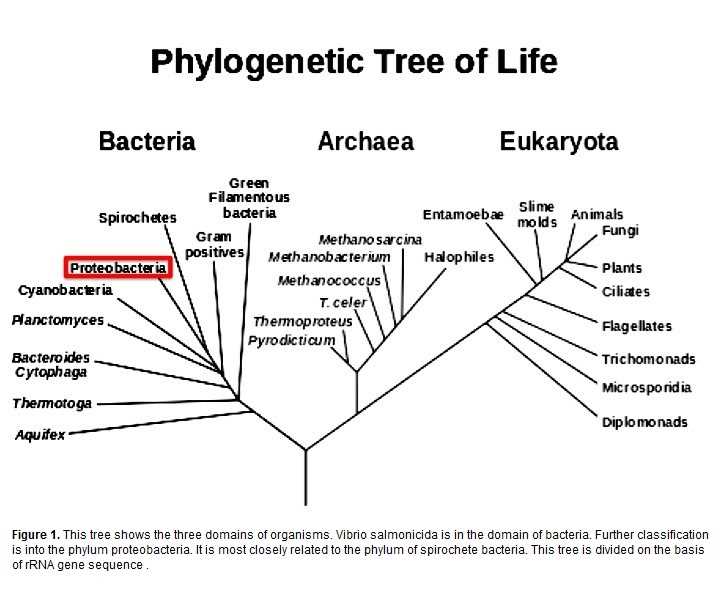
Evolutionary classification is an essential tool in understanding the diversity and relationships among organisms. It allows scientists to categorize and organize species based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary history. The key to this classification lies in tracing the common ancestry and evolutionary relationships between different species.
In the context of 18 2 modern evolutionary classification, scientists have developed several key approaches to classify organisms. One such approach is the use of derived traits, which are unique characteristics that have evolved in a particular lineage. These traits are used to determine the evolutionary relationships between organisms and group them accordingly.
Another important aspect of modern evolutionary classification is the concept of cladistics. Cladistics focuses on identifying and categorizing organisms based on their shared derived traits, called synapomorphies. By analyzing these shared traits, scientists can construct a phylogenetic tree that represents the evolutionary relationships between different species or groups of organisms.
Understanding the 18 2 modern evolutionary classification answer key is crucial for discovering and interpreting the diversity of life on Earth. By analyzing the shared characteristics and evolutionary history of organisms, scientists can uncover the relationships between different species and gain insight into their adaptations, behaviors, and ecological roles. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of the natural world but also has practical applications in fields such as medicine, conservation, and agriculture.
Modern Evolutionary Classification: An Overview
The concept of classification has been an essential part of understanding and studying the diversity of life on Earth. Traditional methods of classification were based on observable traits and physical characteristics of organisms. However, with the advances in genetic and molecular techniques, modern evolutionary classification has emerged as a more accurate and comprehensive approach.
Modern evolutionary classification is based on the principles of evolutionary biology, which state that all living organisms share a common ancestry and have evolved through a process of descent with modification. This approach takes into account not only the physical characteristics of organisms but also their genetic makeup and evolutionary relationships.
In modern evolutionary classification, organisms are classified into groups called taxa based on their genetic similarities, which reflect their evolutionary relationships. The classification system is hierarchical, with broad categories at the top (such as domains and kingdoms) and more specific categories at the lower levels (such as species and subspecies).
Phylogenetic trees play a crucial role in modern evolutionary classification. These trees depict the evolutionary relationships among different taxa by showing their common ancestors and branching patterns. Phylogenetic trees are constructed using molecular data, such as DNA and protein sequences, as well as other evidence from fossils and morphological traits.
Overall, modern evolutionary classification provides a more accurate and dynamic representation of the diversity of life on Earth. It takes into account the evolutionary history and genetic relationships of organisms, allowing scientists to gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms and patterns of evolution.
