Are you struggling with special right triangles in geometry? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this article, we will provide you with 8 skills practice answers to help you master special right triangles.
Special right triangles are an essential concept in geometry that can be challenging to understand. However, by practicing with the right exercises and learning the necessary skills, you can improve your understanding and problem-solving abilities. These skills practice answers will guide you through various scenarios and calculations involving special right triangles, allowing you to gain confidence in your skills.
By going through these 8 practice answers, you will learn how to identify special right triangles, determine their angles and side lengths, and apply the Pythagorean theorem. This comprehensive practice will strengthen your geometric reasoning and help you approach special right triangles with ease. With each answer, you will gain a clearer understanding of the concepts, enabling you to tackle more complex problems in the future.
So, whether you are preparing for a geometry test or simply want to enhance your skills in special right triangles, these practice answers are an invaluable resource. Get ready to take your geometry skills to the next level and ace any special right triangle problem that comes your way!
Understanding the concept and properties of special right triangles
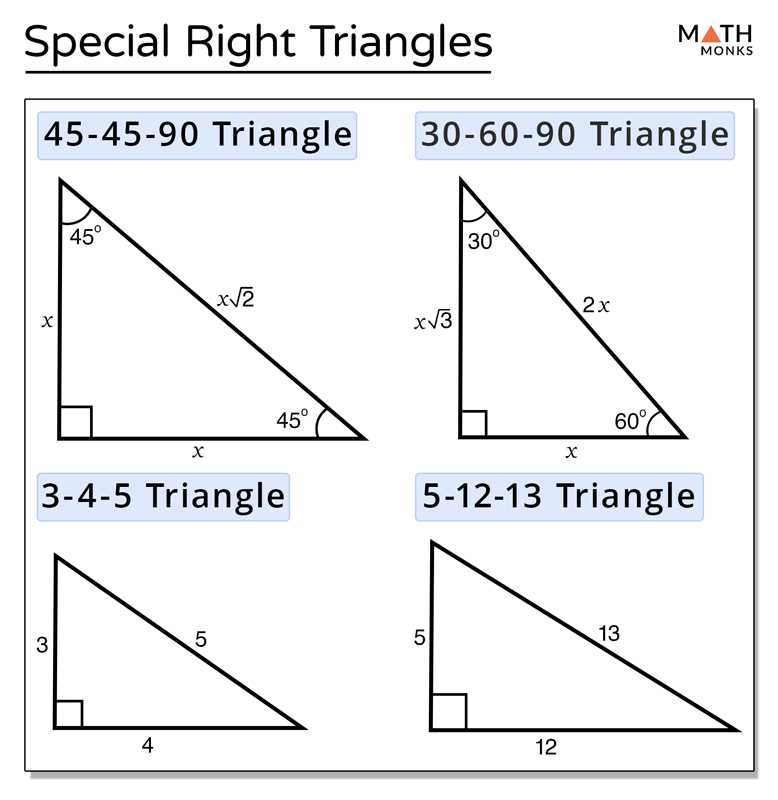
Special right triangles are a specific type of right triangle that have unique properties and can be used to solve a variety of mathematical problems. These triangles have angles that are commonly found in geometric shapes and can be easily identified by their ratios of side lengths.
There are two types of special right triangles: the 45-45-90 triangle and the 30-60-90 triangle. The 45-45-90 triangle is an isosceles triangle, meaning it has two sides of equal length. The angles in this triangle are 45 degrees, 45 degrees, and 90 degrees. The side lengths are in a ratio of 1:1:√2. This means that if one side is x, the other two sides will also be x, and the hypotenuse will be x√2.
The 30-60-90 triangle is also an isosceles triangle, but it has angles of 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees. The side lengths in this triangle are in a ratio of 1:√3:2. If one side is x, the shorter side will be x√3, and the longer side will be 2x. The hypotenuse is always twice the length of the shorter side.
