
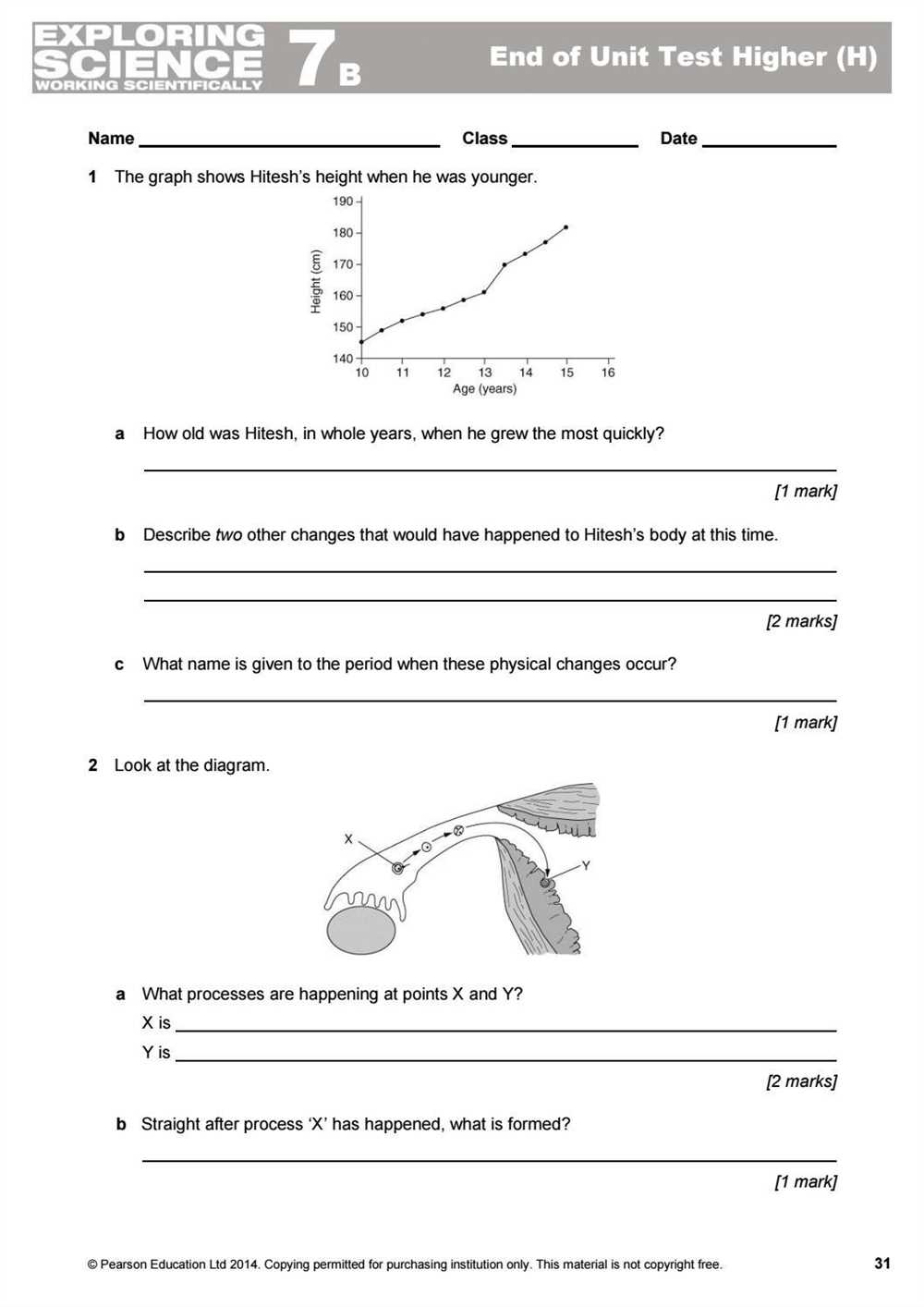
Cell biology is a fundamental branch of science that explores the structure, function, and properties of cells, which are the building blocks of all living organisms. Understanding cell biology is crucial for comprehending the complex processes that occur within living organisms and their role in sustaining life.