The concept of modern evolutionary classification and its significance in the field of biology
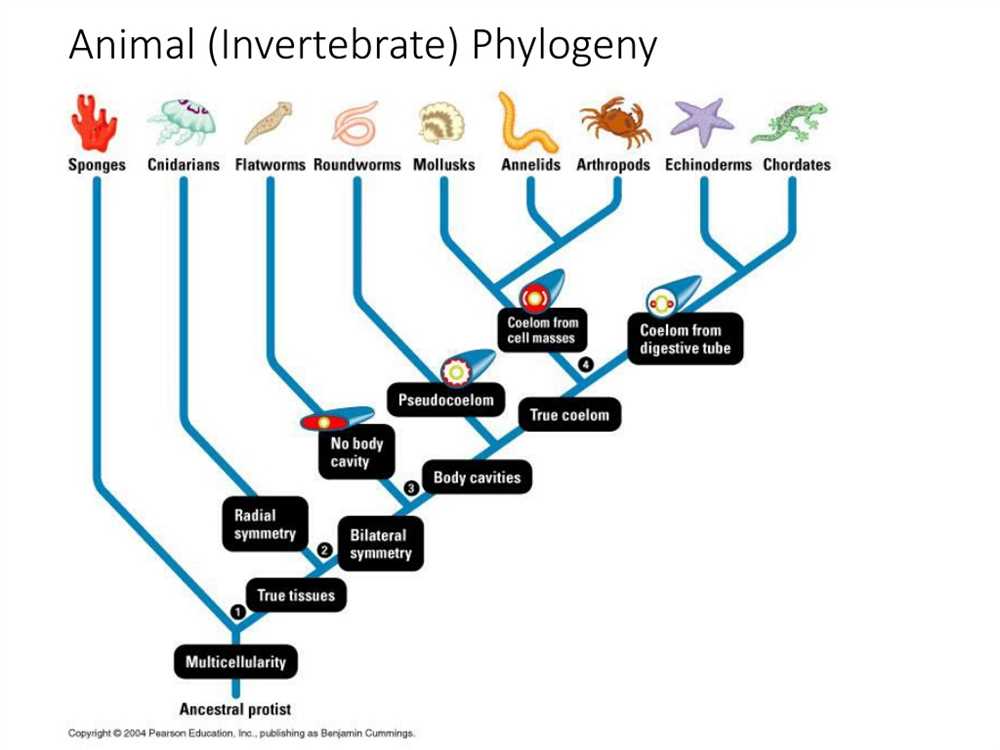
Modern evolutionary classification is a framework for organizing and categorizing organisms based on their evolutionary relationships. It builds upon the classification systems developed by earlier biologists, such as Carolus Linnaeus and Charles Darwin, and incorporates the principles of evolutionary theory into taxonomy. By considering an organism’s evolutionary history and genetic relationships, modern evolutionary classification provides a more accurate and informative way to understand the diversity of life on Earth.
One key aspect of modern evolutionary classification is the use of phylogenetic trees or cladograms. These diagrams depict the evolutionary relationships between different species or groups of organisms. By analyzing similarities and differences in genetic and morphological characteristics, scientists can construct these trees to represent the branching patterns of evolution. This approach allows for the identification of common ancestors and the grouping of organisms into clades, which are monophyletic groups that share a common ancestor.
The significance of modern evolutionary classification in the field of biology is immense. It provides a systematic and logical way to organize and study the immense diversity of life on our planet. By understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species, scientists can make predictions about common ancestry, evolutionary history, and shared traits. This knowledge can then be used to inform a wide range of biological studies, from understanding the genetic basis of diseases to the conservation of endangered species.
Furthermore, modern evolutionary classification helps to illuminate the processes and mechanisms of evolution itself. By examining the patterns of speciation, adaptation, and genetic variation within and between different clades, scientists can gain insights into the forces that drive biological diversity. This knowledge is essential for understanding and addressing pressing biological challenges, such as the impact of climate change on ecosystems and the development of drug resistance in pathogens.
Overall, modern evolutionary classification provides a powerful framework for studying and understanding the natural world. By incorporating the principles of evolution into taxonomy, it allows scientists to unravel the intricate relationships between different species and gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of life on Earth.
Understanding the Key Principles of Modern Evolutionary Classification

The field of evolutionary classification has undergone significant advancements and changes over the years. Modern evolutionary classification is based on several key principles that help scientists organize and categorize living organisms in a more accurate and comprehensive manner.
1. Common Ancestry: One of the fundamental principles of modern evolutionary classification is the recognition that all living organisms share a common ancestor. This principle is based on the theory of evolution proposed by Charles Darwin, which states that all species have descended from a single common ancestor over millions of years.
2. Phylogenetic Relationships: Modern evolutionary classification focuses on understanding the phylogenetic relationships between different living organisms. Phylogenetic relationships are determined by analyzing the similarities and differences in genetic and physical characteristics. This allows scientists to create evolutionary trees or diagrams that depict the branching patterns of different species and their common ancestors.
3. Hierarchical Classification: Another key principle of modern evolutionary classification is the use of a hierarchical classification system. Organisms are grouped into various taxonomic categories, such as kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. This hierarchical system helps in organizing the vast diversity of living organisms into manageable groups.
4. Cladistics: Cladistics is a method used in modern evolutionary classification to determine the relationships between species based on shared characteristics derived from a common ancestor. This method focuses on identifying unique derived characteristics, known as synapomorphies, that are shared by a group of organisms.
5. Evolutionary History: Modern evolutionary classification takes into account the evolutionary history of organisms when categorizing them. By studying the fossil record and evidence from comparative anatomy, embryology, and molecular genetics, scientists can gain insights into the evolutionary relationships and ancestral traits of different species.
By employing these key principles, modern evolutionary classification provides a framework for understanding the vast diversity of life on Earth and how different species are interconnected through their evolutionary history. It helps scientists in their efforts to classify and categorize organisms accurately, thereby contributing to our knowledge and understanding of the natural world.
