
When it comes to hazardous materials, it is important to have answers to all the questions that may arise. Whether you are a professional working with these materials or simply want to stay safe, having a good understanding of their characteristics and potential risks is crucial.
What are hazardous materials? Hazardous materials refer to substances or materials that pose a threat to human health, property, or the environment. These materials can be found in various forms, including liquids, gases, solids, and even biological agents. Examples of hazardous materials include flammable liquids, corrosive substances, radioactive materials, and toxic chemicals.
Why is it important to have answers? Understanding hazardous materials is essential for several reasons. First and foremost, it helps to ensure the safety and well-being of individuals who come into contact with these materials. By having answers, professionals can take the necessary precautions to prevent accidents and mitigate risks. Additionally, having knowledge about hazardous materials allows for proper handling, storage, transportation, and disposal, reducing the potential for harm to the environment and public health.
What are hazardous materials?

Hazardous materials, also known as hazardous substances or dangerous goods, are substances or materials that pose a risk to health, safety, property, or the environment. These materials can be in various forms, such as liquids, solids, gases, or even radiation. They can cause harm or damage through different means, including chemical reactions, fire, explosion, or release of harmful substances.
There are different types of hazardous materials, each with its own specific characteristics and risks. Some examples include flammable liquids, corrosive substances, toxic gases, radioactive materials, and infectious substances. These materials can be found in various settings, including workplaces, households, transportation, and industrial facilities.
Hazardous materials require special handling and precautions to ensure the safety of individuals and the environment. This includes proper storage, transportation, use, and disposal procedures. Organizations and individuals who handle hazardous materials are required to follow specific guidelines and regulations to minimize the risks associated with these substances.
To effectively manage hazardous materials, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of their properties, potential hazards, and appropriate control measures. This knowledge allows for the implementation of safety protocols and emergency response plans to prevent accidents or mitigate the consequences of incidents involving hazardous materials.
Why is it important to understand hazardous materials?
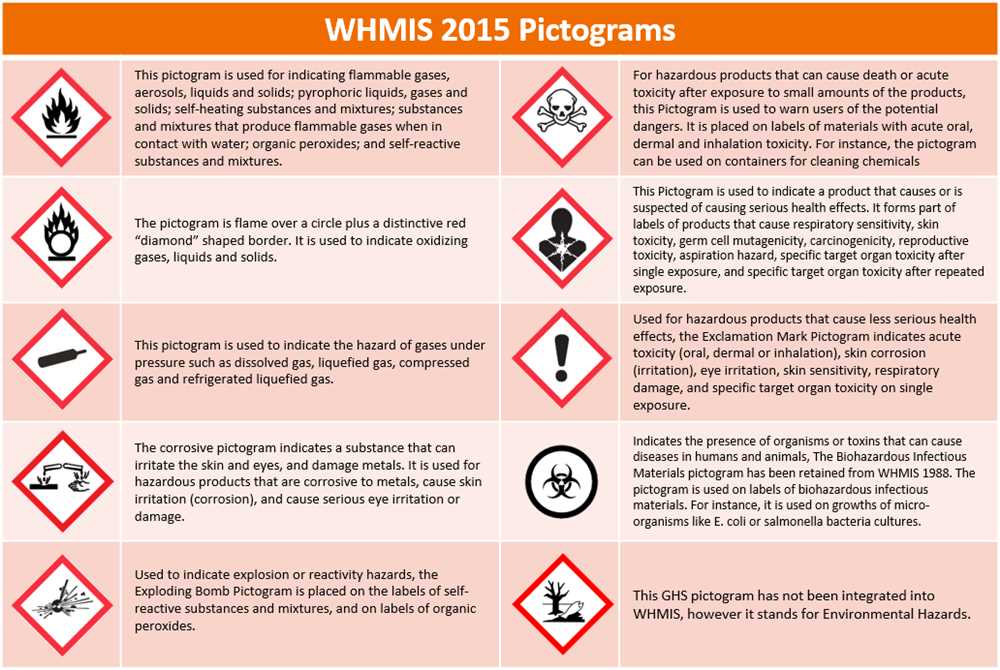
Understanding hazardous materials is of utmost importance in order to ensure the safety of individuals, communities, and the environment. Hazardous materials, also known as hazardous substances or dangerous goods, are substances that can cause harm to living organisms or the environment when not handled or managed properly.
