In the natural world, different regions have distinct biomes that are characterized by specific climate conditions, vegetation patterns, and animal habitats. Understanding these biomes and their key features is crucial for scientists, ecologists, and anyone interested in the diversity of life on Earth.
The 6 2 biomes answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the six major terrestrial biomes and the two major aquatic biomes. These key answers offer important insights into the characteristics, adaptations, and ecological functions of each biome, enabling us to better appreciate the interconnectedness of our planet’s ecosystems.
Let’s delve into each biome. Starting with terrestrial biomes, we have the tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forest, temperate grassland, tropical rainforest, and desert. Each of these biomes is distinguished by its unique climate, soil conditions, and plant and animal life. From the freezing temperatures and limited vegetation of the tundra to the lush biodiversity of the tropical rainforest, each biome supports a remarkable array of organisms that have evolved to thrive in their respective environments.
As for aquatic biomes, we have the freshwater and marine biomes. Freshwater biomes include lakes, ponds, rivers, and wetlands, while marine biomes comprise oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries. These biomes provide habitat for a wide range of aquatic species, from fish and marine mammals to algae and microorganisms. They also play a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate, producing essential oxygen, and supporting global biodiversity.
Overview of biomes and their significance in the study of ecosystems

Biomes are large geographical regions characterized by their specific climatic conditions, vegetation types, and animal communities. They play a crucial role in the study of ecosystems as they represent distinct ecological units with unique characteristics and interactions. Understanding biomes is essential for ecologists and environmental scientists to comprehend the complex dynamics of the natural world and make informed decisions regarding conservation and management efforts.
There are several key biomes found around the world, including forests, grasslands, deserts, tundras, and aquatic ecosystems. Each biome is defined by its climate, such as temperature and precipitation patterns, which in turn influence the types of plants and animals that can survive and thrive within it. For example, tropical rainforests, characterized by high temperatures and abundant rainfall, support an immense diversity of plant and animal species. On the other hand, deserts, with their extreme aridity and limited water availability, have adapted organisms that can withstand drought and heat.
Studying biomes helps scientists gain insights into the functioning and interrelationships of various ecosystems. By examining the biodiversity, ecological processes, and adaptation strategies of organisms in different biomes, researchers can uncover fundamental principles and mechanisms governing ecosystem structure and function. This knowledge is crucial for assessing the impacts of environmental changes, such as climate change and habitat destruction, on biodiversity and ecosystem services. It also provides the foundation for developing effective conservation strategies and managing natural resources sustainably.
Moreover, the study of biomes allows scientists to understand the distribution of species and their interactions across different geographic regions. By identifying patterns in species diversity and community composition, scientists can develop biogeographic theories and models that explain the factors shaping biodiversity and species distributions. This information is vital for biodiversity conservation strategies and predicting the potential impacts of habitat fragmentation and species loss.
In conclusion, biomes are significant in the study of ecosystems as they represent distinct ecological units with unique characteristics and interactions. Understanding biomes helps scientists gain insights into ecosystem dynamics, assess environmental impacts, develop conservation strategies, and predict species distributions. Without studying biomes, our understanding of the natural world and our ability to protect and manage it effectively would be severely limited.
Major Biomes of the World
The world is composed of various ecosystems known as biomes. These biomes are characterized by their distinct climate, vegetation, and animal life. There are six major biomes in the world, each with its own unique features and adaptations.
