The study of cells is vital in understanding the fundamental building blocks of life. Cells are microscopic units that make up all living organisms, including plants, animals, and even us humans. The Amoeba Sisters provide an invaluable resource for learning about cells, and their answer key offers a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricate details of cellular biology.
With the Amoeba Sisters, students can delve into the world of cells and explore their various components and functions. From the cell membrane to the nucleus, mitochondria to ribosomes, these answer keys provide detailed explanations and visual aids to simplify complex concepts. They serve as an invaluable tool for both students and educators alike.
By utilizing the Amoeba Sisters answer key, learners can test their understanding of concepts such as cell organelles, cell processes, and cellular reproduction. The key includes thought-provoking questions and answers that encourage critical thinking and deepen comprehension. Whether you are a student preparing for an exam or an educator looking for a comprehensive resource, the Amoeba Sisters answer key is an essential companion to aid in mastering the world of cells.
What is an amoeba?
An amoeba is a type of single-celled organism that falls under the group of protists. They are typically microscopic in size and have a shapeless or “blob-like” appearance. One distinctive characteristic of amoebas is their ability to constantly change their shape, which they achieve through the use of extensions called pseudopods.
Amoebas are found in diverse environments, including freshwater, marine habitats, and even soil. They have a simple structure, consisting of a cell membrane that encloses the cell’s cytoplasm, where various organelles and genetic material are found. Despite their simple structure, amoebas are capable of carrying out essential life processes, such as feeding, reproduction, and movement.
When it comes to feeding, amoebas are considered heterotrophs, meaning they obtain their nutrients by consuming other organisms or organic matter. They do this by surrounding their prey with their pseudopods and forming a food vacuole, which then allows them to digest and absorb the nutrients. Amoebas can also reproduce asexually by a process called binary fission, where the parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
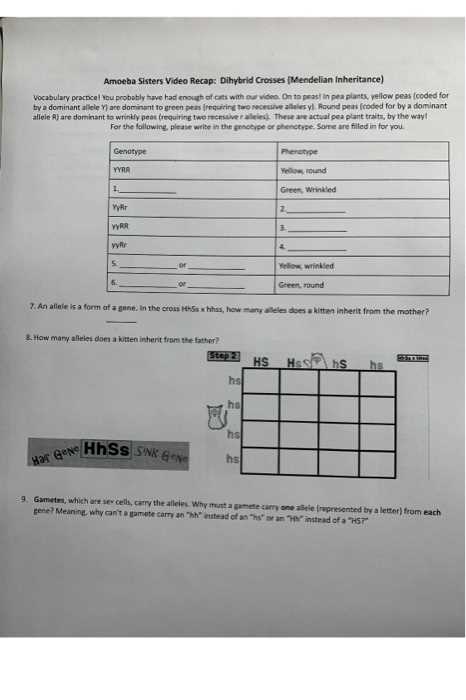
In conclusion, amoebas are fascinating organisms with unique characteristics. Their ability to change shape, survive in different habitats, and carry out essential life processes make them a subject of interest and study in the field of biology.
Sisters and their fascination with cells
The Amoeba Sisters, a dynamic duo of educators, have captured the attention of students and teachers alike with their engaging and informative videos. With their unique approach to teaching, the sisters have fostered a fascination for biology, particularly the study of cells, in learners of all ages.
Through their “Introduction to Cells” video series, the Amoeba Sisters have effectively communicated complex concepts in a simplified manner, making it accessible to students at various levels of understanding. Their ability to break down the intricate processes and structures within cells has sparked curiosity and a hunger for knowledge among their audience.
One of the key strengths of the Amoeba Sisters is their ability to make learning fun and relatable. By using humor, colorful visuals, and memorable characters, they have transformed the traditionally dry subject of cells into an exciting adventure. Students are no longer approaching cell biology with apprehension but are instead eagerly diving into the world of cells.
The sisters’ dedication to education and their passion for biology is evident in the quality of their content. They have created a comprehensive set of resources, including worksheets, answer keys, and study guides, to accompany their videos. These supplemental materials enhance the learning experience, allowing students to reinforce and apply their newly acquired knowledge.
- The Amoeba Sisters’ introduction to cells has not only helped students understand the fundamentals of cell biology but has also fostered a love for science and learning in general.
- Through their innovative teaching methods, the sisters have ignited a spark in students, encouraging them to explore the vast world of biology.
- By demystifying complex concepts and making them accessible, the Amoeba Sisters have empowered students to take charge of their own learning.
- The sisters’ passion for education and their ability to engage with their audience have made them a valuable resource in classrooms and homeschooling environments alike.
The Importance of Studying Cells

Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms. They are responsible for carrying out essential functions that are necessary for life. Understanding the structure and function of cells is crucial in various scientific fields and has numerous practical applications in medicine, biotechnology, and environmental sciences.
Cell Biology Explains Life Processes: Cell biology provides insights into how organisms function and how life processes occur at the cellular level. By studying cells, scientists can understand the mechanisms of metabolism, reproduction, growth, and differentiation. This knowledge is essential for advancing our understanding of diseases and finding new treatments.
Medical Research and Healthcare: Studying cells is critical in medical research and healthcare. It helps in diagnosing diseases, developing treatments, and understanding the molecular basis of genetic disorders. By studying abnormal cell behavior, scientists can identify potential targets for drugs and therapies, improving patient outcomes.