One of the main reasons why it is important to understand hazardous materials is to prevent accidents and minimize the potential risks associated with their use, storage, and transportation. By having a thorough knowledge of the properties, characteristics, and hazards of these materials, individuals and organizations can implement appropriate safety measures and protocols to prevent incidents, such as leaks, spills, fires, or explosions, which can have severe consequences for human health and the environment.
Furthermore, understanding hazardous materials is important for emergency preparedness and response. In the event of an incident involving hazardous materials, first responders need to have the necessary knowledge and skills to safely and effectively handle the situation. This includes knowing how to properly contain and control the hazardous materials, protect themselves and others from exposure, and mitigate the potential impacts on public health and the environment.
Moreover, understanding hazardous materials is essential for proper waste management and disposal. Many hazardous materials require special handling and disposal methods to prevent contamination of the environment and potential harm to living organisms. By understanding the risks and regulations associated with hazardous materials, individuals and organizations can ensure that they are following proper procedures for the storage, transportation, and disposal of these materials, thereby protecting the environment and avoiding legal issues or penalties.
In summary, understanding hazardous materials is crucial for maintaining safety, protecting the environment, and complying with regulations. It enables individuals and organizations to prevent accidents, respond effectively to emergencies, and ensure proper handling and disposal of these materials. By being knowledgeable about hazardous materials, we can significantly reduce the risks and potential harm associated with their use.
How can hazardous materials be identified?
Hazardous materials can be identified using various methods and techniques. One of the most common ways is by referring to the product label or packaging. Manufacturers are legally required to label hazardous materials with specific symbols and warnings. These labels typically include information about the type of hazard, such as flammability, toxicity, or corrosiveness, and provide guidelines for safe handling and storage.
In addition to product labeling, hazardous materials can be identified through safety data sheets (SDS) or material safety data sheets (MSDS). These documents contain detailed information about the hazardous properties of a substance, including its physical and chemical characteristics, potential health effects, and recommended safety precautions. SDS are typically provided by the manufacturer or supplier and must be readily accessible to employees who work with hazardous materials.
Another method of identifying hazardous materials is through the use of hazard communication systems, such as the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). GHS uses standardized pictograms, signal words, and hazard statements to communicate the potential risks associated with a substance. These symbols and phrases are universally recognized and help to ensure consistent identification of hazardous materials across different regions and countries.
Furthermore, trained professionals, such as hazardous materials technicians and emergency responders, can use specialized equipment and testing methods to identify hazardous materials in specific situations. These methods may include air monitoring, pH testing, or spectroscopy to determine the presence and concentration of hazardous substances.
In summary, hazardous materials can be identified through product labeling, safety data sheets, hazard communication systems, and specialized testing methods. It is crucial to accurately identify and communicate the hazards associated with these materials to ensure the safety of workers, emergency responders, and the general public.
What are the different categories of hazardous materials?
Hazardous materials can be classified into various categories based on their potential risks and properties. Understanding these categories is essential for effectively managing and responding to hazardous material incidents.
1. Flammable and combustible materials: These materials have the ability to ignite and burn under certain conditions. They include liquids, solids, and gases that can easily catch fire or explode when exposed to heat, sparks, or open flames. Examples of flammable and combustible materials include gasoline, propane, alcohol, and oils.
2. Toxic materials: Toxic materials are substances that can cause harm or even death to humans, animals, and the environment. They can enter the body through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, and can have both short-term and long-term effects. Examples of toxic materials include pesticides, certain chemicals and solvents, and some pharmaceuticals.
3. Corrosive materials: Corrosive materials are substances that can cause damage to living tissue, metals, and other materials through chemical reactions. They are typically acidic or alkaline and can be in the form of liquids, solids, or gases. Examples of corrosive materials include sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide, and battery acid.
4. Radioactive materials: Radioactive materials emit ionizing radiation, which can cause harm to living organisms. They are often associated with nuclear power plants, medical facilities, and industrial applications. Radioactive materials can be solid, liquid, or gas, and they are classified based on their level of radioactivity. Examples of radioactive materials include uranium, plutonium, and cesium.
5. Explosive materials: Explosive materials have the ability to produce a rapid and violent release of energy. They can include substances that detonate, such as dynamite, as well as those that can explode under certain conditions, such as fireworks. Explosive materials can be classified based on their sensitivity to initiation, storage, and transportation requirements.
6. Oxidizing materials: Oxidizing materials are substances that can provide oxygen and support combustion. They can enhance the intensity of a fire and make it more difficult to extinguish. Examples of oxidizing materials include hydrogen peroxide, nitric acid, and chlorine.
