
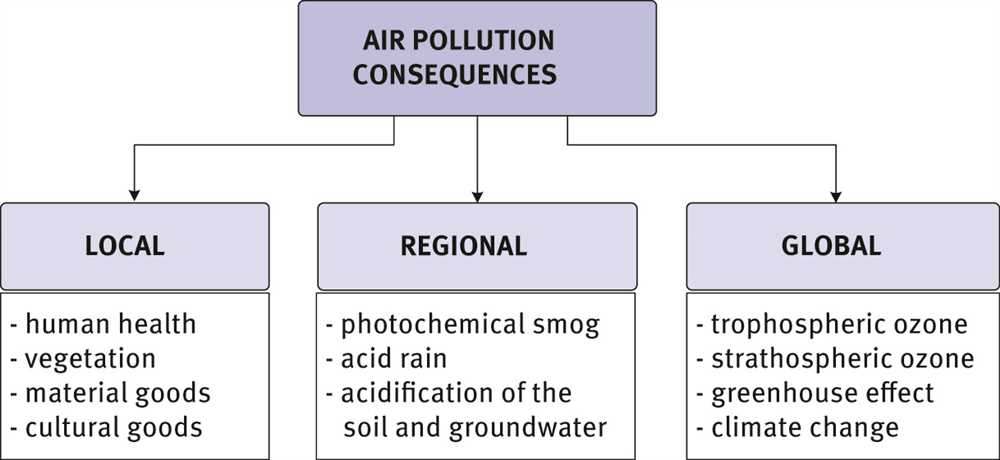
Air pollution is a growing concern worldwide, affecting both urban and rural areas. This environmental challenge has a profound impact on the health of individuals and ecosystems. Researchers and scientists are continuously seeking answers to unravel the mysteries surrounding air pollution, its sources, and its long-term effects.
One of the main sources of air pollution is emissions from vehicles and industrial activities. The combustion of fossil fuels releases harmful pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds into the atmosphere. These pollutants contribute to the formation of smog, acid rain, and climate change.
Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind air pollution is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its consequences. Scientists are investigating the chemical reactions that occur in the atmosphere, studying the role of temperature, humidity, and sunlight in the formation of pollutants. They also aim to identify the specific sources that contribute the most to air pollution, whether it is traffic-related emissions, industrial processes, or agricultural activities.
Air Pollution Mysteries Answers
Air pollution is a pressing issue that affects the well-being of both humans and the environment. It is caused by a variety of factors, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and burning fossil fuels. While the existence of air pollution is well-known, there are still many mysteries surrounding its impact and solutions.
1. Identifying the sources: One of the main challenges in addressing air pollution is identifying its sources. Air pollution can come from various industries, vehicles, and even natural sources such as wildfires and dust storms. Tracking and monitoring these sources can help prioritize efforts and implement targeted solutions.
2. The role of meteorology:
Meteorological conditions play a crucial role in the transport and dispersion of air pollutants. Wind patterns, temperature inversions, and atmospheric stability can influence how pollutants disperse and accumulate in the air. Understanding these meteorological phenomena can provide valuable insight into the behavior of air pollution and help predict its impact.
3. Health effects:
Air pollution has been linked to numerous health issues, such as respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. However, the precise mechanisms through which air pollution affects human health are still being studied. Researchers are investigating the toxic components of air pollutants and how they interact with our bodies to cause these adverse health effects.
4. Solutions:
Developing effective solutions to combat air pollution is another challenge. While some measures, such as reducing emissions from vehicles and industries, are evident, there is still a need for innovative and sustainable solutions. These could include promoting renewable energy sources, implementing stricter regulations, and encouraging lifestyle changes to reduce individual carbon footprints.
In conclusion, air pollution remains a complex issue with many mysteries waiting to be unraveled. Identifying pollution sources, understanding meteorological influences, studying health effects, and finding effective solutions are key areas of research that can contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment.
What is Air Pollution?
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances and pollutants in the Earth’s atmosphere. These pollutants can come from various sources, such as industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, burning of fossil fuels, and natural processes like volcanic eruptions. The release of these pollutants into the air can have adverse effects on human health, the environment, and the overall quality of life.
The most common air pollutants include carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds. These pollutants can have serious health implications when inhaled, leading to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature death. Additionally, air pollution can also harm ecosystems and biodiversity, contaminate water bodies, contribute to climate change and global warming, and cause damage to buildings, monuments, and infrastructure.
