Homeostasis is a vital process that allows organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. It is essential for the survival and proper function of all living organisms. The Amoeba Sisters, a popular educational resource, have provided an answer key for understanding homeostasis and positive-negative feedback mechanisms.
The answer key explains how homeostasis works by using examples from different systems in the human body. For instance, it explores how the body regulates temperature, blood sugar levels, and pH balance. The key also delves into the concept of positive and negative feedback and how they contribute to maintaining homeostasis.
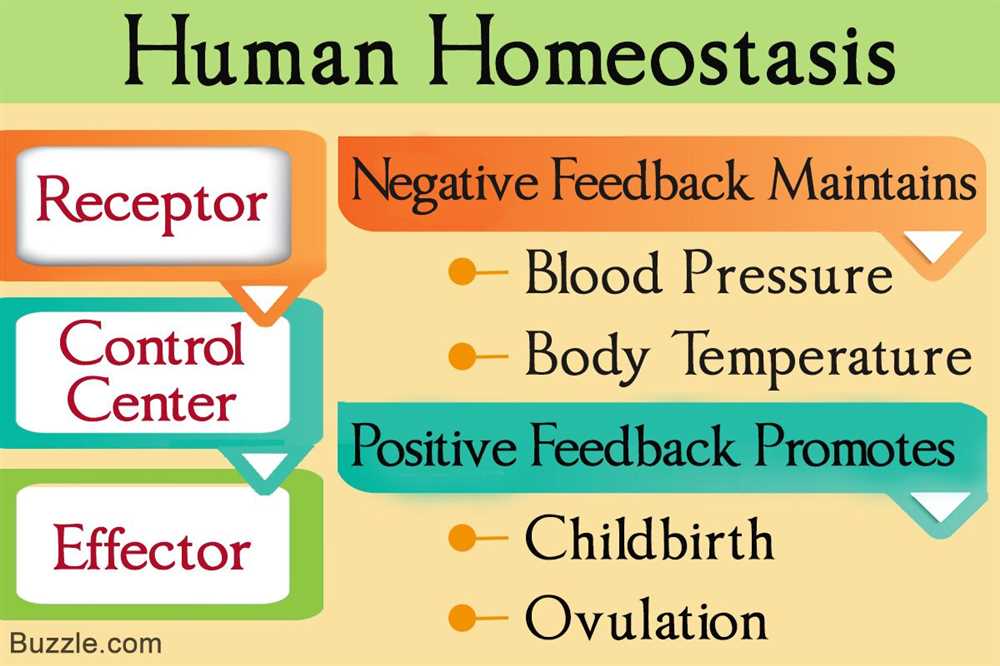
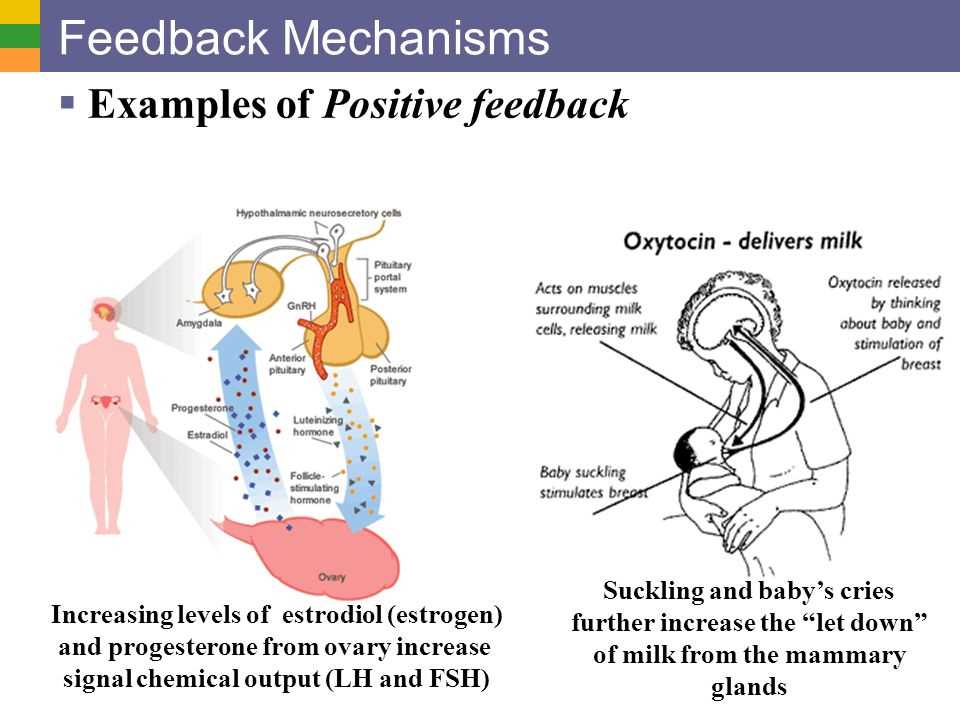
Positive feedback is a mechanism in which a stimulus causes an amplification of the original response, leading to a cascade of events. The answer key provides examples of positive feedback, such as blood clotting and uterine contractions during childbirth. On the other hand, negative feedback is a mechanism that opposes a change and restores the system back to its original state. The answer key discusses examples of negative feedback, like the regulation of blood glucose levels by insulin.