These special right triangles have various applications in geometry and trigonometry. They can be used to find missing side lengths and angle measures in a triangle, as well as in real-world problems involving height, distance, and angles of elevation or depression. Understanding the concept and properties of special right triangles is therefore essential for solving these types of problems efficiently and accurately.
Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental concept in mathematics that is used to find the length of one side of a right triangle when the lengths of the other two sides are known. It states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
Applying the Pythagorean Theorem involves using algebraic equations to solve for the unknown side length. For example, if the lengths of the two legs of a right triangle are given as 3 and 4 units, then the length of the hypotenuse can be found by using the equation c^2 = a^2 + b^2, where c is the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b are the lengths of the legs. Substituting the given values, we get c^2 = 3^2 + 4^2, which simplifies to c^2 = 9 + 16. By adding the two values, we get c^2 = 25. Taking the square root of both sides, we find that c = 5 units.
The Pythagorean Theorem can also be used to determine if a triangle is a right triangle. By measuring the lengths of the three sides of a triangle and applying the theorem, if the equation a^2 + b^2 = c^2 holds true, then the triangle is a right triangle. This property can be useful in various real-life applications, such as architecture and engineering, where it is important to determine if angles are right angles in order to ensure structural stability.
Overall, the Pythagorean Theorem is a powerful tool that has numerous applications in mathematics and beyond. It provides a fundamental understanding of the relationships between the sides of a right triangle and allows for the calculation of unknown side lengths. Its simplicity and versatility make it an essential concept for anyone studying geometry or working in related fields.
Using the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing side lengths in special right triangles
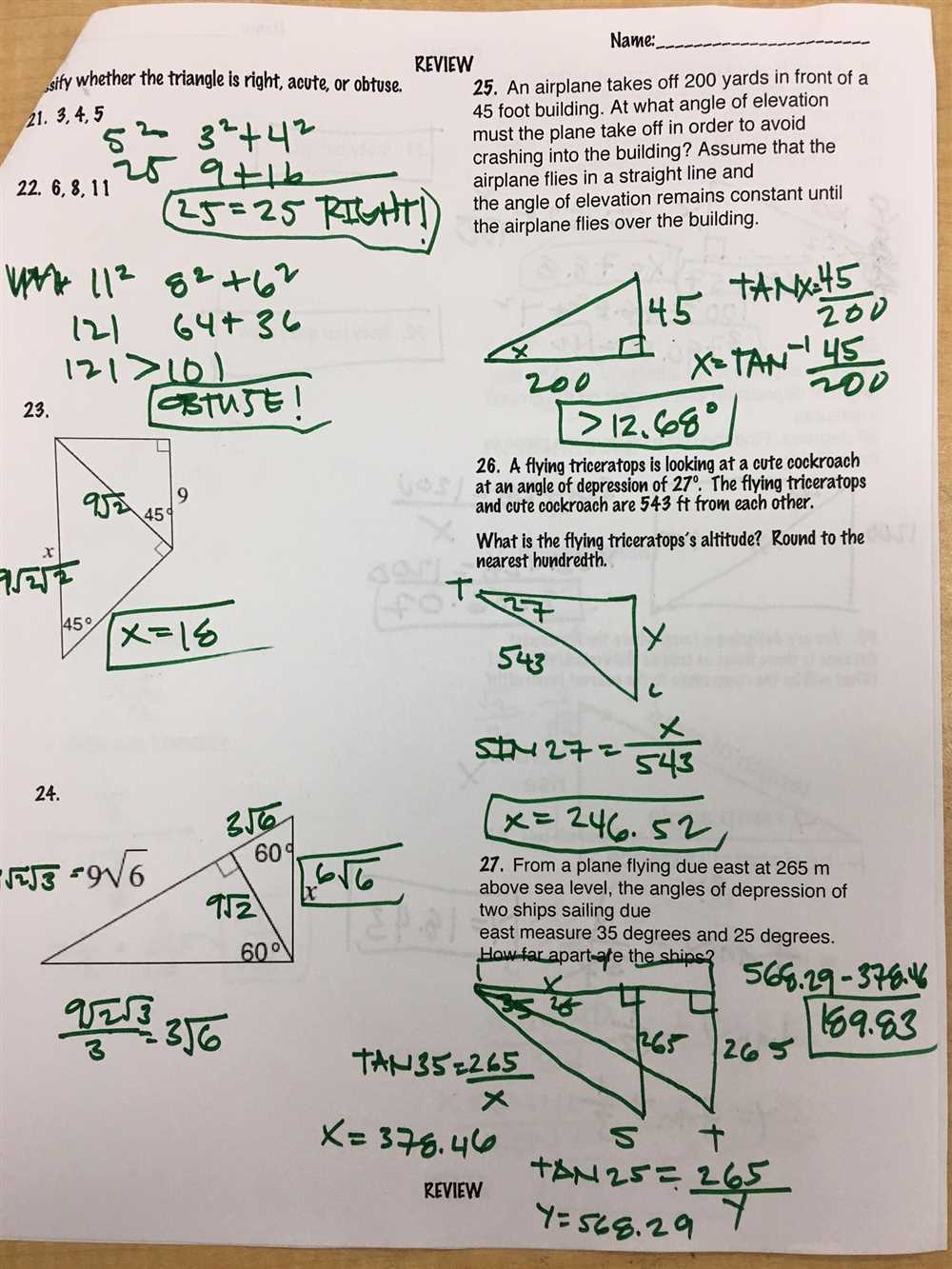
In geometry, special right triangles are triangles that have some specific angles and side lengths. These triangles include the 45-45-90 triangle and the 30-60-90 triangle. One common method of finding the missing side lengths in these triangles is by using the Pythagorean Theorem.
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. In the case of special right triangles, the lengths of the sides have a special relationship that makes it easier to apply the theorem.
For example, in a 45-45-90 triangle, the two legs (the sides opposite the two 45-degree angles) are congruent. If one leg has a length of x, then the other leg also has a length of x. The hypotenuse, which is opposite the right angle, can be found by multiplying the length of one leg by the square root of 2.
