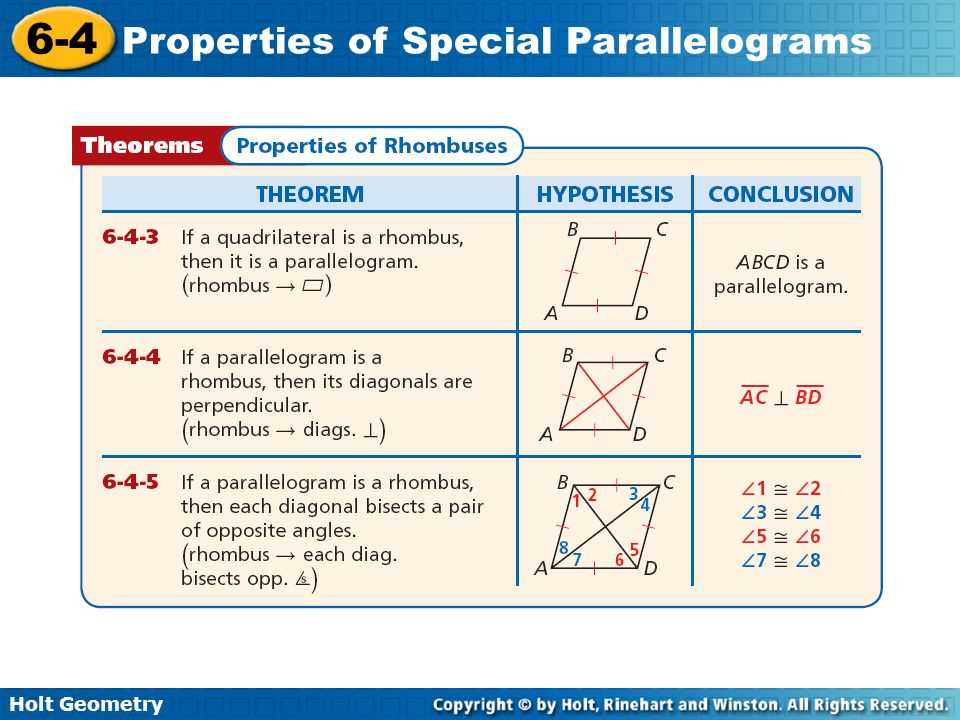
Parallelograms are fascinating shapes in mathematics that possess several unique properties. Understanding these properties can help us solve geometric problems and accurately measure angles and sides within these shapes. In this article, we will explore five key properties of parallelograms that form the foundation of their geometry.
Firstly, one of the fundamental characteristics of a parallelogram is that opposite sides are parallel. This means that you can draw two lines that never intersect, running alongside each other, on opposite sides of the shape. This property allows us to determine the lengths of unknown sides and angles within the parallelogram.
The second property is that opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Congruent means that they have the same length. This property enables us to determine the measurements of unknown sides by using the lengths of the known sides. It also provides a basis for proving other properties of parallelograms.
The third property is related to the angles within a parallelogram. Opposite angles, also known as vertical angles, are congruent. This means that if we measure the two angles formed by the intersection of the diagonals within the parallelogram, we will find that they have the same measurement. This property allows us to find missing angle measurements within a parallelogram using this congruence relationship.
The fourth property deals with the adjacent angles within a parallelogram. Adjacent angles, also known as adjacent interior angles, are supplementary. This means that the sum of the measures of the two adjacent angles is always 180 degrees. This property allows us to find missing angle measurements within the parallelogram by using this supplementary relationship.
Lastly, the fifth property we will discuss is the diagonals of a parallelogram. The diagonals bisect each other, meaning that they intersect at their midpoints, dividing each diagonal into two equal parts. This property provides a method for finding the length of the diagonals using the lengths of the sides of the parallelogram.
By understanding these five key properties of parallelograms, we can confidently solve various geometric problems involving these shapes. Whether it is finding the missing lengths of sides, measuring angles, or determining the properties of the diagonals, these properties serve as the building blocks of parallelogram geometry.
Understanding the Properties of Parallelograms
A parallelogram is a special type of quadrilateral that has several key properties. By understanding these properties, we can better comprehend the characteristics and relationships of these geometric shapes.
1. Opposite sides are parallel: One of the defining features of a parallelogram is that its opposite sides are always parallel. This means that if we were to extend these sides indefinitely, they would never intersect. This property allows us to identify parallelograms and distinguish them from other types of quadrilaterals.
2. Opposite sides are equal in length: In addition to being parallel, the opposite sides of a parallelogram are also equal in length. This symmetry ensures that the shape is balanced and symmetrical. If we were to measure the lengths of the four sides of a parallelogram, we would find that the opposite sides are congruent.