The Amoeba Sisters’ answer key on homeostasis and positive-negative feedback provides a comprehensive understanding of these concepts. By studying this key, students can grasp the significance of maintaining a stable internal environment and how various feedback mechanisms contribute to this process. It is a valuable resource for educators and learners alike, offering a clear and concise explanation of these complex biological mechanisms.
Amoeba Sisters Homeostasis and Positive Negative Feedback Answer Key
Homeostasis is a crucial process that allows organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. The Amoeba Sisters provide an answer key that helps students understand the concept of homeostasis and the role of positive and negative feedback in maintaining it.
The answer key begins by defining homeostasis as the ability of an organism to regulate internal conditions such as body temperature, pH levels, and blood sugar levels. It emphasizes that homeostasis is vital for the survival and proper functioning of cells, tissues, and organs.
The answer key then introduces the concept of positive and negative feedback mechanisms. It explains that positive feedback amplifies a response, while negative feedback opposes or reverses a response. Examples of these mechanisms are provided, such as the role of positive feedback in blood clotting and the role of negative feedback in regulating body temperature.
The answer key also includes a section on disruption of homeostasis. It explains that any deviation from the set point of a regulated variable can lead to an imbalance and potential illness. It further emphasizes the importance of feedback mechanisms in restoring homeostasis and preventing further disruption.
In summary, the Amoeba Sisters Homeostasis and Positive Negative Feedback Answer Key provides a comprehensive understanding of homeostasis and the role of positive and negative feedback mechanisms in maintaining it. It serves as a valuable resource for students studying biology or any related field.
Understanding Positive and Negative Feedback
Homeostasis, or the ability to maintain stable internal conditions, is crucial for the functioning of living organisms. Positive and negative feedback mechanisms play a key role in maintaining this balance.
Positive feedback amplifies the effect of a change and pushes the system further away from its original state. This mechanism is often seen in situations where a rapid response is needed. A classic example is blood clotting. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets release chemicals that attract more platelets, leading to the formation of a clot. This positive feedback loop ensures that the clot continues to grow until the bleeding is stopped.
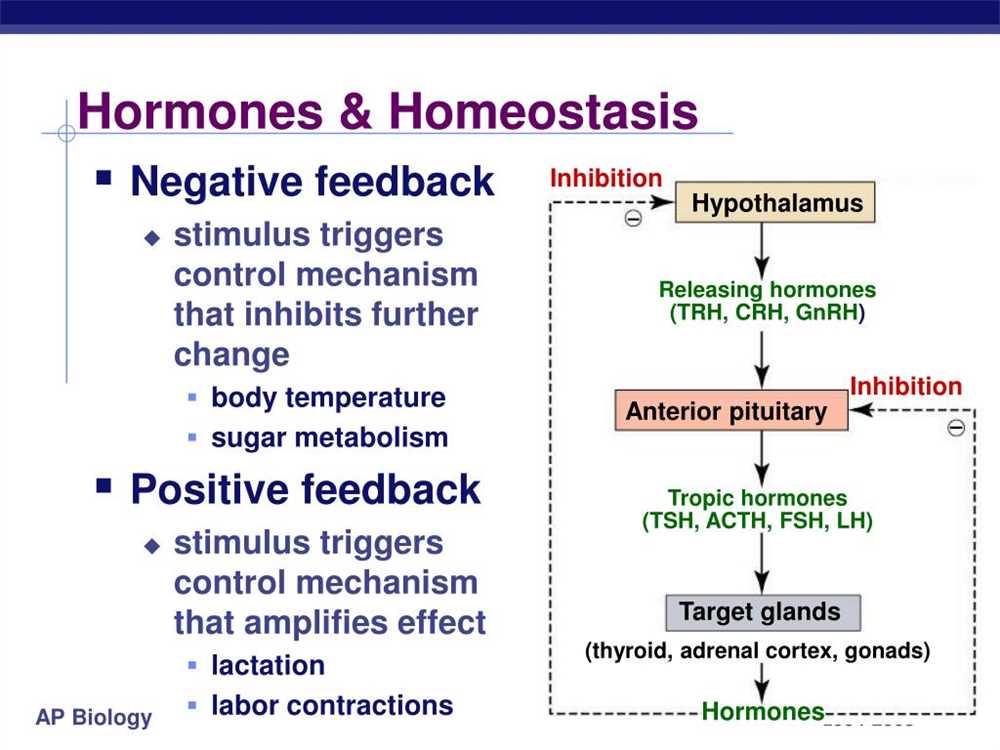
In contrast, negative feedback mechanisms work to counteract changes and bring the system back to its original state. An example of negative feedback can be seen in the regulation of body temperature. When body temperature rises, sweat glands are activated to produce sweat, which evaporates and cools the body down. This negative feedback loop helps to maintain a stable temperature within a narrow range.
