angle and the length of the opposite side, use the formula a/sin(A) = c/sin(C) to solve for the missing side length.
- If you have the length of two sides and the measure of the included angle, use the formula a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) to solve for the missing side length.
- Once you have set up the equation, solve for the missing side length by cross-multiplying and dividing.
Remember to use proper units for your side lengths and angles, and round your answers to the appropriate number of decimal places. Also, keep in mind that the Law of Sines may not work if the triangle is not acute or the given information is not suitable for application of the formula.
By following these steps and using the Law of Sines, you can effectively solve for missing side lengths in triangles and further analyze their properties and relationships.
Using the Law of Sines to find unknown side lengths in triangles
The Law of Sines is a fundamental trigonometric law that relates the ratios of the sides of a triangle to the sines of its opposite angles. This law can be used to find unknown side lengths in triangles when certain angle measures and side lengths are known.
To apply the Law of Sines, we need to have at least one set of a side length and its opposite angle measure, or two angle measures and one side length. With this information, we can set up a proportion using the Law of Sines and solve for the unknown side length.
For example, consider a triangle with side lengths a, b, and c, and opposite angles A, B, and C, respectively. If we know the measures of angles A and B, and the length of side a, we can use the Law of Sines to find the length of side b:
sin(A)/a = sin(B)/b
By cross-multiplying, we can isolate the unknown side length:
b = (a * sin(B))/sin(A)
Similarly, if we know the measures of angles A and C, and the length of side a, we can use the Law of Sines to find the length of side c:
sin(A)/a = sin(C)/c
By cross-multiplying, we can isolate the unknown side length:
c = (a * sin(C))/sin(A)
The Law of Sines provides a powerful tool for finding unknown side lengths in triangles. By leveraging the trigonometric relationship between angles and sides, we can solve for missing lengths and further analyze the properties and relationships within triangles.
Applications of the Law of Sines in real-life scenarios
The Law of Sines is a fundamental concept in trigonometry that allows us to solve triangles when we have information about the lengths of some sides and the measures of some angles. This law has various applications in real-life scenarios, ranging from navigation and engineering to measurement and astronomy.
One practical application of the Law of Sines is in navigation. By using this law, sailors and pilots can determine their position and calculate the distance between two points based on the angles and distances observed. For example, if a ship captain measures the angles to two visible landmarks and the length of the ship’s route between them, the Law of Sines can be used to determine the ship’s position on a map.
The Law of Sines also finds applications in engineering, specifically in the field of surveying. Surveyors use this law to measure distances and establish boundaries accurately. By measuring the angles between known points and using the Law of Sines, surveyors can calculate the distances to unknown points, allowing them to create accurate maps and plans for construction projects.
Furthermore, astronomy is another field that relies on the Law of Sines. Astronomers use this law to calculate the distances between celestial objects, such as stars and planets. By measuring the angles between the Earth, the object, and the Sun, astronomers can apply the Law of Sines to determine the distance to the object, providing crucial information for studying the universe.
In conclusion, the Law of Sines has numerous applications in real-life scenarios, including navigation, engineering, surveying, and astronomy. Its ability to solve triangles based on angle and side information makes it a valuable tool in various fields, contributing to accurate measurements, calculations, and understanding of the physical world.
Exploring practical examples of the Law of Sines in various fields
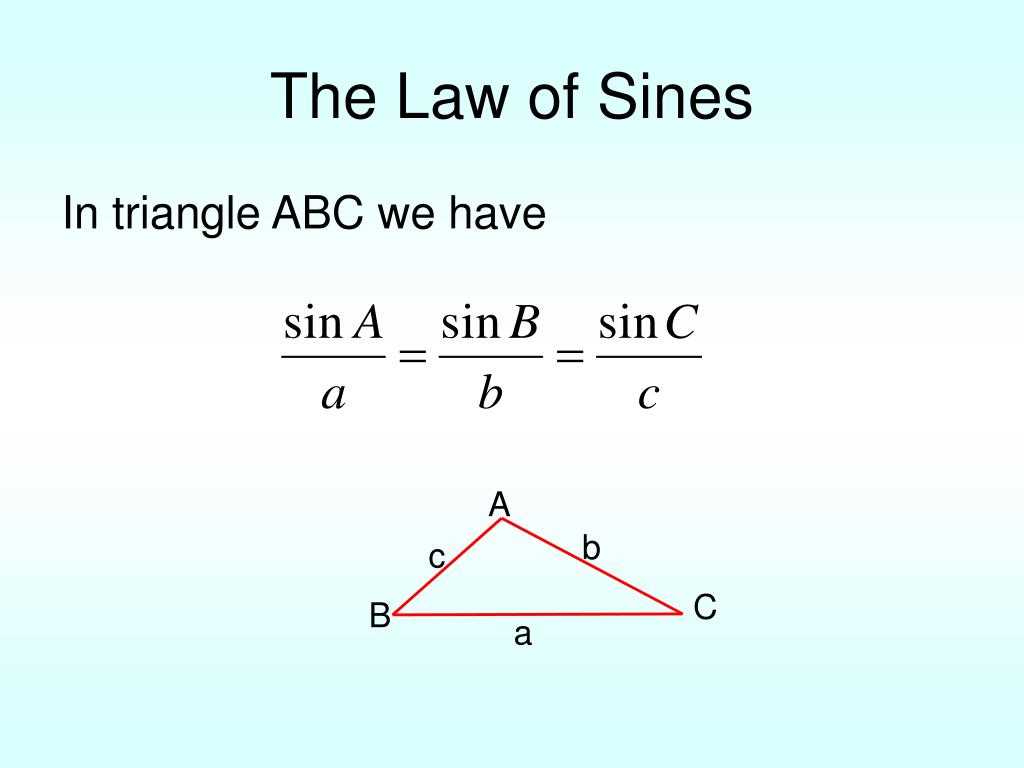
The Law of Sines is a crucial tool in solving triangles and understanding the relationships between their sides and angles. It finds applications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and navigation. Let’s explore some practical examples of how the Law of Sines is used in these fields.
Mathematics:
In mathematics, the Law of Sines is used to solve triangles when the angles and sides are known. It helps in finding unknown side lengths or angles. For example, in trigonometry, the Law of Sines can be used to solve real-world problems involving distances and angles, such as calculating the height of a building or the distance between two points.
Physics:
In physics, the Law of Sines is applied in problems related to waves, vibrations, and optics. For instance, when studying the interference of waves or calculating refraction angles, the Law of Sines assists in finding the relationships between the angles of incidence, reflection, and refraction.
Engineering:
In engineering, the Law of Sines is used in structural analysis and design, especially in civil and aerospace engineering. It helps determine the forces, stresses, and deformations in various components of structures. By applying the Law of Sines to the forces acting on a structure, engineers can ensure its stability and safety.
Navigation:
The Law of Sines has significant applications in navigation, particularly in marine and aerial navigation. It helps determine distances and angles between points using celestial navigation or trigonometric methods. For example, sailors can use the Law of Sines to calculate their position using the angles and distances observed from two or more known landmarks.
In summary, the Law of Sines is a versatile tool that finds applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and navigation. Its ability to solve triangles and establish relationships between angles and sides makes it a valuable technique in various fields. By understanding and utilizing the Law of Sines, professionals can solve complex problems, design structures, and navigate accurately in real-world scenarios.