3. Opposite angles are equal: Another important property of parallelograms is that their opposite angles are always equal in measure. This means that if we were to compare the size of each pair of opposite angles, we would find that they are the same. This property allows us to determine the measures of angles within a parallelogram and find missing angles with known values.
4. Consecutive angles are supplementary: In a parallelogram, the consecutive angles (those that share a side) are always supplementary, which means that their measures add up to 180 degrees. This relationship allows us to calculate the measures of angles by knowing the value of just one angle in the shape.
5. Diagonals bisect each other: Finally, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. This means that they divide each other into two equal segments. This property allows us to find the midpoint of a diagonal or determine the length of a diagonal using the Pythagorean theorem.
Overall, understanding the properties of parallelograms allows us to analyze and manipulate these shapes in various geometric problems and proofs. By applying these properties, we can solve for unknown values, prove theorems, and explore the relationships between different parts of a parallelogram.
The Importance of Knowing the Answer Key to the Properties of Parallelograms
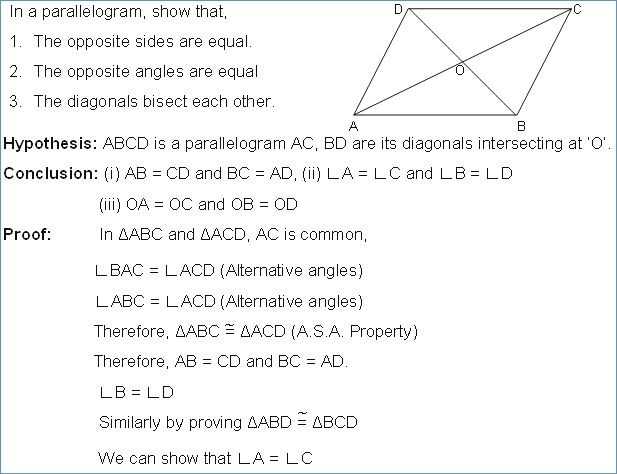
Understanding the properties of parallelograms is essential in the field of geometry. Parallelograms are quadrilaterals with special characteristics that can help solve various mathematical problems. By knowing the answer key to the properties of parallelograms, students and professionals can confidently tackle geometric challenges and arrive at accurate solutions.
One of the key reasons why knowing the answer key is important is that it provides a solid foundation for further learning and problem-solving. Parallelograms have unique attributes such as opposite sides being parallel and congruent, opposite angles being congruent, and diagonals bisecting each other. By understanding these properties and how they relate to each other, individuals can build upon their knowledge and apply it to more complex concepts.
- Clarity and Accuracy: Having access to the answer key ensures that individuals can check their work and verify if they have correctly applied the properties of parallelograms. The answer key serves as a guide by providing correct solutions, thus promoting accuracy in calculations and problem-solving.
- Efficiency in Problem-Solving: With the answer key in hand, individuals can save time and effort by referencing it to check if their approach and solution align with the expected outcomes. This promotes efficiency and streamlines the problem-solving process, allowing individuals to move on to more challenging math concepts.
- Building Conceptual Understanding: The answer key not only provides correct answers but also helps individuals understand the reasoning behind each solution. By reviewing the answer key, individuals can grasp the underlying principles and logic behind the properties of parallelograms, strengthening their conceptual understanding.
In conclusion, knowing the answer key to the properties of parallelograms is crucial for students and professionals in the field of geometry. It helps build a strong foundation, promotes accuracy in problem-solving, enhances efficiency, and contributes to a deeper conceptual understanding. The answer key serves as a valuable tool that enables individuals to confidently approach and solve geometric problems, paving the way for further mathematical growth and success.
Definition of a parallelogram

A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. This means that opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel and have the same length. In addition, the opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent, meaning they have the same measure. These properties make parallelograms a special type of quadrilateral, with unique characteristics that set them apart from other shapes.
One key property of parallelograms is that their opposite sides are equal in length. This can be seen by measuring the lengths of the sides or by using the properties of parallel lines. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are always congruent, which means they have the same length.
Another important property of parallelograms is that their opposite angles are congruent. This can be proven using the properties of parallel lines and transversals. If we draw a transversal that intersects the parallel sides of a parallelogram, we can show that the corresponding angles are congruent. This means that the opposite angles of a parallelogram are always equal in measure.
Overall, the definition of a parallelogram includes the properties of having two pairs of parallel sides, opposite sides being equal in length, and opposite angles being congruent. These properties make parallelograms a distinct type of quadrilateral and allow us to identify and work with them in geometry.
Basic characteristics of a parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel and congruent. It is known for its unique properties and characteristics that set it apart from other types of quadrilaterals.
1. Opposite sides are parallel: One of the defining features of a parallelogram is that its opposite sides are parallel. This means that if you extend the sides, they will never intersect. The parallel sides create a sense of symmetry and balance in the shape.
