As a vital part of the American government system, the judicial branch plays a significant role in upholding the laws and ensuring justice is carried out. This crossword puzzle focuses on key terms and concepts related to the judicial branch, offering a fun and educational way to test your knowledge.
This puzzle consists of seventeen answers that represent different aspects of the judicial branch, including important figures, legal procedures, and key terms. By completing this crossword, you will not only reinforce your understanding of the judicial branch but also learn new vocabulary related to the American legal system.
Challenge yourself by solving this crossword and see how many answers you can correctly fill in. Whether you’re a student studying civics or simply interested in learning more about the judicial branch, this crossword puzzle will provide an enjoyable and educational experience.
What is the judicial branch?
The judicial branch is one of the three branches of government in the United States, alongside the executive and legislative branches. Its main function is to interpret and apply the law in order to resolve disputes and administer justice. The judicial branch consists of a system of courts, with the Supreme Court as the highest court in the country.
The Supreme Court: The Supreme Court is the highest judicial authority in the United States. It consists of nine judges, known as justices, who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The Supreme Court has the power to review cases that come before it, and its decisions are final and binding. It plays a crucial role in shaping the interpretation of the Constitution and establishing legal precedents.
Lower federal courts: In addition to the Supreme Court, the judicial branch includes lower federal courts, such as the U.S. Court of Appeals and the U.S. District Courts. These courts hear a wide range of cases, including those involving federal laws, constitutional issues, and disputes between parties from different states. The decisions of these lower courts can be appealed to the Supreme Court.
State and local courts: The judicial branch also encompasses state and local courts, which handle a variety of cases within their respective jurisdictions. These courts have the authority to interpret and apply state laws, as well as local ordinances and regulations. Their decisions can be appealed to higher state courts or, in some cases, to the Supreme Court.
Judicial review: One of the key powers of the judicial branch is judicial review. This refers to the ability of the courts to review the constitutionality of laws and government actions. If a court determines that a law or action is unconstitutional, it can declare it null and void. This power acts as a check on the other branches of government and helps to ensure that they operate within the bounds of the Constitution.
In conclusion, the judicial branch is an essential component of the U.S. government, responsible for interpreting and applying the law. Through its system of courts and the power of judicial review, it plays a vital role in upholding the principles of justice and maintaining the balance of power between the three branches of government.
Importance of the Judicial Branch
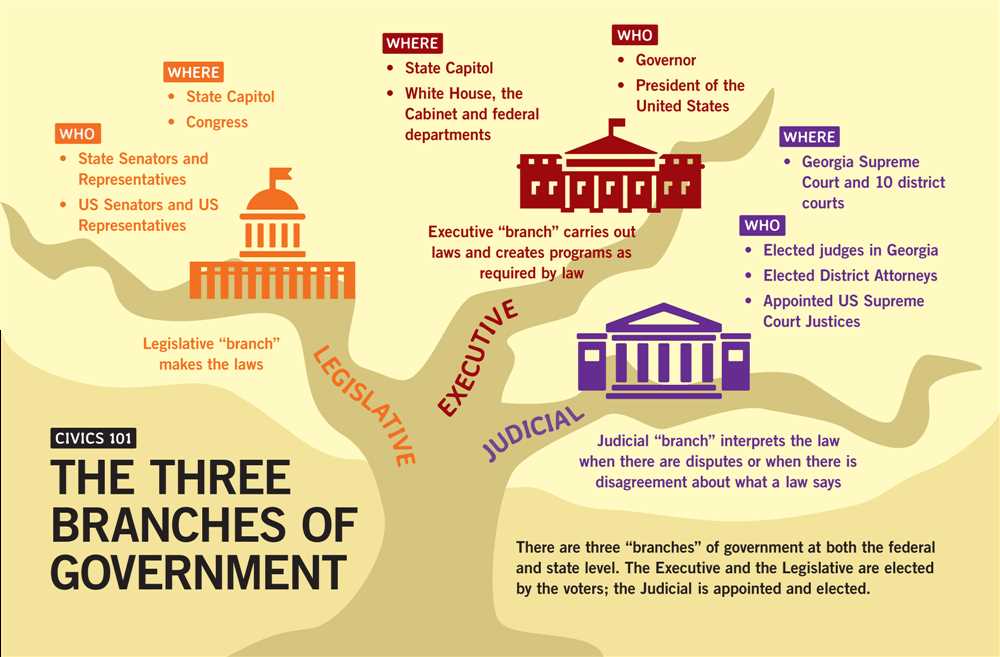
The judicial branch plays a crucial role in maintaining a fair and just society through its interpretation and application of the law. This branch of government ensures that laws are enforced, and that the rights and liberties of individuals are protected. Without a strong and independent judiciary, the principles of due process, equality before the law, and the rule of law would be undermined.