Both positive and negative feedback mechanisms are vital for the proper functioning of biological systems. Positive feedback can be useful in certain situations where a rapid response is necessary, while negative feedback acts as a stabilizing force and maintains homeostasis. Understanding these feedback mechanisms allows scientists to better understand how living organisms maintain balance and respond to changes in their environment.
Importance of Homeostasis in Living Organisms
Homeostasis is a fundamental process that plays a crucial role in the survival and well-being of living organisms. It refers to the ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in its external environment. This balance is necessary for the proper functioning of cells, tissues, organs, and systems within the body.
One key aspect of homeostasis is maintaining temperature regulation. Organisms have specific temperature ranges within which their cells can function optimally. Any significant deviation from this range can have detrimental effects on the organism’s health and survival. For example, in humans, if the body temperature rises too high or drops too low, it can lead to heatstroke or hypothermia, respectively.
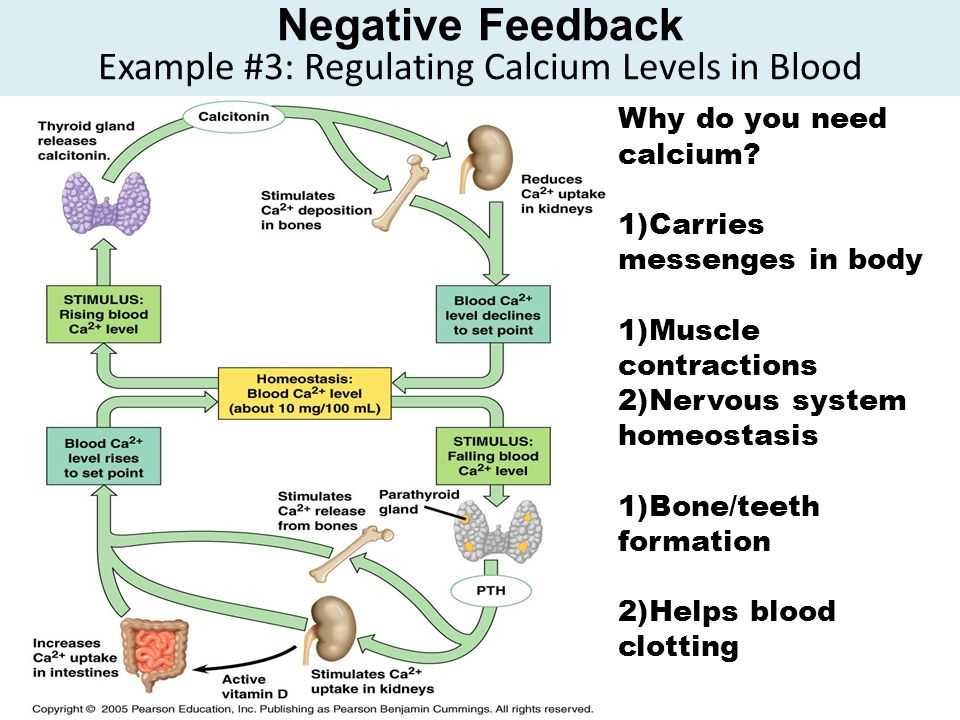
Similarly, homeostasis is vital for the regulation of pH levels in the body. Most biochemical reactions in living organisms require specific pH conditions to occur. Fluctuations in pH levels can disrupt these reactions, leading to various health issues. For instance, if the pH of blood deviates from the normal range, it can affect the functioning of enzymes and compromise the delivery of oxygen to tissues.
