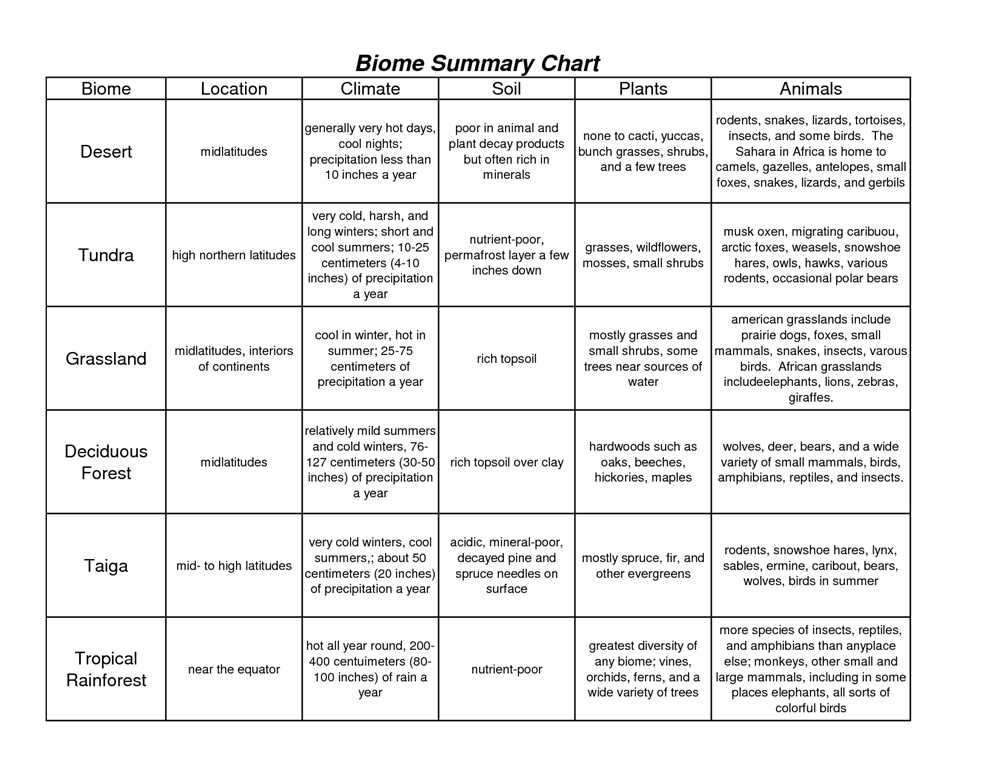
In the study of biology, understanding different biomes is vital to comprehending the diverse ecosystems that exist around the world. Biomes are large geographic regions with distinct climate, plants, and animals. To successfully identify and classify these biomes, scientists utilize various characteristics and factors.
One key factor in determining biomes is temperature. Temperature affects the types of plants and animals that can survive in a specific area. For example, tropical rainforests are found near the Equator and have high temperatures year-round, resulting in a rich diversity of plant and animal species. On the other hand, tundra biomes, found in the Arctic and Antarctic regions, experience extremely low temperatures, limiting the number of species that can survive.
Precipitation is another crucial factor in defining biomes. Different amounts of rainfall or snowfall determine the types of plants that can thrive in a particular region. Deserts, characterized by very little rainfall, have adapted plants that can conserve water, such as cacti. Rainforests, with their high levels of rainfall, support vegetation that grows quickly and densely.
One commonly used classification system for biomes is the Köppen Climate Classification. This system categorizes the world’s biomes based on temperature and precipitation patterns. The division of biomes into groups such as tropical rainforest, tundra, desert, and grassland is helpful in understanding the global distribution of ecosystems and their unique characteristics.
What are biomes?