One of the key functions of the judicial branch is to act as a check on the powers of the executive and legislative branches. Through the power of judicial review, the courts have the authority to declare laws or executive actions unconstitutional. This function is vital in safeguarding the separation of powers and preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful. Additionally, the judiciary provides a means for individuals and groups to seek justice and challenge the actions of the government.
The decisions made by the courts set legal precedents, which guide future interpretations of the law. This ensures consistency and predictability in the application of the law, promoting stability and trust in the judicial system. The judicial branch is responsible for resolving disputes, both criminal and civil, and providing a forum for individuals to pursue justice and seek redress for any perceived violations of their rights.
Furthermore, an independent judiciary is essential for upholding the principles of democracy. Judges must be free from political influence and pressure in order to make impartial and objective decisions based on the law and the facts of the case. This independence ensures that justice is served without favoritism or bias. It also helps to protect the rights of minority groups and marginalized individuals against potential encroachments by the majority.
In conclusion, the judicial branch is of utmost importance in maintaining a fair and just society. It acts as a check on the powers of the other branches of government, upholds the rule of law, and protects the rights and liberties of individuals. Its independence and role in interpreting and applying the law are essential for the functioning of a democratic society.
Structure of the judicial branch
The judicial branch of government in the United States consists of the Supreme Court and other federal courts. These courts are organized in a hierarchical structure that ensures the fair and efficient administration of justice.
At the top of the structure is the Supreme Court, which is the highest court in the land and has the final authority to interpret the Constitution and federal laws. The Supreme Court consists of nine justices, including one Chief Justice, who are appointed for life by the President and confirmed by the Senate. They hear cases that involve significant constitutional questions or conflicts between federal laws and state laws.
Beneath the Supreme Court are the federal appellate courts, also known as circuit courts of appeals. There are 13 appellate courts in the United States, each covering a specific geographic area called a circuit. These courts review decisions made by lower courts and decide whether they were correct based on the law. The appellate courts do not hold trials; instead, they review the record of the case and listen to arguments from the lawyers.
Below the appellate courts are the federal district courts, which are the trial courts of the federal judiciary. There are 94 district courts spread across the United States. These courts are responsible for holding trials, receiving evidence, and determining the facts of a case. They also have the authority to interpret and apply the law to the cases before them.
In addition to the federal courts, each state has its own judicial branch, with its own structure of courts. These state courts handle most of the cases in the United States, including criminal trials, civil lawsuits, and family law matters. The structure of state courts varies from state to state, but typically includes trial courts, appellate courts, and a state supreme court.
The judicial branch plays a vital role in the American system of government by interpreting and applying the law in a fair and impartial manner. Its structure ensures that the power of the judiciary is balanced with the executive and legislative branches, helping to maintain the checks and balances that are fundamental to democracy.
Powers and Responsibilities of the Judicial Branch
The judicial branch of the government is responsible for interpreting laws, resolving disputes, and ensuring justice within the legal system. It plays a crucial role in upholding the rule of law and protecting the rights and liberties of individuals. The powers and responsibilities of the judicial branch are outlined in the Constitution and are designed to provide a system of checks and balances to prevent abuse of power.
One of the key powers of the judicial branch is judicial review. This allows the courts to review the constitutionality of laws passed by the legislative branch and executive actions. Through judicial review, the judiciary can strike down laws or actions that are found to be unconstitutional, ensuring that they do not violate the rights of individuals or exceed the powers granted to the government.
Another important responsibility of the judicial branch is to settle disputes between individuals, organizations, and the government. The courts have the authority to hear cases, evaluate evidence, and make decisions based on the interpretation of the law. They provide a forum for parties to present their arguments and seek redress for grievances. By resolving disputes in a fair and impartial manner, the judiciary ensures justice and maintains social order.