Homeostasis also plays a critical role in maintaining nutrient and water balance within the body. Organisms need a constant supply of nutrients and water for various metabolic processes. Changes in the availability or loss of these essential substances can disrupt cellular functions and compromise overall health. For example, dehydration due to an imbalance in water levels can cause electrolyte imbalances, muscle cramps, and impaired organ functions.
Overall, homeostasis is essential for the proper functioning and survival of living organisms. It allows them to adapt and respond to changes in their environment while maintaining internal stability. Without homeostasis, organisms would be unable to regulate temperature, pH, nutrients, water balance, and other vital factors necessary for their well-being.
Amoeba Sisters’ Approach to Teaching Homeostasis
The Amoeba Sisters have developed a unique approach to teaching homeostasis, focusing on the key concepts of positive and negative feedback. They emphasize the importance of these feedback mechanisms in maintaining stability in living organisms. The sisters use engaging visuals and interactive activities to illustrate the concept of homeostasis and its role in keeping our bodies functioning properly.
One of the key strategies the Amoeba Sisters employ is the use of analogy. They compare homeostasis to a thermostat, which is a familiar device to many students. Just as a thermostat regulates the temperature in a room by turning the heat on or off, our bodies constantly monitor and adjust various parameters to maintain a stable internal environment. This analogy helps students grasp the concept of homeostasis more easily, as they can relate it to something they encounter in their everyday lives.
The Amoeba Sisters also place great emphasis on the importance of feedback mechanisms in maintaining homeostasis. They explain how positive feedback loops amplify a signal in the body, leading to a rapid response, while negative feedback loops aim to counteract any changes and restore balance. Through visually appealing animations and concrete examples, they demonstrate how these feedback loops work in different physiological processes, such as the regulation of body temperature and blood glucose levels.
Furthermore, the Amoeba Sisters provide clear and concise explanations of the various components involved in homeostasis, such as receptors, control centers, and effectors. They break down complex concepts into digestible pieces, ensuring that students can easily understand the different roles these components play in maintaining stability in the body. By doing so, they help students develop a solid foundation of knowledge on which to build their understanding of homeostasis.
In conclusion, the Amoeba Sisters’ approach to teaching homeostasis is engaging, interactive, and easily understandable. By using analogies, visuals, and clear explanations, they help students grasp the concept of homeostasis and its importance in living organisms. Their approach effectively simplifies complex concepts, making homeostasis more accessible and relatable to students of all levels.
Key Concepts in Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis refers to the ability of living organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment. It is a fundamental concept that is essential for the proper functioning of cells, tissues, and organ systems. Homeostasis is regulated by various mechanisms, including feedback loops, which involve both positive and negative feedback.
Positive feedback is a mechanism in which a change in a certain variable triggers a response that amplifies the change, further pushing the variable away from its set point. This type of feedback is typically associated with processes that need to be accelerated or reinforced, such as blood clotting or childbirth. For example, during childbirth, the contractions of the uterus increase in intensity and frequency due to positive feedback, leading to the expulsion of the baby.
Negative feedback, on the other hand, is a mechanism in which a change in a certain variable triggers a response that opposes the change, bringing the variable back towards its set point. This type of feedback is commonly involved in maintaining stability and balance in the body. For example, when body temperature increases, receptors in the skin send signals to the brain, which then triggers mechanisms like sweating and vasodilation to cool down the body and restore its temperature to the desired set point.
Homeostasis is crucial for the survival and functioning of organisms. It allows them to respond and adapt to changes in their external environment while maintaining internal stability. Failure to maintain homeostasis can lead to various disorders and diseases, such as diabetes or hypertension. Understanding the key concepts in homeostasis, including positive and negative feedback, helps researchers and healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating these conditions effectively.
Exploring Positive Feedback in Homeostasis
The concept of homeostasis refers to the ability of living organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. This balance is maintained through various mechanisms, including feedback loops. Feedback loops are essential for regulating homeostasis, and they can be either positive or negative. In this article, we will focus on exploring positive feedback in the context of homeostasis.
Positive feedback is a mechanism that amplifies a physiological response, leading to an even greater change in the system. Unlike negative feedback, which works to counteract changes and restore a steady state, positive feedback reinforces and enhances the initial stimulus. It can be thought of as a self-amplifying loop that pushes the system further away from equilibrium.
