The era of reform was a period of significant changes and advancements that took place during a particular time frame. Various key factors contributed to this transformative era, including social, political, economic, and technological developments. These changes led to the need for reform across various sectors, paving the way for a more progressive society.
One of the driving forces behind the era of reform was the recognition of social injustices and inequalities. Activists and reformers sought to address issues such as poverty, child labor, and unequal treatment of marginalized groups. They advocated for social and political reforms that would create a more just and equitable society for all individuals.
The era of reform also witnessed major political changes. Movements such as suffrage and abolition were instrumental in pushing for political rights and freedoms. Women fought for their right to vote, challenging the prevailing gender norms and advocating for equal representation. Similarly, the abolition movement aimed to end slavery and ensure the rights and freedom of African Americans.
Economically, the era of reform saw the rise of industrialization and the need for labor reforms. As industries grew, workers faced poor working conditions, low wages, and long hours. Labor unions and activists fought for workers’ rights, pushing for better wages, safer working conditions, and fair treatment. These economic reforms aimed to address the exploitative practices prevalent during this period.
Technological advancements also played a crucial role in driving the era of reform. Innovations such as the printing press and telegraph revolutionized communication, enabling ideas and information to spread more rapidly. This facilitated the sharing of reform ideas and allowed for greater awareness and mobilization among activists.
In conclusion, the era of reform was a transformative period characterized by social, political, economic, and technological advancements. Activists and reformers recognized social injustices and fought for changes that would address these inequalities. The political landscape underwent significant shifts with movements advocating for suffrage and abolition. Economically, labor reforms were necessary to ensure fair treatment of workers, and technological advancements played a crucial role in facilitating the spread of reform ideas. The era of reform paved the way for a more progressive and just society.
An Era of Reform Answer Key
In the early 19th century, the United States went through a period of significant reform and social change. This era, often referred to as the “Era of Reform,” was marked by a series of movements aimed at addressing various social and economic issues.
One of the key movements during this era was the abolitionist movement, which sought to end slavery in the United States. Activists such as Frederick Douglass and Harriet Tubman played crucial roles in the Underground Railroad, helping enslaved individuals escape to freedom. The publication of anti-slavery literature, such as Harriet Beecher Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin, also played a significant role in raising awareness about the horrors of slavery.
Another important movement during this time was the women’s rights movement. Led by activists such as Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony, this movement sought to secure equal rights for women, including the right to vote. The Seneca Falls Convention of 1848 marked a significant moment in the women’s rights movement, as it was the first women’s rights convention held in the United States.
- The reform movement also extended to education. Horace Mann, often referred to as the “father of the common school movement,” advocated for free public education for all children. His efforts led to the establishment of public school systems throughout the United States.
- Additionally, the temperance movement, which aimed to reduce or eliminate the consumption of alcohol, gained traction during this era. Activists argued that alcohol consumption led to a variety of social problems, including domestic violence and poverty. The movement eventually led to the passage of the 18th Amendment, which prohibited the manufacture, sale, and transportation of alcoholic beverages in the United States.
Overall, the Era of Reform was a time of significant social change in the United States. Through the efforts of various reform movements, significant progress was made in addressing issues such as slavery, women’s rights, education, and alcohol consumption. The legacy of these movements can still be seen in modern-day America, as many of the reforms and changes advocated for during this era continue to shape our society.
Key Figures of the Reform Movement
The era of reform in the United States was marked by the emergence of several key figures who played a crucial role in advancing various social and political causes. These individuals, through their relentless efforts and influential ideas, helped shape the country’s history and bring about significant changes.
Fredrick Douglass was one such figure who fought passionately against slavery and advocated for the rights of African Americans. As a former slave himself, Douglass used his powerful voice and eloquence to expose the harsh realities of slavery and promote the abolitionist movement. His autobiographical works, such as “Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave,” gained widespread attention and contributed to the growing anti-slavery sentiment in the country.
Another influential figure during this era was Susan B. Anthony, a prominent leader in the women’s suffrage movement. Anthony dedicated her life to championing women’s rights, most notably the right to vote. She co-founded the National Women’s Suffrage Association and traveled extensively across the country, delivering passionate speeches and organizing protests to demand equal rights for women. Anthony’s relentless activism paved the way for the eventual passage of the 19th Amendment, which granted women the right to vote in 1920.