The judicial branch also plays a role in safeguarding individual rights. It has the power to protect citizens’ rights to due process of law, freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and other fundamental rights enshrined in the Constitution. The courts can intervene to prevent the violation of these rights and provide remedies and compensation to individuals whose rights have been infringed upon.
In addition to these powers and responsibilities, the judicial branch also has administrative functions, such as managing court operations, establishing rules of procedure, and overseeing the legal profession. It relies on a hierarchy of courts, with the Supreme Court serving as the final arbiter of legal disputes and the highest authority in interpreting the Constitution.
In conclusion, the judicial branch plays a vital role in ensuring the rule of law, protecting individual rights, and resolving disputes within the legal system. Its powers and responsibilities are essential for maintaining a just and balanced society, where the rights and liberties of individuals are safeguarded.
The Role of Judges in the Judicial Branch

Within the judicial branch of government, judges play a crucial role in upholding the law and ensuring justice is served. They have the responsibility of interpreting the laws and making impartial decisions based on the evidence presented in court. Judges are appointed or elected to serve on various levels of the judiciary, from the local courts to the highest court of the land.
Judges act as neutral arbiters: One of the key roles of judges is to remain impartial and unbiased in their decision-making process. They are expected to set aside personal beliefs and opinions and base their rulings solely on the law and the facts of the case. This ensures that the judicial system operates fairly and that all individuals receive equal treatment under the law.
Judges make legal interpretations: Judges have the authority to interpret the laws and apply them to specific cases. They analyze the language and intent of the law, consider past legal precedents, and determine how the law should be applied in a given situation. This interpretation helps to clarify the meaning and scope of the law and guides future legal decisions.
Judges ensure due process: Due process is a fundamental principle of the judicial system, ensuring that individuals are treated fairly and have the opportunity to present their case before a court. Judges play a vital role in safeguarding due process rights by overseeing courtroom procedures, ensuring all parties have a fair chance to present their evidence and arguments, and ruling on any violations of constitutional rights.
Judges hand down judgments and sentences: Once a case has been heard and all evidence has been presented, judges are responsible for making a final judgment and deciding on an appropriate sentence or legal remedy. Their decisions have the power to impact individuals’ lives and shape the legal landscape, serving as a means of promoting justice and preserving the rule of law.
- Overall, judges in the judicial branch play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of the legal system.
- They ensure that justice is served, that laws are applied correctly, and that all individuals receive equal treatment under the law.
- Through their impartiality, legal expertise, and commitment to due process, judges contribute to the fair and effective functioning of the judiciary.
In the United States, judicial appointments and nominations are an important aspect of the judicial branch. The process of appointing and confirming federal judges is outlined in the Constitution and involves multiple steps. The President has the power to nominate individuals for judicial positions, including Supreme Court Justices, and the Senate has the authority to confirm or reject these nominations.
When a vacancy occurs in a federal judgeship, the President typically consults with advisors and legal experts to identify potential candidates. The nomination process often involves a thorough vetting of the nominee’s qualifications, including their legal experience, education, and past judicial rulings. The President may also consider factors such as the nominee’s ideology and views on constitutional interpretation.
Confirmation Process
Once a nomination is made, the Senate Judiciary Committee conducts hearings to review the nominee’s qualifications and allow senators to ask questions. During these hearings, senators may inquire about the nominee’s legal philosophy, past decisions, and potential conflicts of interest. The committee may also seek input from legal experts and organizations to evaluate the nominee’s qualifications.
After the hearings, the committee votes on whether to recommend the nominee to the full Senate for confirmation. If the committee approves the nomination, the full Senate then votes on whether to confirm the nominee. A simple majority vote is typically required for confirmation.
Impact and Importance
Judicial appointments and nominations have a significant impact on the composition and direction of the federal judiciary. The appointment of Supreme Court Justices, in particular, can shape the interpretation of the Constitution and influence major legal decisions. As a result, the nomination and confirmation process is often a subject of intense scrutiny and political controversy, as different parties and interest groups seek to advance their preferred nominees.
Overall, the process of judicial appointments and nominations is a crucial aspect of the checks and balances within the U.S. government. It ensures that the judiciary remains independent and impartial, while also allowing the executive branch and Senate to collectively shape the direction of the federal judiciary.