The 3 12 Mid Unit Test in cell biology is designed to assess students’ knowledge and understanding of key concepts and principles in cell biology. This test covers topics such as cell structure, cell functions, cell division, and cellular processes.
By taking this mid-unit test, students have the opportunity to demonstrate their grasp of concepts such as the different types of cells, the components of a cell, and the functions of cellular organelles. Students will also be tested on their understanding of vital cellular processes like cell division and the cell cycle.
Overall, the 3 12 Mid Unit Test in cell biology plays a crucial role in evaluating students’ understanding of cell biology concepts and their ability to apply this knowledge to real-world scenarios. By assessing students’ comprehension of these fundamental principles, this test aims to enhance their scientific thinking and problem-solving abilities in the field of cell biology.
Understanding the Importance of Cell Biology
Cell biology is a fundamental branch of science that focuses on the study of cells, which are the basic building blocks of life. It plays a crucial role in understanding various biological processes and how they contribute to the overall functioning of living organisms. By studying cell biology, scientists are able to gain insights into the structure, function, and behavior of cells, leading to advancements in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
Cell structure: One of the key aspects of cell biology is the examination of cell structure. Cells have a complex organization, consisting of various organelles and membranes that carry out specific functions. By understanding the structure of cells, scientists can determine how different organelles interact and work together to support the overall function of the cell. This knowledge is essential for developing targeted therapies and treatments for various diseases.
Cell function: Another important area of cell biology is the study of cell function. Cells carry out numerous functions, such as metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli. By thoroughly understanding these functions, scientists can develop a deeper understanding of biological processes and how they contribute to the overall health and functioning of organisms. This understanding is crucial in areas such as genetic engineering, where scientists manipulate cell functions to produce desired outcomes.
Cell behavior: Cell biology also delves into the behavior of cells, including their division, growth, and interaction with other cells. By studying cell behavior, scientists can gain insights into processes such as embryonic development, tissue formation, and wound healing. This knowledge has implications in regenerative medicine, where scientists aim to promote the growth and repair of damaged tissues and organs.
Applications: The field of cell biology has numerous applications in various sectors. In medicine, cell biology is used to understand diseases at the cellular level and develop targeted treatments. In agriculture, it helps improve crop yields and develop disease-resistant plants. In biotechnology, it plays a crucial role in genetic engineering, cloning, and the production of pharmaceuticals. Overall, understanding cell biology is essential for advancing scientific knowledge and revolutionizing various industries.
Cell Biology: Definition and Overview
Cell biology, also known as cytology, is a branch of biology that focuses on the study of cells and their structure, function, and organization. Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and they are found in all living organisms, from single-celled bacteria to complex multicellular organisms like humans. Understanding cell biology is crucial for comprehending the fundamental processes that occur in living organisms and their various functions.
Cells are incredibly diverse in their size, shape, and function. They can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic, and each type has its own unique characteristics. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, while eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, have a distinct nucleus that houses the genetic material. The study of cell biology involves examining the different components of cells, including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, and the various biomolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, that make up these structures.