The reform movement also saw the rise of Henry David Thoreau, a transcendentalist philosopher and writer known for his essay “Civil Disobedience.” Thoreau’s ideas on nonviolent resistance and individual conscience influenced future leaders such as Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr. His work emphasized the importance of personal integrity and the power of peaceful protest in effecting social change.
In addition to these key figures, there were numerous others who made significant contributions to the reform movement, including Dorothea Dix who advocated for the rights and humane treatment of individuals with mental illnesses, and Horace Mann who championed the cause of public education and worked to establish free public schools for all children.
The tireless efforts of these key figures, along with many others, helped pave the way for a more just and equal society. Their passion, dedication, and influential ideas continue to inspire and shape the ongoing fight for social justice and reform.
Impact of the Reform Movement
The Reform Movement of the 19th century had a profound impact on American society, changing the way people thought about social and political issues. One of the key goals of the movement was to address the inequalities and injustices that existed in society, and many reforms were aimed at achieving this.
Women’s Rights: One of the most significant achievements of the reform movement was the advancement of women’s rights. Activists like Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony advocated for women’s suffrage and fought for equal rights for women. As a result of their efforts, the 19th Amendment was passed in 1920, granting women the right to vote.
Social Reform
- Education Reform: The reform movement also led to significant changes in the education system. Horace Mann, known as the “Father of American Education,” fought for free public education for all children, regardless of their social and economic background. This led to the establishment of public schools throughout the country and helped to increase literacy rates.
- Abolition of Slavery: The reform movement played a crucial role in the abolition of slavery. Activists like Frederick Douglass and Harriet Tubman fought tirelessly for the freedom and rights of enslaved African Americans. The efforts of these activists, along with the Civil War, eventually led to the passage of the 13th Amendment, which abolished slavery in the United States.
Political Reform
- Temperance Movement: Another important aspect of the reform movement was the temperance movement, which aimed to reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption. The movement gained momentum in the mid-19th century and eventually led to the passage of the 18th Amendment, which prohibited the production, sale, and distribution of alcoholic beverages.
- Prison Reform: The reform movement also focused on improving the conditions in prisons and advocating for the rehabilitation of prisoners. Activists pushed for the establishment of prison reforms, such as the separation of prisoners by age and gender, as well as the introduction of education and vocational training programs.
Overall, the Reform Movement of the 19th century had a lasting impact on American society. It brought about significant changes in areas such as women’s rights, education, abolition of slavery, temperance, and prison reform. These reforms helped to create a more just and equitable society and laid the foundation for future social and political movements in the United States.
Reform Policies and Initiatives

The era of reform in the late 1800s and early 1900s brought about significant changes in various sectors of society. As the country faced unprecedented social and economic challenges, policymakers and activists implemented a range of policies and initiatives aimed at addressing these issues and improving the lives of the American people.
Progressive Era Reforms
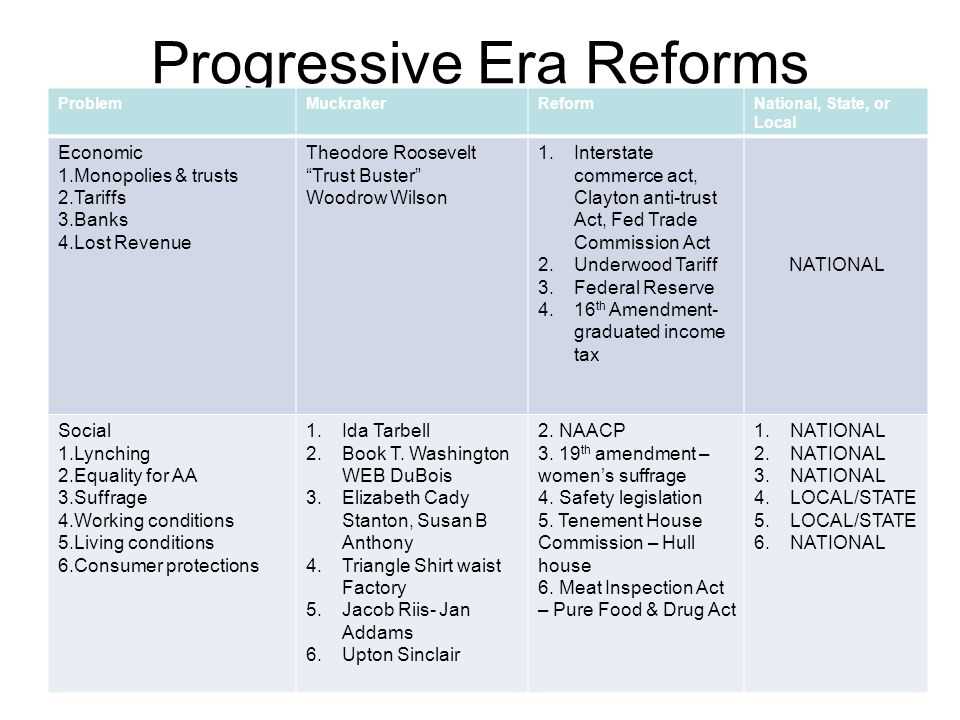
During the Progressive Era, a wide range of reforms were implemented to address the social and economic inequalities that existed at the time. One of the key initiatives was the establishment of labor rights and improved working conditions. Activists fought for the eight-hour workday, better wages, and safer working environments. This led to the creation of labor laws and regulations that protected workers and improved their quality of life.