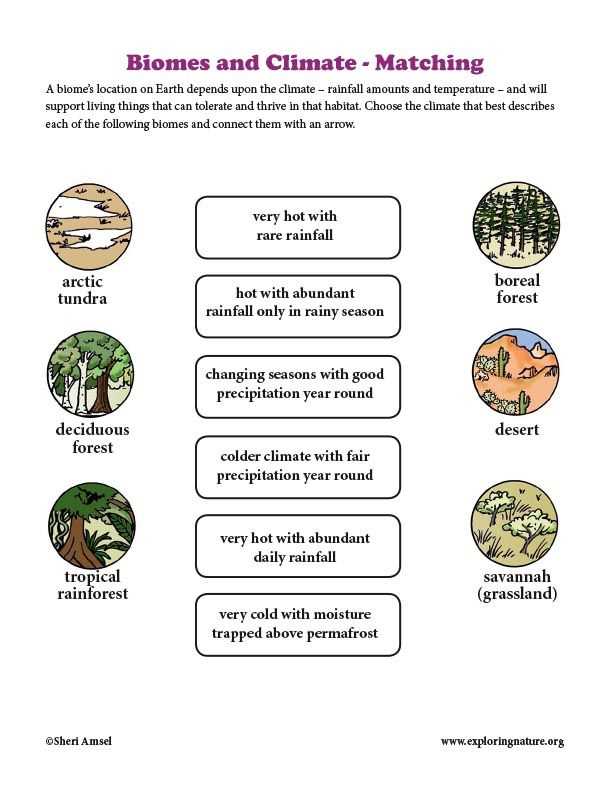
Biomes are large, distinct regions of the Earth’s surface that are characterized by a unique combination of climate, geography, and plant and animal life. They are defined by the types of ecosystems and habitats that occur within them. Biomes can be found across the world, from the frozen tundra of the Arctic to the lush rainforests of the Amazon.
There are several key factors that determine the characteristics of a biome. Climate plays a major role, as it determines the temperature and precipitation patterns within a region. The amount of rainfall and temperature fluctuations can greatly impact the types of plants and animals that can survive in a particular biome. The geography of an area, including factors such as elevation and soil composition, also influences the types of ecosystems that can exist.
There are four main types of biomes: forest, grassland, desert, and tundra. Each of these biomes has its own unique set of plant and animal species that have adapted to the specific conditions of their environment. Forest biomes, for example, are characterized by dense tree cover and a variety of plant and animal life. Grassland biomes, on the other hand, are dominated by grasses and are home to many grazing animals.
Biomes are important for sustaining life on Earth. They provide habitats for countless species of plants and animals, and they also play a crucial role in regulating the planet’s climate. Unfortunately, many biomes are under threat due to human activities such as deforestation and climate change. It is important for us to understand and protect these fragile ecosystems to ensure the survival of the diverse life forms that depend on them.
Biomes and their characteristics
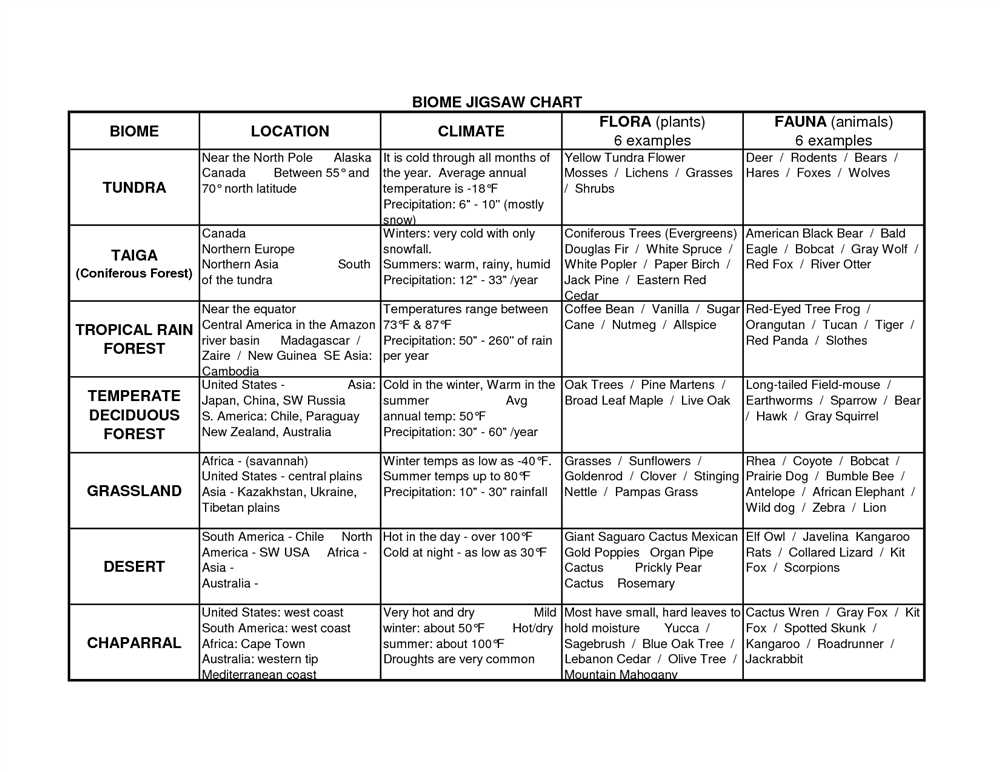
Biomes are large geographical areas characterized by distinct climate, vegetation, and animal species. They are classified based on several factors such as temperature, precipitation, and the types of plants and animals that inhabit them. Each biome has its own unique set of characteristics that define its ecosystem and determine the types of organisms that can survive and thrive within it.