Efforts to combat air pollution involve implementing strict environmental regulations, promoting cleaner and sustainable technologies, and raising public awareness about the importance of reducing emissions. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of air pollution on a global scale. It is crucial for individuals, communities, governments, and industries to work together to address air pollution and protect the health and well-being of both present and future generations.
Common Air Pollutants:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): a colorless and odorless gas produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. It can be harmful when inhaled, reducing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and leading to headaches, nausea, and even death in high concentrations.
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2): a reddish-brown gas produced by the burning of fossil fuels, primarily in vehicles and power plants. It can cause respiratory problems, lung inflammation, and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections.
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2): a gas released from burning fossil fuels, particularly in power plants and industrial processes. It can cause respiratory illnesses, harm plant life, and contribute to the formation of acid rain.
- Particulate matter (PM): tiny particles suspended in the air, including dust, soot, and various chemicals. These particles can enter the respiratory system and cause respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): a group of organic chemicals that can evaporate at room temperature. They are emitted from various sources, including paints, solvents, fuels, and household products. VOCs can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and cause respiratory irritation, eye irritation, and other health issues.
Causes of Air Pollution
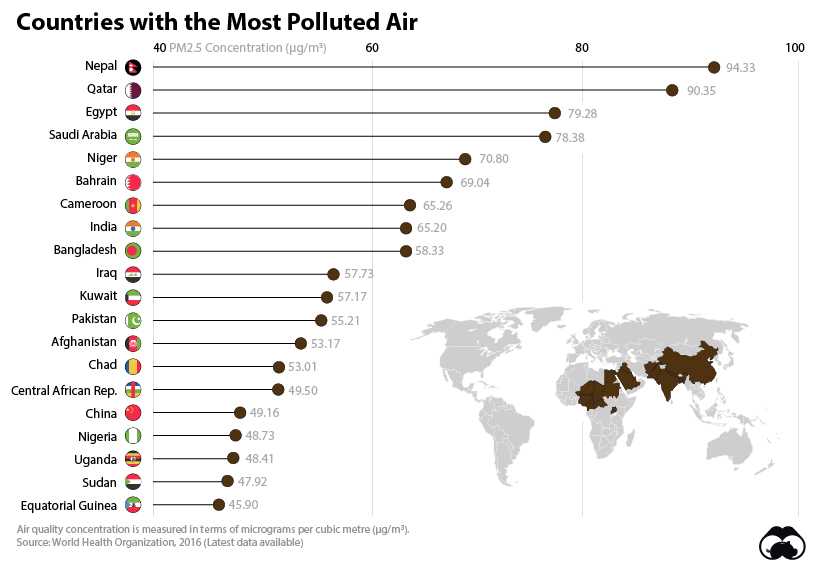
Air pollution is a major environmental issue that affects millions of people around the world. It occurs when harmful substances are released into the atmosphere, leading to the deterioration of air quality. There are several primary factors contributing to air pollution.
1. Industrial Emissions
Industrial emissions, including the release of harmful gases and particulate matter from factories, power plants, and other manufacturing facilities, are one of the leading causes of air pollution. These pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and carbon monoxide, contribute to the formation of smog and respiratory problems in humans.
2. Exhaust from Vehicles
The transport sector, particularly cars and trucks, is a significant source of air pollution. Vehicle emissions, which contain nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds, not only contribute to smog formation but also have adverse effects on human health, such as respiratory diseases and cardiovascular problems.
3. Agricultural Activities
Agricultural activities, including livestock farming and the use of fertilizers and pesticides, release harmful pollutants into the air. Ammonia, which is emitted from animal waste and the application of manure, can lead to the formation of particulate matter and contribute to respiratory problems. Additionally, the burning of agricultural waste can release large amounts of smoke and harmful gases.
4. Household and Cooking Emissions

Household activities, such as burning wood or coal for cooking and heating purposes, can release pollutants into the air, including carbon monoxide and particulate matter. These emissions can significantly contribute to indoor and outdoor air pollution, particularly in developing countries where access to clean energy sources is limited.
5. Natural Sources
Natural sources, such as volcanic eruptions, wildfires, and dust storms, also contribute to air pollution. While these sources are natural events, their emissions can release large amounts of particulate matter and gases, impacting air quality over both localized and widespread areas.
In conclusion, air pollution is caused by a combination of factors, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, agricultural activities, household and cooking emissions, and natural sources. Addressing these causes requires a comprehensive approach, including the implementation of stricter regulations, use of cleaner technologies, and promotion of sustainable practices to reduce air pollution levels and protect human health and the environment.
