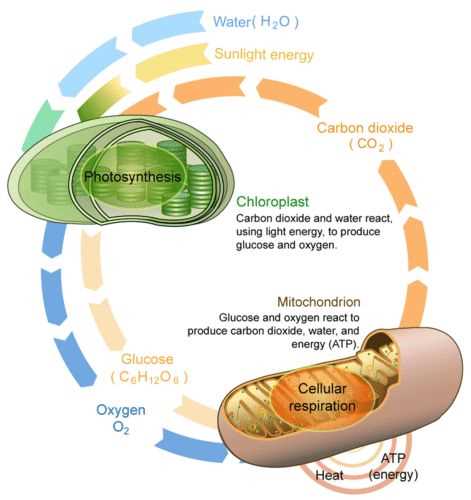
Algae bead photosynthesis is a captivating subject that has piqued the interest of scientists and researchers for decades. By studying the intricate process of photosynthesis in these microscopic organisms, we can gain valuable insights into the environmental impacts, energy production, and the overall health of aquatic ecosystems.
During a recent lab experiment, the focus was on understanding how algae beads respond to changes in light intensity and carbon dioxide concentration. The goal was to observe and measure the rate of photosynthesis under different conditions, shedding light on the factors that influence these crucial biological processes.
By exposing the algae beads to varying levels of light and carbon dioxide, researchers were able to track changes in oxygen production and carbon dioxide consumption. These measurements serve as indicators of photosynthetic activity, providing valuable data on the efficiency and adaptability of these fascinating organisms.
The lab findings revealed intriguing patterns. As light intensity increased, the rate of photosynthesis also increased, showcasing the algae beads’ ability to harness and convert light energy into chemical energy. Furthermore, as carbon dioxide concentration increased, the rate of photosynthesis exhibited a similar upward trend, indicating the algae beads’ reliance on this critical gas for efficient energy production.
Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab Answers
In the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab, we conducted an experiment to investigate the effects of light intensity and CO2 concentration on the rate of photosynthesis in algae beads. The purpose of this lab was to determine how varying these two factors would influence the rate at which algae beads produce oxygen through photosynthesis.
We used algae beads, which are gel-like spheres containing photosynthetic algae, and a dissolved oxygen probe to measure the amount of oxygen produced. The algae beads were placed in a cuvette filled with a solution of water and sodium bicarbonate, which served as the source of CO2. The cuvette was then placed in a spectrophotometer, and we recorded the changes in dissolved oxygen concentration over time.
Our results showed that both light intensity and CO2 concentration had a significant impact on the rate of photosynthesis in algae beads. When the light intensity was increased, we observed a higher rate of oxygen production, indicating that the algae beads were able to photosynthesize more efficiently. Similarly, when the CO2 concentration was increased, we also observed an increase in the rate of oxygen production.
These findings support the hypothesis that light intensity and CO2 concentration are important factors in regulating photosynthesis in algae. The increased availability of light and CO2 provides the necessary resources for the algae beads to carry out photosynthesis and produce oxygen. This lab demonstrates the importance of understanding the environmental conditions that can affect the rate of photosynthesis in algae, which plays a crucial role in the global carbon cycle and the production of oxygen.
Purpose of the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab
The purpose of the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab is to investigate the process of photosynthesis in algae beads under different conditions and to measure the rate of oxygen production during this process. By conducting this lab, students will gain a better understanding of the factors that affect photosynthesis and the importance of this process in sustaining life on Earth.
During the lab, algae beads containing photosynthetic pigments will be exposed to various levels of light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature. The goal is to determine how these factors impact the rate of photosynthesis. Oxygen production will be measured using an oxygen sensor, providing quantitative data for analysis and comparison.
The key questions that the lab aims to address are:
- How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis in algae beads?
- What is the relationship between carbon dioxide concentration and photosynthesis?
- How does temperature influence the rate of photosynthesis?
The lab also serves as an opportunity for students to practice proper experimental techniques, including sample preparation, data collection, and analysis. By conducting the lab, students will enhance their scientific inquiry skills and learn to interpret and draw conclusions from experimental results. Additionally, this lab provides a hands-on experience that allows students to observe and understand the process of photosynthesis in action.