One of the most well-known biomes is the tropical rainforest, which is characterized by high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and dense vegetation. These forests are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, including colorful birds, exotic insects, and towering trees. The tropical rainforest biome is known for its high levels of biodiversity, with countless species coexisting within its lush and vibrant ecosystem.
In contrast, the desert biome is characterized by extremely low levels of rainfall and sparse vegetation. Deserts are often hot during the day and cold at night, and they are home to unique plants and animals that have adapted to survive in harsh and arid conditions. Cacti, succulents, and camels are some of the iconic species found in desert biomes.
Other biomes include grasslands, which are characterized by an abundance of grasses and a lack of trees, and taiga, which is characterized by its cold temperatures and evergreen forests. Each biome has its own set of environmental conditions that shape the organisms and ecosystems within it, making them fascinating to study and explore.
Forest Biome
The forest biome is a complex ecosystem that is characterized by an abundance of trees and other vegetation. It is one of the most diverse biomes on the planet, supporting a wide variety of plant and animal species. Forests can be found in different parts of the world, from tropical rainforests to temperate deciduous forests.
Key features of the forest biome include a dense canopy formed by the tall trees, which provide shade and create a unique microclimate. The forest floor is covered with fallen leaves, branches, and other organic matter, creating a rich layer of soil that supports the growth of plants. The understory, or the layer of vegetation beneath the canopy, is home to smaller trees, shrubs, and herbaceous plants.
- Types of Forest Biomes: There are several types of forest biomes, including tropical rainforests, temperate deciduous forests, coniferous forests, and boreal forests. Each of these biomes has its own distinct characteristics and supports different types of plant and animal life.
- Plant Life: Forest biomes are known for their lush vegetation, with a wide range of tree species. In tropical rainforests, you can find tall trees such as mahogany, palm trees, and orchids. In temperate deciduous forests, you can find oak, maple, and beech trees. Coniferous forests are dominated by evergreen trees like pine, spruce, and fir. Boreal forests, also known as taiga, are characterized by coniferous trees and shrubs.
- Animal Life: Forest biomes are home to a diverse array of animal species. In tropical rainforests, you can find animals like jaguars, monkeys, and toucans. In temperate deciduous forests, you can find deer, squirrels, and a variety of bird species. Coniferous forests are home to animals like bears, wolves, and owls. Boreal forests are known for their populations of moose, lynx, and wolves.
The forest biome plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting biodiversity. Forests help regulate the climate, absorb carbon dioxide, and provide habitat for numerous species. They also provide valuable resources for humans, such as timber, medicine, and recreational opportunities. However, deforestation and habitat loss are major threats to forest biomes, leading to the endangerment and extinction of many species. Conservation efforts are essential to protect and sustain the forest biome for future generations.
Desert Biome
The desert biome is a harsh and extreme environment characterized by low rainfall and high temperatures. It is one of the most challenging ecosystems for organisms to survive in. Despite the harsh conditions, the desert biome is home to a surprising diversity of plant and animal species that have adapted to the extreme environment.
Plants: Desert plants are specially adapted to conserve water due to the scarcity of rainfall. Examples of desert plants include cacti, succulents, and shrubs. These plants have developed various adaptations such as storing water in their tissues, reducing leaf surface area to minimize water loss, and having long roots to access underground water sources.
Animals: Desert animals have also evolved unique adaptations to survive in the desert environment. Some animals, like the camel, have specialized physiological adaptations that allow them to go without water for long periods of time. Others, such as the kangaroo rat, have the ability to extract water from food and can survive without drinking water at all. Many desert animals are also nocturnal, as the cooler temperatures during the night help them avoid extreme heat during the day.
- Camel: The camel is often considered the symbol of the desert biome. It has numerous adaptations to survive in the harsh desert environment, including the ability to store water in its hump and to withstand high temperatures.
- Desert tortoise: The desert tortoise is a reptile that lives in desert regions. It has a hard shell that provides protection from predators and extreme temperatures.
- Golden eagle: The golden eagle is a bird of prey that can be found in desert areas. It has excellent eyesight and powerful talons, making it a formidable hunter in the desert ecosystem.
The desert biome is not only home to unique and fascinating plant and animal species, but it also plays an important role in regulating the Earth’s climate. The dry climate and lack of vegetation in deserts lead to high temperatures during the day and low temperatures at night. These temperature extremes can influence weather patterns and contribute to the formation of deserts in certain regions of the world.