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering: Cells are used in biotechnology to produce valuable compounds such as enzymes, hormones, and antibiotics. The knowledge of cell biology aids in genetically modifying cells to enhance their productivity or introduce beneficial traits. This has applications in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and biofuel production.
Environmental Sciences: Studying cells enables scientists to understand the impact of pollutants, toxins, and environmental factors on living organisms. It helps in assessing ecological health and developing strategies for environmental preservation. By studying cells, researchers can also develop bioremediation techniques to clean up contaminated environments.
In conclusion, studying cells is of utmost importance as it provides a foundation for understanding life processes, advancing medical research, improving healthcare, and developing solutions to environmental challenges. It is a crucial field of scientific study that has widespread implications for human health, the economy, and the preservation of our planet.
Structure of a cell
A cell is the smallest unit of life that can function independently. The structure of a cell can be divided into two main parts: the cell membrane and the organelles.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds and protects the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which consists of two layers of phospholipids. The phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail, which helps to maintain the integrity of the cell membrane. The cell membrane also contains proteins that help with various functions such as transport of molecules and communication between cells.
- Cell membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that regulates what enters and leaves the cell.
- Organelles: These are specialized structures within the cell that carry out specific functions. Some of the important organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the genetic material, DNA. It is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, which protects the DNA and regulates the movement of molecules between the nucleus and the rest of the cell. The mitochondria are responsible for producing energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration. They have their own DNA and can divide independently within the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. It consists of a network of interconnected tubes and sacs. The Golgi apparatus processes and packages proteins for transport within the cell or secretion outside the cell. Ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins based on the instructions provided by the DNA.
In conclusion, the structure of a cell is complex and organized, with the cell membrane serving as the outer boundary and the organelles carrying out various functions within the cell. Understanding the structure of a cell is essential for understanding how cells function and interact with their environment.
Types of cells
Cells are the building blocks of life and come in many different types. Each type of cell has its own unique structure and function, allowing it to perform specific tasks within an organism. There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells are the most primitive type of cells and are found in bacteria and archaea. They are simple in structure and lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Instead, their genetic material is located in the cytoplasm. Prokaryotic cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall, and they may have flagella or pili for movement and attachment. They are capable of carrying out essential functions such as reproduction and metabolism.
Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane, as well as other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells and have a more organized internal structure. They are specialized to perform specific functions, such as photosynthesis in plant cells or neuron transmission in animal cells.
In addition to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, there are also specialized cells in multicellular organisms. These cells have unique structures and functions that enable them to carry out specific tasks within the organism. For example, red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body, while muscle cells are specialized for contraction and movement. The diversity of cell types reflects the immense complexity and versatility of life on Earth.
Cell functions
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. They are responsible for carrying out various functions that are essential for the survival and functioning of an organism.
1. Energy production: One of the key functions of cells is to produce energy. This energy is generated through cellular respiration, a process that takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to release energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
2. Protein synthesis: Cells are responsible for producing proteins, which are essential for various biological processes. Protein synthesis occurs in the ribosomes of the cell. First, DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which then moves to the ribosomes where it is translated into a specific sequence of amino acids to create a protein.
3. Cell division: Cells have the ability to divide and replicate themselves. This process, known as cell division, is crucial for growth, repair, and reproduction in multicellular organisms. There are two types of cell division: mitosis, which produces two identical daughter cells, and meiosis, which produces gametes for sexual reproduction.
4. Transport of materials: Cells are responsible for the transport of various substances, such as nutrients, ions, and waste products. This is achieved through the cell membrane, which selectively allows certain substances to enter or leave the cell. Additionally, cells may also have specialized structures like the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus for intracellular transport.
5. Regulation of biochemical reactions: Cells regulate and control various biochemical reactions that occur within them. This regulation ensures that these reactions occur at the appropriate time and in the right conditions. Enzymes, which are proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions, play a crucial role in regulating these processes.
Overall, these are just a few of the many functions that cells carry out to maintain the proper functioning of an organism. Each type of cell in the body may have specific functions that contribute to the overall functioning of the organism as a whole.
Energy production
Energy production is a vital process in cells that allows them to perform all of their necessary functions. Cells require energy to carry out activities such as growth, movement, and reproduction. The main molecule that cells use for energy production is adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is often referred to as the “energy currency” of the cell, as it is used to power various cellular processes.
One of the main ways in which cells produce ATP is through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that occur within the mitochondria of cells. During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down and transformed into ATP. This process releases energy that is stored in the bonds of glucose. Without cellular respiration, cells would not be able to generate the ATP needed for survival.
Another important process for energy production in cells is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria, and is responsible for converting sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. This glucose is then used for energy production through cellular respiration. Photosynthesis is crucial for the production of oxygen in the atmosphere and serves as the foundation for most ecosystems on Earth.
In addition to cellular respiration and photosynthesis, cells also rely on other metabolic pathways to produce energy. These pathways include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Each pathway involves a series of chemical reactions that ultimately result in the production of ATP. These pathways are regulated by various enzymes and molecules in order to maintain the proper balance of energy production within the cell.
In conclusion, energy production is a fundamental process in cells that is necessary for their survival and functioning. Through processes such as cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and other metabolic pathways, cells are able to generate the ATP needed to carry out their vital functions. Understanding the mechanisms and regulation of energy production is key to understanding cellular biology and the overall functioning of living organisms.