The Effects of Air Pollution on Health
Air pollution is a serious environmental issue that can have significant effects on human health. Breathing in polluted air can lead to a variety of health problems, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. The pollutants in the air, such as fine particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone, can cause inflammation and damage to the lungs, which can result in respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Exposure to air pollution can also have a detrimental impact on cardiovascular health. The fine particulate matter and other pollutants can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation, leading to an increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, long-term exposure to air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including lung cancer.
Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable to the health effects of air pollution. For children, exposure to air pollution can hinder lung development and increase the risk of respiratory infections. Pregnant women exposed to air pollution may also face risks to the health of their unborn child, including an increased risk of premature birth and low birth weight.
To protect ourselves from the health effects of air pollution, it is important to reduce our exposure to polluted air. This can be done by staying indoors on days with high pollution levels, using air purifiers in our homes, and wearing masks when outdoors in heavily polluted areas. Additionally, taking steps to reduce air pollution at the source, such as driving less and using cleaner forms of transportation, can help mitigate the health risks associated with air pollution.
In summary, air pollution has significant negative effects on human health, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and an increased risk of cancer. Vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly, are particularly at risk. To protect ourselves, it is important to reduce exposure to polluted air and take steps to reduce air pollution at the source.
Air Pollution and Global Warming
Air pollution and global warming are closely interconnected environmental issues that have significant impacts on the health of our planet. Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air, such as particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide, which are released from various sources, including industrial activities, transportation, and the burning of fossil fuels.
When these pollutants are released into the atmosphere, they can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. They contribute to the formation of smog, which can lead to respiratory problems and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, air pollution is a major factor in global warming, which refers to the gradual increase in the Earth’s average temperature due to the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect is the process by which certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat from the sun, causing the planet to warm up. The main greenhouse gases responsible for global warming are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases are released into the atmosphere through human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels for energy.
When carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere, they form a layer that traps heat near the Earth’s surface, preventing it from escaping into space. This leads to an increase in global temperatures, which has far-reaching consequences.
- Rising sea levels: As global temperatures rise, ice caps and glaciers melt, causing sea levels to rise. This poses a significant threat to coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Extreme weather events: Global warming can lead to more frequent and intense heatwaves, hurricanes, floods, and droughts, which can result in loss of life and property.
- Disruption of ecosystems: Climate change caused by global warming can disrupt ecosystems and lead to the extinction of plant and animal species.
- Health impacts: The increase in air pollution caused by global warming can worsen respiratory conditions, such as asthma, and increase the spread of infectious diseases.
In conclusion, air pollution and global warming are interconnected environmental problems that have severe impacts on our planet. It is crucial to take immediate action to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of global warming and protect the health of future generations. Governments, industries, and individuals all have a role to play in adopting sustainable practices and transitioning to cleaner sources of energy.
Indoor Air Pollution: A Silent Danger
When we think of air pollution, we often imagine smog-filled skies and congested traffic. However, air pollution is not only an outdoor problem but also a silent danger lurking indoors. In fact, indoor air pollution can be even more harmful than outdoor pollution, as we spend the majority of our time indoors.
Indoor air pollution refers to the presence of harmful pollutants in the air we breathe inside buildings, such as homes, offices, and schools. These pollutants can come from various sources, including household cleaning products, tobacco smoke, building materials, and furniture. One of the major contributors to indoor air pollution is poor ventilation, which can lead to the accumulation of pollutants and lack of fresh air circulation.
Harmful chemicals and pollutants present in indoor air can have serious health effects on individuals. Exposure to indoor air pollution can cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and allergies, as well as cardiovascular diseases and even cancer. Children, elderly people, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable to the harmful effects of indoor air pollution.
To tackle the issue of indoor air pollution, it is crucial to prioritize proper ventilation and reduce the use of potentially harmful products or materials. Opening windows regularly, using exhaust fans, and investing in air purifiers can help improve indoor air quality. Additionally, choosing natural and eco-friendly cleaning products and materials can minimize the release of harmful chemicals into the air. Regular maintenance of HVAC systems and thorough cleaning of carpets and upholstery are also important for reducing indoor air pollution.
Indoor air pollution may be a silent danger, but it is one that cannot be ignored. By taking necessary steps to improve indoor air quality, we can create a healthier and safer environment for ourselves and our loved ones.