Materials and Methods Used in the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab
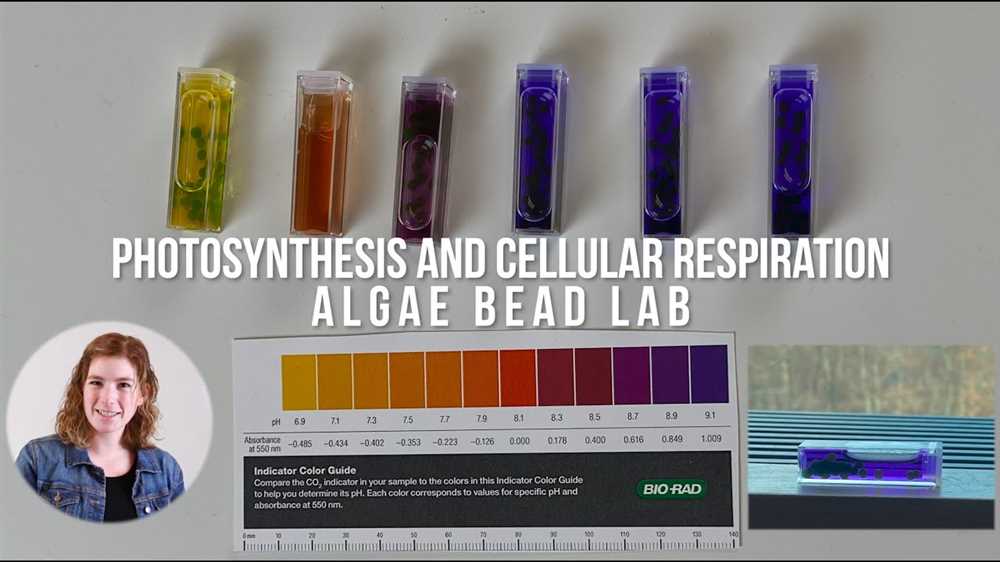
The Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab was conducted to investigate the process of photosynthesis in algae using algae beads. The lab was divided into several steps, each requiring specific materials and methods.
Materials
- Algae beads
- Water
- Carbon dioxide
- Light source (lamp)
- Timer or stopwatch
- Graduated cylinder
- Test tubes
- Baking soda
- pH indicator (Bromothymol blue)
Methods
- Prepare the algae beads by soaking them in water for a few minutes to rehydrate.
- Fill the graduated cylinder with a specific amount of water and record the volume.
- Add a known amount of baking soda to the water to provide carbon dioxide for the algae beads.
- Add the algae beads to the graduated cylinder and ensure they are fully submerged.
- Place the graduated cylinder with the algae beads under the light source, ensuring they receive sufficient light for photosynthesis.
- Start the timer and allow the algae beads to undergo photosynthesis for a designated period of time.
- Observe the color change of the pH indicator in the water. It should change from blue to green or yellow, indicating the production of carbonic acid due to carbon dioxide absorption by the algae beads.
- Record the final volume of the water in the graduated cylinder and calculate the difference to determine the amount of oxygen produced by the algae beads.
By following these materials and methods, the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab provided insights into the process of photosynthesis in algae, demonstrating their ability to absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. The lab also highlighted the importance of light and carbon dioxide availability for efficient photosynthesis in algae.
Results of the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab
The Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab aimed to investigate the impact of different light conditions on the rate of photosynthesis in algae beads. Algae beads are a type of artificial photosynthetic system that contain living algal cells embedded in alginate beads. These beads can carry out photosynthesis, producing oxygen as a byproduct.
In the lab, three different light conditions were tested: full sunlight, reduced sunlight, and complete darkness. The rate of photosynthesis was measured by counting the number of bubbles released by the algae beads over a set period of time. The more bubbles produced, the higher the rate of photosynthesis.
- Full sunlight: Under this condition, the algae beads were exposed to direct sunlight. This provided the maximum amount of light energy for photosynthesis. As a result, the algae beads released the highest number of bubbles, indicating a high rate of photosynthesis.
- Reduced sunlight: In this condition, the algae beads were partially shaded, receiving less light energy compared to the full sunlight condition. As a result, the rate of photosynthesis decreased, and fewer bubbles were released by the algae beads.
- Complete darkness: In this condition, the algae beads were kept in complete darkness, with no light energy available for photosynthesis. As expected, the algae beads did not release any bubbles, indicating an absence of photosynthetic activity.
These results confirm the hypothesis that light is an essential factor for photosynthesis in algae beads. The experiment clearly demonstrated that the rate of photosynthesis is directly proportional to the amount of light energy available. This is because light energy is required for the conversion of CO2 and water into glucose and oxygen, the key components of photosynthesis.
Overall, the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab results provide valuable insights into the role of light in the photosynthetic process of algae beads. Understanding the factors that affect photosynthesis is crucial for optimizing algae-based technologies, such as biofuels production and wastewater treatment.
Discussion of the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab Results
The results of the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab provided valuable insights into the process of photosynthesis in algae. The experiment aimed to investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of oxygen production in algae beads. Based on the data collected, it can be concluded that light intensity directly influences the rate of photosynthesis in algae.