2. Opposite sides are congruent: In addition to being parallel, the opposite sides of a parallelogram are also congruent. This means that they have the same length. The equality of the sides further contributes to the shape’s symmetry and stability.
3. Opposite angles are congruent: Another important characteristic of a parallelogram is that its opposite angles are congruent. This means that if you measure the angles across from each other, they will have equal measures. The congruent angles add to the overall symmetry and regularity of the shape.
4. Consecutive angles are supplementary: Consecutive angles in a parallelogram are supplementary, meaning that their measures add up to 180 degrees. This property is a direct consequence of the parallel sides and congruent opposite angles.
5. Diagonals bisect each other: The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, dividing each other into two equal segments. This property is a result of the parallelogram’s symmetry and helps to create a sense of balance within the shape.
These are just a few of the basic characteristics that define a parallelogram. These properties make it a unique and interesting shape in the field of geometry. Whether you are studying mathematics or simply curious about shapes, understanding the properties of a parallelogram can help you appreciate the beauty and intricacy of this quadrilateral.
The defining properties of a parallelogram

A parallelogram is a special type of quadrilateral that has several defining properties. By understanding these properties, we can easily identify and classify parallelograms.
Property 1: Opposite sides are parallel
One of the most fundamental properties of a parallelogram is that the opposite sides are parallel. This means that if we take any two sides of a parallelogram, they will never intersect and will always remain equidistant throughout their length. This property is what sets parallelograms apart from other quadrilaterals.
Property 2: Opposite angles are congruent
Another defining property of a parallelogram is that the opposite angles are congruent. This means that if we take any two angles that are opposite to each other in a parallelogram, they will have the same measure. In other words, if one angle is x degrees, then the opposite angle will also be x degrees. This property highlights the symmetry and balance present in parallelograms.
Property 3: Consecutive angles are supplementary
In addition to having congruent opposite angles, the consecutive angles of a parallelogram are also supplementary. This means that if we take any two angles that are adjacent to each other in a parallelogram, their sum will always be 180 degrees. For example, if one angle is x degrees, then the adjacent angle will be 180 – x degrees. This property further emphasizes the symmetry and balance of parallelograms.
These three properties – parallel sides, congruent opposite angles, and supplementary consecutive angles – are the defining characteristics of a parallelogram. By recognizing and applying these properties, we can easily identify and work with parallelograms in various mathematical and geometrical contexts. Furthermore, these properties enable us to derive and prove additional theorems and formulas related to parallelograms.
Theorem 1: Opposite sides of a parallelogram
In a parallelogram, the opposite sides are congruent.
Let’s consider a parallelogram ABCD with sides AB, BC, CD, and DA. According to Theorem 1, the opposite sides AB and CD are congruent. This means that the length of AB is equal to the length of CD.
- Proof:
To prove that the opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent, we can start by drawing a diagonal, such as AC, dividing the parallelogram into two congruent triangles, namely ΔABC and ΔCDA. By the definition of a parallelogram, opposite sides and angles are congruent; thus, AB ≅ CD and ∠ABC ≅ ∠CDA. Since ΔABC and ΔCDA are congruent, corresponding sides and angles are congruent as well. Therefore, AB and CD are congruent.
This property of parallelograms is useful in various geometric and mathematical calculations. For example, if we know the length of one side of a parallelogram, we can use Theorem 1 to find the length of the opposite side. It also helps in determining the dimensions and properties of parallelograms in real-life applications, such as designing buildings, constructing bridges, and creating geometric artwork.
Explanation of the First Property
The first property of parallelograms states that opposite sides are congruent.
In a parallelogram, the opposite sides are parallel and have the same length. This means that if we take any two sides of a parallelogram that are opposite to each other, they will be equal in length. The reason for this is that when two lines are parallel, they never intersect, and therefore their lengths remain the same throughout.
To further illustrate this property, let’s consider a parallelogram ABCD. If we take sides AB and CD, which are opposite to each other, we can measure their lengths using a ruler. We will find that AB is equal to CD. Similarly, if we take sides AD and BC, which are also opposite to each other, their lengths will be equal.
This property can also be proven using the principles of Euclidean geometry. We can show that if two sides of a quadrilateral are parallel, then the opposite sides must also be parallel. By using geometric theorems and proofs, we can conclude that the opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent.
This property is important in geometry because it allows us to make deductions and solve problems related to parallelograms. For example, if we are given the length of one side of a parallelogram, we can use this property to find the lengths of the other sides. We can also use it to determine if a given quadrilateral is a parallelogram or not. By checking if the opposite sides are congruent, we can confirm if the quadrilateral satisfies the definition of a parallelogram.