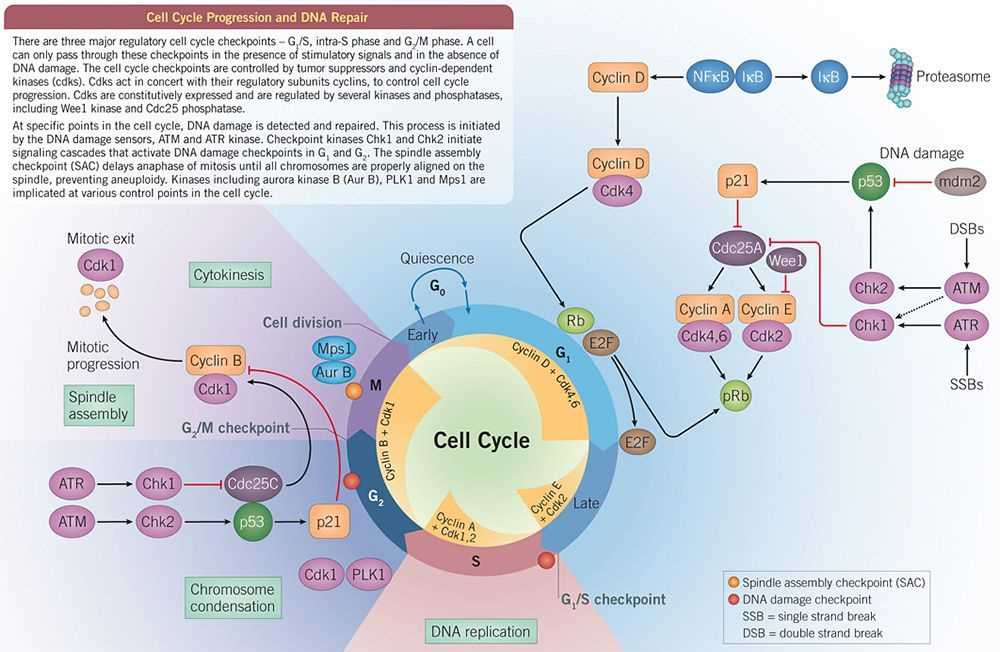
Cell biology encompasses a wide range of research areas, including cell division, cell signaling, cell cycle regulation, cellular interactions, and cellular metabolism. Advances in cell biology have led to significant breakthroughs in medicine, biotechnology, and other related fields. For example, the discovery of stem cells and their potential for tissue regeneration has revolutionized the field of regenerative medicine, offering hope for treating various diseases and injuries. Additionally, an understanding of cell biology has shed light on the underlying causes of numerous diseases, leading to the development of targeted therapies and interventions.
Overall, cell biology is a dynamic and evolving field that continues to unravel the mysteries of life at the cellular level. By studying cells, scientists gain valuable insights into the intricate mechanisms that drive biological processes and contribute to the overall functioning of living organisms. Through further research and exploration, cell biology will continue to pave the way for advancements in medicine, biotechnology, and our understanding of life itself.
The Role of Cell Biology in Scientific Research and Medical Advancements
Cell biology plays a crucial role in scientific research and medical advancements, providing a foundation for understanding the intricacies of life at the cellular level. By studying cells, scientists can unravel the complex processes that occur within our bodies, leading to significant discoveries and breakthroughs in various fields.
One area where cell biology has made a tremendous impact is in the field of cancer research. By examining cancer cells at the cellular level, researchers have been able to identify key molecular pathways and genetic mutations that drive the development and progression of cancer. This knowledge has paved the way for the development of targeted therapies and personalized medicine, revolutionizing cancer treatment and improving patient outcomes.
In addition to cancer research, cell biology has also played a crucial role in understanding the mechanisms of various diseases and disorders. Through studying cells, researchers have been able to uncover the underlying causes of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and diabetes. This knowledge has not only deepened our understanding of these diseases but has also opened up new avenues for treatment and prevention.
The impact of cell biology extends beyond the realm of human health. By studying cells in plants and animals, scientists can better understand the processes that govern growth, development, and evolution. This knowledge has important implications for agriculture, as researchers can use cell biology to improve crop yields, develop disease-resistant plants, and enhance food security.
In conclusion, cell biology serves as the foundation for scientific research and medical advancements, providing insights into the fundamental processes that govern life. Through studying cells, researchers can tackle complex diseases, develop targeted therapies, and improve our understanding of the natural world. The discoveries made in the field of cell biology have the potential to make significant impacts on human health, agriculture, and our overall understanding of life on Earth.
Studying Cell Structures and Functions
The study of cell structures and functions is crucial for understanding the complex machinery that drives all living organisms. Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and they carry out a wide array of functions that are essential for the survival and growth of an organism. By studying cell structures and functions, scientists can gain insights into how cells work and how they interact with each other and their environment.