One example of positive feedback in homeostasis is childbirth. During the process of labor, oxytocin is released in response to contractions. Oxytocin stimulates more intense and frequent contractions, which in turn lead to the release of even more oxytocin. This positive feedback loop continues until the baby is delivered. The amplification of contractions through oxytocin helps to ensure a successful and efficient birth.
Another example of positive feedback in homeostasis is blood clotting. When a blood vessel is injured, a series of reactions occur that lead to the formation of a blood clot. As the clot forms, it releases chemicals that activate nearby platelets, causing them to adhere to the site and release more chemicals. This amplifies the clotting process, ensuring that a clot forms quickly and effectively to prevent excessive bleeding.
In conclusion, positive feedback plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis by amplifying specific physiological responses. While negative feedback helps to restore equilibrium, positive feedback pushes the system further away from it to achieve a desired outcome. Understanding the mechanisms of positive feedback in homeostasis can provide valuable insights into how our bodies maintain stability and respond to changes.
Investigating Negative Feedback in Homeostasis
In order to understand how negative feedback works in maintaining homeostasis, it is important to investigate the various systems within the body that rely on this mechanism. One such system is the regulation of body temperature. When the body detects an increase in temperature, it initiates a series of responses to cool down and bring the temperature back to its normal range. This is accomplished through negative feedback, where the body detects a change and activates responses to counteract it.
One example of negative feedback in temperature regulation is the activation of sweat glands. When the body becomes too hot, the hypothalamus in the brain sends signals to the sweat glands to produce sweat. As the sweat evaporates from the skin, it absorbs heat from the body, cooling it down. Once the body temperature returns to the normal range, the sweating response is stopped through negative feedback, preventing excessive cooling.
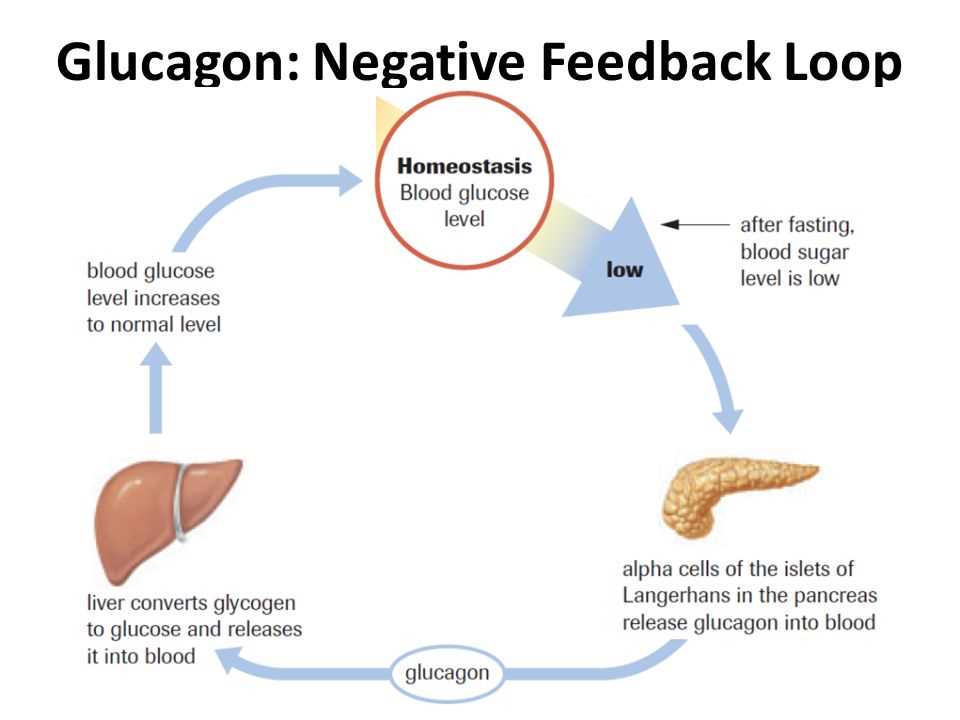
It is important to note that negative feedback is crucial in maintaining homeostasis in many other systems as well. For example, in the regulation of blood glucose levels, the body relies on negative feedback to ensure that glucose levels are kept within a specific range. When blood glucose levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin, which allows cells to take up glucose from the blood and lowers blood glucose levels. Once the levels return to normal, insulin production is decreased through negative feedback.
Overall, investigating negative feedback in homeostasis helps us understand how the body maintains stability and balance in various physiological processes. By studying the specific mechanisms and responses involved, we can gain valuable insights into the intricate systems that keep our bodies functioning optimally.