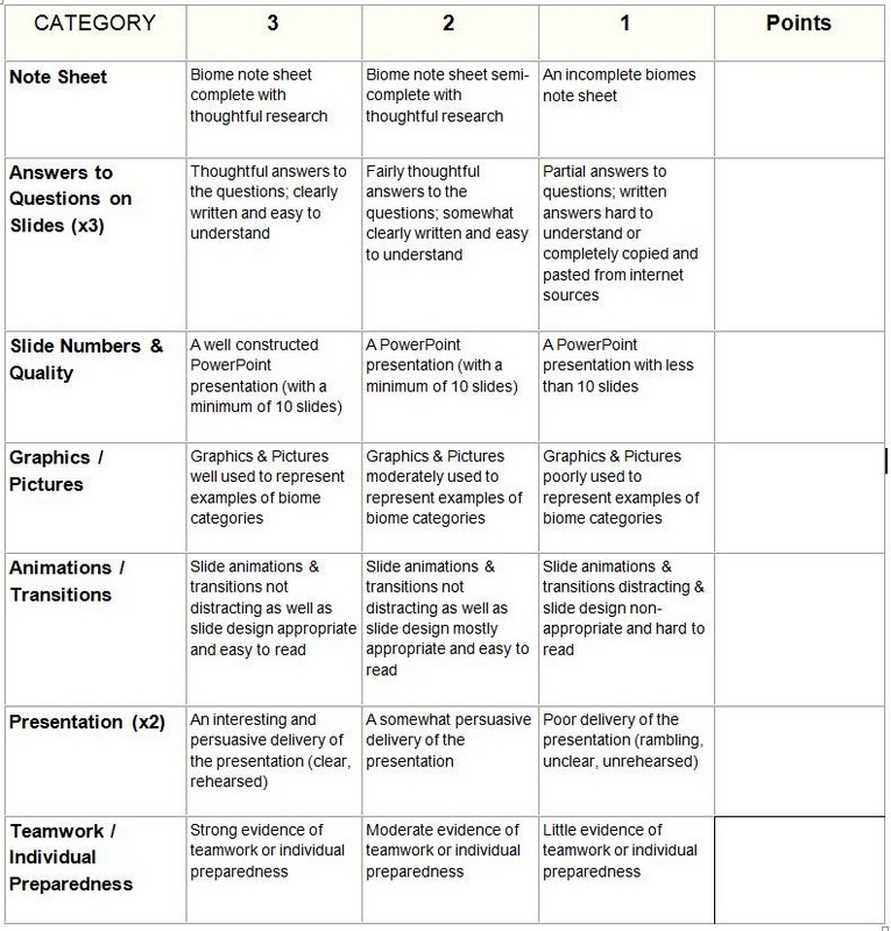
The first major biome is the tundra. Found in the far northern regions of the world, the tundra is a cold and treeless landscape. It is characterized by frozen soil and harsh winters, with very little precipitation. Despite these challenging conditions, the tundra is home to hardy plants such as mosses, lichens, and shrubs, as well as animals like reindeer, musk oxen, and Arctic foxes.
The next major biome is the taiga, also known as the boreal forest. This biome is found in the northern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. It is characterized by its vast coniferous forests and cold temperatures. The taiga is home to trees such as spruce, fir, and pine, as well as animals like moose, wolves, and bears. This biome experiences long, cold winters and short, mild summers.
Further south, we find the temperate deciduous forest biome. This biome is characterized by its moderate climate and four distinct seasons. It is found in the eastern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. The temperate deciduous forest is home to trees such as oak, maple, and beech, as well as animals like deer, squirrels, and birds. This biome experiences hot summers, cold winters, and a moderate amount of precipitation throughout the year.
The next major biome is the grassland. These vast, open landscapes are characterized by their flat terrain and grasses that dominate the vegetation. Grasslands are found on every continent except Antarctica. They are home to a variety of animals like bison, zebras, and prairie dogs. Grasslands have a climate with hot summers and cold winters, and a moderate amount of rainfall.
Moving on to the desert biome, which is characterized by its arid climate and sparse vegetation. Deserts are found in many parts of the world, including Africa, the Middle East, and North America. They receive very little rainfall and can be extremely hot during the day and cold at night. Despite these harsh conditions, deserts are home to unique plants like cacti, as well as animals like snakes, lizards, and camels.
Lastly, we have the tropical rainforest biome. These are lush, dense forests found near the equator, in regions such as the Amazon rainforest in South America and the Congo Basin in Africa. Tropical rainforests are characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and incredible biodiversity. They are home to a wide variety of plant species, such as orchids, bromeliads, and towering trees, as well as a diverse array of animals, including monkeys, toucans, and jaguars.