One of the key areas of study in cell biology is the investigation of cellular organelles, which are specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions. These organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and many others. Each organelle has its own unique structure and function, and understanding their roles is fundamental to understanding how cells work.
In addition to studying organelles, cell biologists also examine the various processes that occur within cells. This includes processes such as cell division, DNA replication, protein synthesis, and cellular energy production. By studying these processes, scientists can gain insights into how cells grow, replicate, and maintain their structure and function.
Furthermore, studying cell structures and functions has practical applications in fields such as medicine and biotechnology. For example, understanding how cancer cells differ from normal cells at the molecular level can help in the development of targeted therapies. Similarly, studying the functions of specific cellular organelles can lead to the development of new drugs that target these structures.
In conclusion, the study of cell structures and functions is a fundamental area of research in biology. By unraveling the complex machinery of cells, scientists can gain insights into the fundamental processes that underlie life. This knowledge not only improves our understanding of the natural world but also has practical applications in fields such as medicine and biotechnology.
Exploring the Different Types of Cells
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. They come in various shapes, sizes, and functions. Understanding the different types of cells is crucial in comprehending the complexity of life.
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most primitive type of cells. They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria and archaea are examples of prokaryotic cells. Despite their simplicity, prokaryotic cells possess remarkable adaptability and are found in diverse habitats.
Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and evolved. They have a distinctive nucleus and numerous membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, lysosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum. Eukaryotic cells can be found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Animal cells are a specific type of eukaryotic cells. They lack a rigid cell wall and have unique structures, such as centrioles and cholesterol-laden plasma membranes. Animal cells are highly specialized and carry out specific functions necessary for the organism’s survival.
Plant cells, in contrast, have a cell wall made of cellulose, which provides structural support. They also contain chloroplasts, which enable photosynthesis and give plants their green color. Additionally, plant cells have large central vacuoles, responsible for storing water and other substances.
Additionally, there are specialized cells such as nerve cells, muscle cells, and red blood cells. Nerve cells, or neurons, transmit electrical signals, while muscle cells generate force for movement. Red blood cells, on the other hand, are responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
In conclusion, cells are incredibly diverse and intricate. Each type of cell has unique characteristics and functions that contribute to the overall complexity of life. By studying and understanding these different types of cells, scientists gain valuable insights into the fundamental processes that drive living organisms.
Investigating Cell Structures and Organelles
In the field of cell biology, scientists are constantly investigating the structures and organelles that make up cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms, and understanding their structures and functions is essential for understanding life itself. By studying cell structures and organelles, scientists can gain insights into how cells function, how they communicate with each other, and how they contribute to the overall health and functioning of an organism.
One of the key tools used in investigating cell structures and organelles is microscopy. With the help of powerful microscopes, scientists are able to visualize and study the intricate details of cells at a microscopic level. They can examine the different organelles within cells, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, and determine their functions and interactions.
For example, using fluorescence microscopy, scientists can label specific organelles with fluorescent dyes or proteins to track their movements and dynamics within cells. This technique allows them to observe processes such as protein synthesis, organelle transport, and cell division in real time. By studying these processes, scientists can gain insights into the fundamental mechanisms that govern cell function and behavior.
In addition, advances in imaging technologies have allowed researchers to go beyond traditional microscopy and explore cells in even greater detail. Techniques such as electron microscopy and super-resolution microscopy enable scientists to visualize the ultrastructure of cells and organelles at an unprecedented level of resolution. This has opened up new avenues for understanding cell biology and has led to important discoveries about the organization and function of cellular components.
- Overall, investigating cell structures and organelles is crucial for understanding the complexities of life at a cellular level.
- By gaining insights into the inner workings of cells, scientists can develop new treatments for diseases, improve agricultural practices, and advance our knowledge of the natural world.
- With ongoing advancements in technology and techniques, the field of cell biology continues to unravel the mysteries of cells and contribute to various areas of science and medicine.