The experiment consisted of four different light intensities: low light, medium light, high light, and control (no light). The algae beads were exposed to each intensity for a set period of time, and the rate of oxygen production was measured. The results showed a clear trend: as light intensity increased, the rate of oxygen production also increased. This suggests that algae beads require sufficient light energy to carry out photosynthesis effectively.
Furthermore, the control group, which was kept in the dark, showed the lowest rate of oxygen production. This confirms that light is an essential factor for photosynthesis to occur. The data collected from the experiment can be used to create a graph illustrating the relationship between light intensity and oxygen production in algae beads. This graph would likely show a positive correlation, indicating that higher light intensity leads to higher rates of photosynthesis.
Overall, the Algae Bead Photosynthesis Lab results support the hypothesis that light intensity affects the rate of oxygen production in algae beads. This experiment provides a better understanding of how photosynthesis works in algae and highlights the importance of light in this process. Further studies could explore the effect of other factors, such as temperature or nutrient availability, on photosynthesis in algae beads.
Analysis of the Factors Affecting Algae Bead Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a vital process for the survival of most life forms on Earth, as it is responsible for converting sunlight into energy. Algae, being photosynthetic organisms, play a crucial role in this process. Algae beads, which consist of a gel matrix containing living algae cells, are often used in lab experiments to study photosynthesis. In order to gain a better understanding of the factors affecting algae bead photosynthesis, several key factors must be analyzed.
One important factor to consider is the intensity of light. Light is the primary source of energy for photosynthesis, and the rate of photosynthesis is directly proportional to the light intensity. By exposing algae beads to different light intensities and measuring the rate of oxygen production, researchers can determine the optimal light intensity for maximum photosynthetic efficiency.
The concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) is another factor that greatly influences algae bead photosynthesis. CO2 is one of the primary reactants in the photosynthetic process, and an increase in CO2 concentration can enhance the rate of photosynthesis. By varying the CO2 concentration and measuring the oxygen production, researchers can determine the ideal CO2 level for promoting maximum photosynthetic activity.
- Temperature: Temperature affects the rate of chemical reactions, including photosynthesis. As temperature increases, the rate of photosynthesis initially increases up to an optimum temperature, beyond which it starts to decrease. This is due to the denaturation of enzymes involved in photosynthesis. By studying the effect of temperature on algae bead photosynthesis, researchers can identify the optimum temperature range for optimal photosynthetic activity.
pH Level: The pH level of the surrounding environment can also impact algae bead photosynthesis. Algae typically prefer slightly alkaline conditions, as a low pH can inhibit photosynthetic activity. By manipulating the pH level and monitoring the oxygen production, researchers can determine the optimal pH for promoting efficient photosynthesis in algae beads.
In conclusion, understanding the factors that affect algae bead photosynthesis is crucial for optimizing the growth and productivity of algae in various applications, such as biofuel production and water quality management. By studying the impact of light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and pH level on photosynthetic activity, researchers can further improve our understanding of algae’s role in the global carbon cycle and develop strategies to enhance its efficiency.
Applications and Significance of Algae Bead Photosynthesis Research
The research on algae bead photosynthesis has numerous applications and significant implications in various fields. This research provides valuable insights into the role of algae in carbon dioxide absorption and oxygen release, which is vital for understanding and mitigating the effects of climate change. Algae bead photosynthesis research also offers potential solutions for renewable energy production and wastewater treatment.
One of the applications of algae bead photosynthesis research is in the development of biofuels. Algae are known for their high oil content, and their ability to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen through photosynthesis makes them an attractive option for sustainable energy production. By studying the photosynthetic process in algae beads, scientists can optimize the conditions for maximum oil production and explore ways to scale up algae cultivation for biofuel production.
Another important application of this research is in wastewater treatment. Algae are capable of removing harmful pollutants from water through their photosynthetic activity. The beads encapsulating the algae provide a controlled environment for efficient pollutant removal. By studying the photosynthetic rates of algae beads, researchers can determine the optimal conditions for pollutant removal and develop effective wastewater treatment strategies.
The significance of algae bead photosynthesis research extends beyond energy production and wastewater treatment. Algae-based products such as food supplements, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals have gained popularity in recent years. Understanding the photosynthetic performance of algae beads can help improve the production and quality of these products.
In conclusion, algae bead photosynthesis research has diverse applications and significant implications in fields such as renewable energy, wastewater treatment, and algae-based products. By studying the photosynthetic process in algae beads, researchers can contribute to the development of sustainable solutions for environmental challenges and pave the way for a more sustainable future.