- In a 30-60-90 triangle, the side opposite the 30-degree angle is half the length of the hypotenuse, and the side opposite the 60-degree angle is the length of the hypotenuse multiplied by the square root of 3.
- Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we can determine the missing side lengths by substituting the known values into the equation and solving for the unknown side.
- Once the missing side lengths are found, we can use them to calculate other properties of the triangle, such as the area or the angle measures.
By understanding the properties of special right triangles and using the Pythagorean Theorem, we can easily find the missing side lengths and solve various problems involving these triangles. These skills are important in geometry and can be applied to real-world situations where right triangles are encountered.
Solving for the Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. One of the main concepts in trigonometry is the use of trigonometric ratios to find unknown angles or sides of a triangle. These ratios, which include sine, cosine, and tangent, are based on the relationships between the sides of a right triangle.
To solve for the trigonometric ratios, first identify the given information. This may include the lengths of certain sides or the measures of certain angles. With this information, you can determine which trigonometric ratio to use. For example, if you have the lengths of the opposite and hypotenuse sides of a right triangle, you can use the sine ratio (sin) to find the measure of the angle opposite the given side.
To use a trigonometric ratio, plug in the known values into the appropriate formula. For example, the sine ratio is defined as the opposite side divided by the hypotenuse side, so you would substitute the known values for these sides into the formula. Once you have the formula set up, you can solve for the unknown angle or side by performing the necessary calculations.
It’s important to be familiar with the special right triangles, such as the 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 triangles, as they have specific ratios that can be used to quickly solve for unknown angles and sides. These special triangles have angles of 45 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees, which make the trigonometric ratios simpler to calculate.
In conclusion, solving for the trigonometric ratios involves identifying the known information, choosing the appropriate ratio, plugging in the values, and performing calculations. With practice, you can become proficient in solving for unknown angles and sides using trigonometry, making it a valuable tool in various fields such as engineering, physics, and navigation.