Aquatic Biome
The aquatic biome is a vast ecosystem that covers approximately 70% of the Earth’s surface. It includes both freshwater and marine environments, ranging from lakes and rivers to oceans and seas. This biome is characterized by its high moisture content and is home to a diverse array of plants and animals.
One key feature of the aquatic biome is the presence of water, which serves as a vital resource for all living organisms within this ecosystem. Water provides a habitat for countless species, supports various ecological processes, and helps regulate the Earth’s climate. Additionally, it provides a medium for nutrient cycling and acts as a transportation system for many organisms.
The aquatic biome can be divided into two main categories: freshwater and marine. Freshwater biomes include lakes, rivers, streams, and wetlands, while marine biomes encompass oceans, seas, coral reefs, and estuaries. Each of these subcategories has its own unique characteristics and supports a distinct set of organisms.
In freshwater biomes, the water has a low salt concentration, allowing for the existence of numerous species of fish, amphibians, and plants. These biomes are often characterized by high levels of biodiversity and provide essential resources for local communities and wildlife.
On the other hand, marine biomes house a wide range of marine life, including fish, mammals, reptiles, and various types of algae. These biomes are known for their vastness and complexity, with diverse ecosystems like coral reefs and kelp forests thriving in marine waters.
In conclusion, the aquatic biome plays a crucial role in supporting life on Earth. Its vastness, diversity, and unique characteristics make it a fascinating ecosystem to study. Moreover, the aquatic biome is essential for maintaining the ecological balance and providing various resources that are vital for the survival of both aquatic and terrestrial organisms.
Tundra biome
The tundra biome is a unique and fascinating region found in the northernmost parts of the world. It is characterized by extremely cold temperatures, little precipitation, and a frozen landscape for most of the year. The tundra biome is divided into two types: the Arctic tundra, found in the northern hemisphere, and the alpine tundra, found in high mountain regions.
The Arctic tundra is located in the Arctic Circle and spans across Alaska, Canada, Greenland, and Russia. It is covered with a layer of permafrost, which is frozen soil that remains frozen throughout the year. The vegetation in the Arctic tundra is adapted to survive in harsh conditions, with low-growing plants like mosses, lichens, and small shrubs dominating the landscape. Due to the short growing season, these plants have developed the ability to photosynthesize and reproduce quickly.
- The tundra biome experiences extreme temperatures, with winters reaching as low as -30°C (-22°F) and summers staying around 10°C (50°F).
- Animals in the tundra biome have also adapted to survive in this harsh environment. Species like polar bears, Arctic foxes, caribou, and muskoxen are well-suited to the cold temperatures and limited food resources.
- The tundra biome is also an important breeding ground for migratory birds, such as ducks, geese, and shorebirds. These birds travel long distances to take advantage of the short summer season and abundant food sources.
Overall, the tundra biome is an incredibly fragile and unique ecosystem that relies on its specialized plants and animals to survive in its extreme conditions. It is also an important region in terms of climate regulation, as the permafrost in the tundra stores large amounts of carbon. However, due to climate change, the tundra biome is facing significant challenges, including thawing permafrost and the loss of habitat for its iconic wildlife.
The Importance of Understanding Biomes
Biomes are essential ecosystems that exist all around the world. Understanding biomes is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, biomes are home to an incredible variety of plant and animal species. Each biome has its own unique set of conditions, such as climate, soil composition, and availability of water, which determine the types of organisms that can survive and thrive in that particular environment. By understanding these conditions, scientists and conservationists can work towards preserving and protecting the biodiversity within each biome.
Furthermore, biomes play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate and overall balance. Different types of biomes, such as rainforests, deserts, and tundras, have distinct patterns of weather and climate. For instance, tropical rainforests help regulate global temperature and act as a carbon sink, absorbing and storing large amounts of carbon dioxide. On the other hand, polar tundras reflect sunlight and contribute to cooling the Earth’s surface. Understanding the functioning of these biomes is crucial in addressing climate change and maintaining the stability of our planet.
Key Phrases:
- variety of plant and animal species
- climate
- soil composition
- availability of water
- preserving and protecting biodiversity
- regulating Earth’s climate
- balance
- weather and climate patterns
- tropical rainforests
- carbon sink
- polar tundras
- addressing climate change
- maintaining stability
In conclusion, understanding biomes is vital for the conservation of biodiversity, the regulation of the Earth’s climate, and the overall sustainability of our planet. By studying and appreciating the unique characteristics of each biome, we can make informed decisions and take actions to ensure the long-term survival of these essential ecosystems.