- Tundra: cold, treeless, mosses, lichens, reindeer
- Taiga: coniferous forests, cold, spruce, moose
- Temperate Deciduous Forest: moderate, four seasons, oak, deer
- Grassland: flat, grasses, bison, zebras
- Desert: arid, sparse vegetation, cacti, snakes
- Tropical Rainforest: lush, dense, high temperatures, orchids, monkeys
Explanation of the Six Major Biomes and Their Characteristics
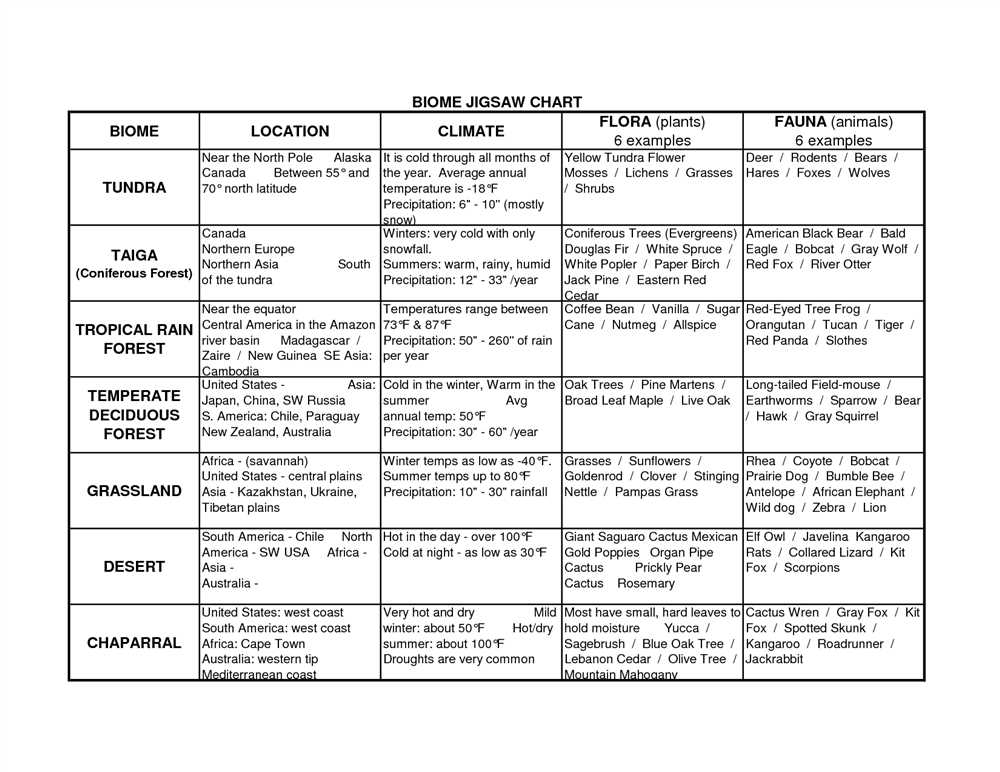
The Earth is divided into six major biomes, each with its own unique characteristics and environmental conditions. These biomes include the tropical rainforest, temperate forest, taiga, grassland, desert, and tundra. Understanding the characteristics of each biome is essential for understanding the distribution of plant and animal species and their interactions within these habitats.
Tropical Rainforest
The tropical rainforest biome is characterized by high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year. It is home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, including towering trees, lush vegetation, and diverse wildlife. The rainforests are known for their incredible biodiversity and unique ecosystems, making them one of the most important biomes on Earth.
Temperate Forest
The temperate forest biome is characterized by moderate temperatures and distinct seasons. It is comprised of diverse tree species, such as oak, maple, and beech, and supports a wide range of wildlife, including deer, squirrels, and birds. The temperate forests are important for timber production and provide critical habitats for many species.
Taiga
The taiga biome, also known as the boreal forest, is characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. It is dominated by cone-bearing trees, such as spruce and fir, and is home to animals like wolves, moose, and bears. The taiga plays a crucial role in regulating global climate and is the largest terrestrial biome on Earth.
Grassland
The grassland biome is characterized by wide expanses of grasses and few trees. It experiences moderate rainfall and is subject to periodic wildfires. Grasslands support a variety of herbivores, such as bison and gazelles, as well as predators like lions and wolves. These biomes are important for agriculture and provide important habitat for migratory birds.
Desert

The desert biome is characterized by extreme temperatures and minimal precipitation. It is covered in sand and rocks, with sparse vegetation and adapted animal species, such as camels and lizards. Deserts are challenging environments due to their harsh conditions, but they are also home to unique adaptations and survival strategies.
Tundra
The tundra biome is characterized by extremely cold temperatures and low-growing vegetation. It is found in the far northern regions of the world and experiences long, dark winters and short, cool summers. The tundra is home to animals like musk oxen, polar bears, and Arctic foxes, which have adapted to survive in this harsh environment. The tundra plays a crucial role in global climate regulation and is vulnerable to climate change.
In conclusion, the six major biomes are diverse and fascinating ecosystems, each with its own set of characteristics. These biomes provide habitats for countless species and play vital roles in regulating Earth’s climate. Understanding and conserving these biomes is crucial for maintaining the balance and biodiversity of our planet.