Exploring how to calculate sine, cosine, and tangent in special right triangles
Special right triangles, such as the 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 triangles, have ratios of their side lengths that are consistent and can be used to calculate the values of trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
In a 45-45-90 triangle, the two legs are congruent, and the hypotenuse is equal to the length of one leg multiplied by √2. The sine of the acute angles is equal to 1/√2, the cosine is equal to 1/√2, and the tangent is equal to 1. These ratios allow us to quickly find the values of sine, cosine, and tangent for any angle measure in a 45-45-90 triangle.
In a 30-60-90 triangle, the ratio of the side lengths is 1 : √3 : 2. The side opposite the 30-degree angle is half the length of the hypotenuse, the side opposite the 60-degree angle is √3 times the length of the shorter leg, and the hypotenuse is twice the length of the shorter leg. Using these ratios, we can determine the values of sine, cosine, and tangent for the angles in a 30-60-90 triangle.
To calculate the values of sine, cosine, and tangent in special right triangles, we can simply divide the length of the side opposite the desired angle by the length of the hypotenuse for sine, the length of the adjacent side by the length of the hypotenuse for cosine, and the length of the side opposite the angle by the length of the adjacent side for tangent. By understanding these ratios, we can efficiently solve problems involving special right triangles and apply trigonometric functions in various mathematical contexts.
Identifying Special Right Triangle Types
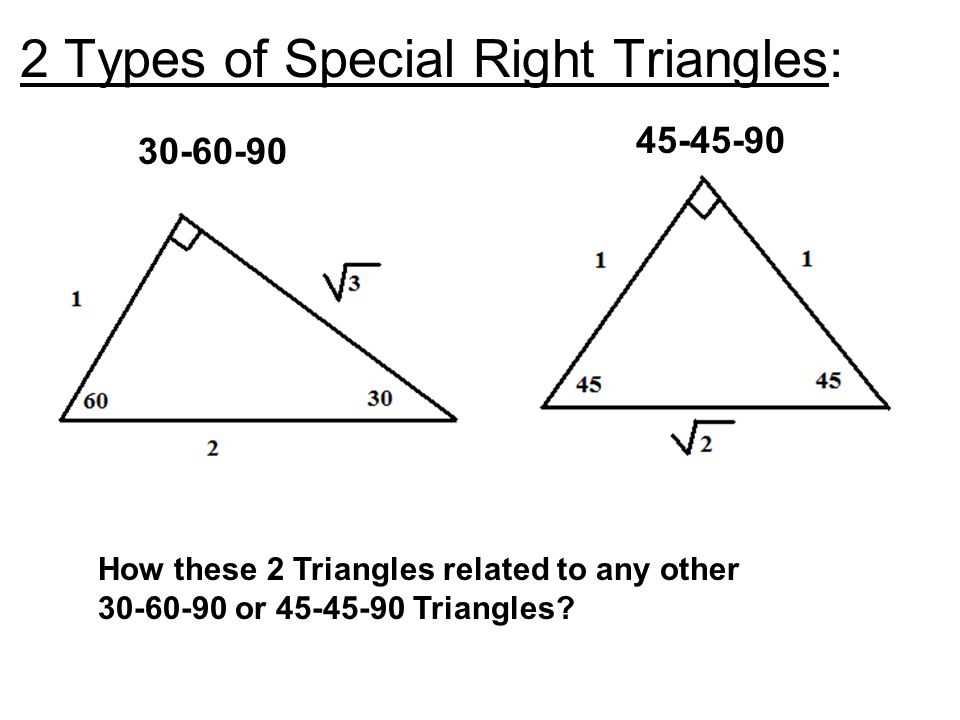
Special right triangles are a subset of right triangles that have distinct properties and ratios between their sides. By identifying these special types, we can easily determine the length of their sides and calculate their angles without the need for complex trigonometric functions.
There are two main types of special right triangles: the 45-45-90 and the 30-60-90 triangles. These triangles are named after the measures of their angles.