An examination of the core principles that shape the modern approach to classifying organisms
The field of taxonomy, the science of classifying organisms, has evolved significantly over the years. The modern approach to classifying organisms is built upon several core principles that aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the relationships between different species. These principles, including the concepts of common descent, homology, and phylogenetic trees, shape the way scientists organize and categorize living organisms.
One of the fundamental principles of modern evolutionary classification is the idea of common descent. This principle suggests that all living organisms share a common ancestor and have evolved from that ancestor over time. By tracing the evolutionary history of organisms, scientists can identify similarities and differences between species and determine their relationships. This concept helps to group organisms into larger categories, such as kingdoms, based on their shared ancestry.
Another key principle is the concept of homology, which refers to the similarity of traits or characteristics in different species that are inherited from a common ancestor. Homologous structures, such as the forelimbs of mammals, provide evidence of shared ancestry and can be used to determine evolutionary relationships. By comparing these homologous structures and other genetic and biochemical data, scientists can further refine the classification of organisms.
To visualize the relationships between different species, taxonomists use phylogenetic trees. These trees represent the evolutionary history of organisms and show their relatedness based on shared characteristics. By analyzing the branching patterns and the sequence of splits in these trees, scientists can reconstruct the evolutionary relationships among different species, genera, families, and other taxonomic groups. This approach allows for a more detailed and precise understanding of the diversity of life on Earth.
In conclusion, the modern approach to classifying organisms is shaped by core principles such as common descent, homology, and phylogenetics. These principles provide a framework for organizing and categorizing living organisms based on their evolutionary relationships. By understanding and applying these principles, scientists can continue to refine our understanding of the vast array of species on our planet and their evolutionary history.
The Role of Phylogenetics in Modern Evolutionary Classification
Phylogenetics plays a crucial role in modern evolutionary classification by helping scientists understand the relationships and evolutionary history of different species. Through the use of molecular and genetic data, phylogenetics allows researchers to create evolutionary trees that illustrate the branching patterns and common ancestry among organisms.
One key aspect of phylogenetics is the identification of homologous traits, which are traits that are inherited from a common ancestor. By comparing the presence or absence of these traits across a variety of species, scientists can determine how closely related they are and place them in the appropriate branches of the evolutionary tree. This allows for a more accurate classification system, as it takes into account the shared genetic and evolutionary history of different organisms.
Phylogenetics also helps in classifying species based on their evolutionary relationships by providing a quantitative measure of relatedness. By analyzing genetic sequences, scientists can calculate the genetic distance between different species and use this information to determine their evolutionary proximity. This allows for a more objective and precise classification system.
Furthermore, phylogenetics enables scientists to make predictions about the characteristics of species based on their placement in the evolutionary tree. For example, if two species are closely related, it is likely that they will share similar traits and behaviors. This predictive power of phylogenetics also aids in the discovery of new species, as scientists can use the evolutionary tree to determine where a new species may fit in and what its characteristics might be.
In conclusion, phylogenetics plays a fundamental role in modern evolutionary classification by providing a framework for understanding the relationships and evolutionary history of different species. Its use of molecular and genetic data allows for a more accurate classification system based on shared ancestry and evolutionary relationships. Furthermore, phylogenetics enables predictions about the characteristics of species and aids in the discovery of new species. Overall, phylogenetics advances our understanding of evolution and helps us better comprehend the diversity of life on Earth.
Exploring how the study of phylogenetics contributes to the classification of organisms
The study of phylogenetics plays a crucial role in the classification of organisms by providing a systematic framework for understanding their evolutionary relationships. Phylogenetics seeks to reconstruct the evolutionary history of species based on shared characteristics and genetic information, allowing scientists to create phylogenetic trees that illustrate the relationships between different groups of organisms. These trees serve as a map of evolutionary history, helping to organize and categorize species based on their common ancestry.
One key way in which phylogenetics contributes to classification is by providing a way to identify and define clades, which are groups of organisms that share a common ancestor. By examining genetic and morphological data, scientists can determine which species belong to which clades, helping to organize organisms into distinct groups based on their evolutionary history. This allows for a more accurate and precise classification system that reflects the true relationships between different species.
Phylogenetics also helps in determining the evolutionary relationships between different taxa, such as families or orders. By comparing the genetic sequences of different species, scientists can determine when divergences occurred and how different groups are related to each other. This information can then be used to create phylogenetic trees that illustrate these relationships, providing a visual representation of the evolutionary history and allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of how different organisms are related.
In addition to its contribution to classification, the study of phylogenetics also has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology and medicine. By understanding the evolutionary relationships between different species, scientists can make more informed decisions about conservation efforts, protecting entire clades rather than individual species. In medicine, phylogenetics can help identify the origin and spread of diseases, allowing for more effective prevention and treatment strategies.
In conclusion, the study of phylogenetics is essential for the classification of organisms as it provides a systematic framework for understanding their evolutionary relationships. By reconstructing the evolutionary history of species and creating phylogenetic trees, scientists can organize and categorize organisms based on their common ancestry, leading to a more accurate and comprehensive classification system. Additionally, phylogenetics has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology and medicine, further highlighting its importance in the study of classification.