The Tundra Biome
The Tundra is a unique and extreme biome found in the northern parts of the world, including areas of Alaska, Canada, Russia, and Scandinavia. It is characterized by extremely cold temperatures and a short growing season, resulting in a lack of trees and vegetation. The Tundra is divided into two main types: the Arctic Tundra, which is found in the polar regions, and the Alpine Tundra, which is found at high altitudes in mountains.
Climate: The Tundra experiences long, cold winters with temperatures often dropping below freezing. The average temperature in the summer is only around 10°C (50°F), and it can drop to below freezing at night. The short growing season of about 50-60 days limits the amount of plant growth. Precipitation in the Tundra is low, with most of it occurring as snow.
- Geography: The Tundra is characterized by flat, treeless plains and low-lying hills. The ground is often frozen and covered by permafrost, a layer of permanently frozen soil. This frozen layer prevents water from draining and leads to the formation of marshes, bogs, and lakes.
- Vegetation: Due to the harsh conditions, the Tundra has very limited vegetation. The dominant plants in the Arctic Tundra are mosses, lichens, and dwarf shrubs. The Alpine Tundra is home to grasses, wildflowers, and small shrubs. Trees are absent in both types of Tundra.
- Animals: Despite the extreme conditions, the Tundra is home to a variety of animal species that have adapted to survive. Common animals found in the Tundra include caribou, musk oxen, Arctic foxes, polar bears, and migratory birds.
In conclusion, the Tundra biome is characterized by its cold temperatures, short growing season, and limited vegetation. It is a challenging environment for both plants and animals, but many species have adapted to survive and thrive in these extreme conditions.
Key features of the tundra biome and its unique adaptations
The tundra biome is characterized by extremely cold temperatures, short growing seasons, and a lack of trees. It is found in the far northern regions of the world, such as the Arctic. The tundra is a unique and harsh environment that has shaped the plants and animals that inhabit it.
One key feature of the tundra biome is permafrost, which is a layer of frozen soil that remains frozen year-round. This frozen ground makes it difficult for plants to establish deep root systems, resulting in a lack of trees in the tundra. Instead, the tundra is dominated by low-growing plants such as mosses and lichens that can survive in the cold, harsh conditions.
- Unique plant adaptations: Plants in the tundra have adapted to the cold temperatures and short growing seasons by having tiny leaves or no leaves at all. This reduces the surface area for water loss and helps them conserve energy. Many tundra plants also have the ability to grow close to the ground, which helps protect them from the wind and retain heat.
- Unique animal adaptations: Animals in the tundra have also adapted to the harsh environment. For example, some animals have thick layers of insulation, such as the polar bear’s thick layer of blubber, to help them stay warm. Others, like the Arctic hare, have adapted to blend in with their surroundings to avoid predation. Some animals, like the lemming, have even developed the ability to change the color of their fur depending on the season to provide camouflage.
In conclusion, the tundra biome is a unique and challenging environment characterized by extreme cold temperatures and permafrost. The plants and animals that inhabit the tundra have developed unique adaptations to survive and thrive in these harsh conditions.
The Desert Biome
The desert biome is an extreme environment characterized by arid conditions, minimal precipitation, and high temperatures. It is a harsh and challenging ecosystem where only specially adapted plants and animals can survive.
Plants: In the desert biome, plants have evolved unique adaptations to conserve water and withstand the harsh conditions. Some examples include cacti, which have thick, waxy stems that store water, and succulents, which have fleshy leaves that can retain moisture. These plants often have shallow roots to quickly absorb any available water from infrequent rainfall.
Animals: Desert animals have also developed remarkable adaptations to survive in this harsh environment. They are often active during the cooler night hours and burrow underground during the scorching daytime temperatures. Some examples of desert animals include camels, which can store water and withstand long periods without drinking, and kangaroo rats, which can extract water from the seeds they eat.
Climate: The desert biome experiences extreme temperature fluctuations, with scorching hot days and cold nights. Precipitation is minimal, often less than 10 inches per year, and irregularly distributed. The lack of vegetation and moisture in the air contributes to the rapid cooling of the desert at night.
Biodiversity: While deserts may seem desolate and barren, they are home to a surprising variety of plant and animal species. Desert ecosystems are finely tuned to this extreme environment, and the organisms that inhabit them have developed unique strategies to survive and thrive. The biodiversity of desert biomes is an important component of the overall global ecosystem.
In conclusion, the desert biome is a challenging environment characterized by arid conditions, minimal precipitation, and high temperatures. Plants and animals in deserts have adapted unique strategies to survive in this extreme environment, making the desert biome a remarkable and fascinating ecosystem.