45-45-90 Triangle:
- A 45-45-90 triangle is an isosceles right triangle, meaning it has two equal angles of 45 degrees and a right angle of 90 degrees.
- The ratio of the lengths of its sides is 1:1:√2.
- For example, if one side of the triangle is 4 units, then the hypotenuse would be 4√2 units.
30-60-90 Triangle:
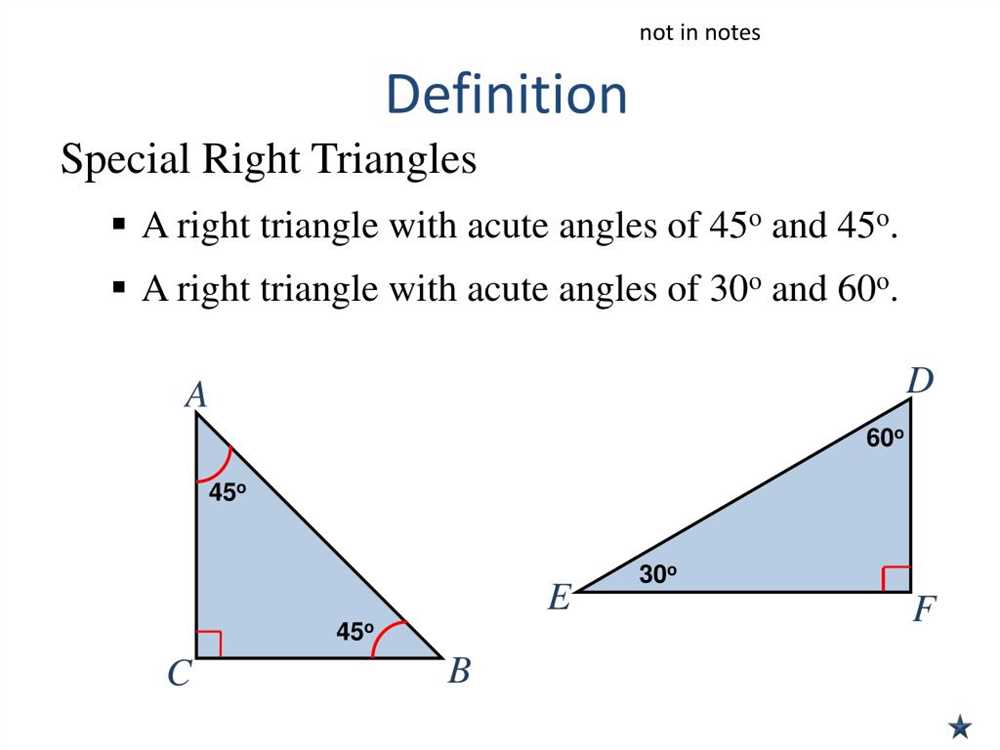
- A 30-60-90 triangle is an equilateral right triangle, meaning it has angles of 30, 60, and 90 degrees.
- The ratio of the lengths of its sides is 1:√3:2.
- For example, if one side of the triangle is 6 units, then the shorter leg would be 6√3 units, and the longer leg would be 12 units.
By recognizing these special right triangle types, we can quickly determine the lengths of their sides and use them to solve various geometry and trigonometry problems. Understanding these properties can greatly simplify calculations and make mathematical problem-solving more efficient.