Another significant reform during this time was the push for women’s suffrage. Women’s rights activists campaigned tirelessly for the right to vote, culminating in the ratification of the 19th Amendment in 1920. This landmark legislation ensured that women had equal political participation and representation.
Trust-Busting and Anti-Monopoly Legislation
One of the major issues of the era was the growing power of monopolies and trusts, which stifled competition and harmed smaller businesses. In response, the government implemented trust-busting policies and passed antitrust laws. These measures aimed to break up monopolies and promote fair competition, ensuring a level playing field for businesses and consumers.
- The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 was one of the first significant laws enacted to combat monopolies. It prohibited contracts, combinations, and conspiracies that restrained trade or monopolized commerce.
- Another important piece of legislation was the Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914, which strengthened existing antitrust laws and prohibited practices such as price discrimination, exclusive dealings, and tying arrangements.
- The Federal Trade Commission Act of 1914 established the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to investigate and prevent unfair methods of competition and deceptive practices in commerce.
Social Welfare Programs
The era of reform also saw the implementation of various social welfare programs aimed at improving the lives of the most vulnerable members of society. One such program was the establishment of public schools and educational reforms, which aimed to provide free and compulsory education for all children.
Additionally, social welfare initiatives such as the establishment of settlement houses and the introduction of progressive taxation aimed to address the issues of poverty and inequality. Settlement houses provided social services and support for immigrants and the urban poor, while progressive taxation sought to redistribute wealth and create a more equitable society.
Overall, the era of reform brought about significant changes in various sectors of society. Through the implementation of reform policies and initiatives, policymakers and activists sought to address social and economic inequalities, promote fair competition, and improve the overall well-being of the American people.
Social and Cultural Changes during the Era of Reform
The era of reform brought significant social and cultural changes to various aspects of society. One of the key areas of focus during this period was education. Prior to the reform era, education was often limited and inaccessible to many individuals, particularly those from marginalized communities. However, reformers recognized the importance of education as a means of social mobility and sought to expand educational opportunities.
As a result, reforms were implemented to establish public schools and improve access to education for all. These changes had a profound impact on society, as education became more widespread and accessible to individuals from different backgrounds. This not only contributed to the overall literacy rates but also encouraged the development of a more educated and informed citizenry.
In addition to education, the era of reform also witnessed changes in the realm of women’s rights. The women’s suffrage movement gained momentum during this period, as women began to advocate for their right to vote and equal representation. This movement challenged the traditional gender roles and sparked discussions about gender equality and women’s empowerment.
The era of reform also saw a shift in cultural attitudes and behaviors. The temperance movement, for example, aimed to address the issue of alcohol abuse by advocating for the reduction or complete prohibition of alcohol consumption. This movement not only influenced legislation regarding alcohol but also contributed to a change in social norms surrounding drinking.
- Education reforms expanded access to education and literacy rates.
- The women’s suffrage movement challenged traditional gender roles.
- The temperance movement aimed to address alcohol abuse and change social norms.
In conclusion, the era of reform brought about significant changes in society and culture. These changes included the expansion of education, the fight for women’s rights, and the efforts to address social issues such as alcohol abuse. These reforms had a lasting impact and helped shape the society we live in today.