Distinguishing between 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 triangles and their unique characteristics
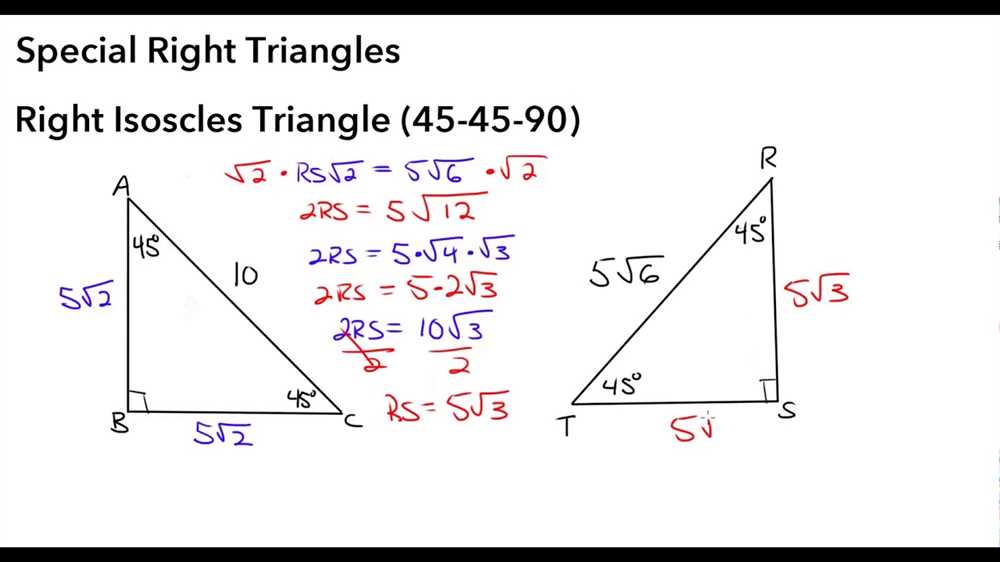
Special right triangles play a significant role in geometry, and two of the most commonly encountered types are the 45-45-90 triangle and the 30-60-90 triangle. These triangles have distinct characteristics that make them easily recognizable and enable us to determine their side lengths and angle measures without the need for complex calculations.
The 45-45-90 triangle, also known as an isosceles right triangle, is a triangle with two congruent sides and a right angle. Its defining characteristic is that the angles opposite the congruent sides are also congruent, measuring 45 degrees each. This triangle is particularly useful in solving problems involving square roots, as the ratio of the lengths of its sides is a simple whole number relationship: the length of the hypotenuse is sqrt(2) times the length of either leg, and each leg is equal in length. For example, if one leg has a length of 3, the hypotenuse would be 3*sqrt(2) and the other leg would also be 3.
The 30-60-90 triangle is an equilateral triangle with a right angle. It is called a 30-60-90 triangle because its angle measures are 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees. The side opposite the 30-degree angle is half the length of the hypotenuse, while the side opposite the 60-degree angle is the square root of 3 times the length of the side opposite the 30-degree angle. This triangle is often encountered in problems involving trigonometric functions, as the relationships among its side lengths and angles can be used to find exact values of trigonometric ratios.
By understanding the unique characteristics of 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 triangles, we can quickly identify them and apply their properties to solve geometric problems. Recognizing these special triangles can simplify calculations and provide a valuable tool in navigating the world of geometry.
Utilizing Special Right Triangles in Real-world Problems
Special right triangles, such as the 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 triangles, are an integral part of problem-solving in various fields. These triangles have unique properties that allow us to quickly and efficiently solve real-world problems involving angles and side lengths.
One practical application of special right triangles is in construction and engineering. Architects and builders often need to determine the height of a structure or the length of a diagonal. By recognizing special right triangles within the design, they can use the ratios of their side lengths to easily calculate the missing dimensions.
For example, when creating a roof with a 45-degree angle, architects can use the properties of a 45-45-90 triangle to determine the length of the roof’s pitch. By knowing the length of one side (the base of the triangle), they can easily calculate the height of the pitched roof, ensuring proper construction and stability.
Another practical application of special right triangles is in navigation and surveying. For instance, a ship captain may need to determine the distance to an island or the height of a lighthouse. By utilizing the ratios of a 30-60-90 triangle, they can use the measured angles and known side lengths to find the missing distances.
Overall, special right triangles provide a valuable tool for solving real-world problems that involve angles and side lengths. Whether it’s in construction, engineering, navigation, or other fields, recognizing and utilizing the properties of these triangles can save time and effort in solving complex problems.