In conclusion,
These are just some of the different categories of hazardous materials. It’s important to note that some materials can fall into multiple categories, depending on their properties and risks. Proper handling, storage, transportation, and disposal of hazardous materials are crucial to minimizing the potential risks they pose to human health and the environment.
How are hazardous materials regulated?
Hazardous materials are regulated by various government agencies to ensure their safe handling, transportation, and disposal. These regulations are put in place to protect the environment, public health, and the safety of workers and communities. The regulations differ by country and region, but there are some common components that are typically included.
Identification and Classification
One of the first steps in the regulation of hazardous materials is the identification and classification of substances that pose a risk to human health or the environment. Different criteria are used to determine if a substance is hazardous, such as its toxicity, flammability, or corrosivity. Hazardous materials are assigned specific codes or symbols to indicate their potential danger.
Packaging and Labeling
Hazardous materials must be properly packaged and labeled to ensure safe handling and transportation. Regulations specify the types of containers, packaging materials, and labeling requirements that must be met. Labels typically include information about the hazards associated with the material, such as the type of hazard, safety precautions, and emergency contact information.
Transportation
Hazardous materials transportation regulations outline specific requirements for the movement of dangerous goods. These regulations cover various modes of transportation, including road, rail, air, and sea. They include rules for packaging, labeling, documentation, and the training of personnel involved in the transportation process. Transportation regulations aim to prevent accidents, spills, and leaks during transit.
Storage and Disposal
Regulations also govern the proper storage and disposal of hazardous materials. Storage requirements include guidelines for the handling, segregation, and storage conditions of different types of hazardous substances. Disposal regulations specify the proper methods for disposing of hazardous waste to prevent contamination of the environment.
Overall, the regulation of hazardous materials plays a critical role in minimizing the risks associated with these substances. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure the safety of individuals and the environment.
Risks of Hazardous Materials
Hazardous materials pose significant risks to human health, the environment, and property. These substances have the potential to cause immediate harm or long-term effects, depending on their nature and the level of exposure. It is crucial to understand the potential risks associated with hazardous materials to ensure proper handling, storage, and disposal.
1. Health Risks: Exposure to hazardous materials can lead to a range of health problems, including respiratory issues, neurological disorders, skin irritations, and even cancer. These substances may enter the body through inhalation, ingestion, or absorption through the skin, leading to immediate or delayed adverse effects.
2. Environmental Risks: Hazardous materials can cause severe damage to the environment. When released into soil, water, or air, they can contaminate ecosystems, pollute water sources, and harm wildlife. These substances may persist in the environment for extended periods, causing long-term environmental degradation and disrupting the balance of ecosystems.
3. Fire and Explosion Hazards: Many hazardous materials are flammable or reactive and can pose a significant fire or explosion hazard. When improperly stored or handled, these substances can ignite, resulting in fires that are difficult to control. Explosions can cause extensive property damage, injuries, and even fatalities.
4. Chemical Burns and Corrosion: Hazardous materials that are corrosive can cause chemical burns to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. These burns can be severe and result in permanent damage. Additionally, corrosive substances can damage equipment, infrastructure, and structures, leading to financial losses.
5. Toxicity: Many hazardous materials are toxic and can poison living organisms. Exposure to high concentrations may lead to acute poisoning or chronic health effects. These substances can accumulate in the body over time, causing long-term damage to organs, tissues, and biological processes.
How should hazardous materials be stored and handled?
Proper storage and handling of hazardous materials is crucial to ensure the safety of both individuals and the environment. It is important to follow specific guidelines and regulations when it comes to storing and handling hazardous materials in order to minimize the risk of accidents, spills, leaks, and other potentially harmful incidents.
1. Storage:
Hazardous materials should be stored in appropriate containers that are specifically designed for their contents. These containers should be labeled clearly with the name of the material, any hazards associated with it, and any necessary precautions to take when handling it. Additionally, hazardous materials should be stored in well-ventilated areas that are cool, dry, and away from direct sunlight or any sources of heat or ignition. They should also be segregated from incompatible materials to prevent any chemical reactions or potential hazards.
2. Handling:
When handling hazardous materials, it is important to wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing to minimize any potential exposure. Handling should be done with caution, following proper procedures and techniques to prevent spills, leaks, or other accidents. It is vital to always be aware of the specific hazards associated with the material being handled and to take the necessary precautions to avoid any potential harm.
3. Training and education:
In addition to proper storage and handling practices, it is essential for those who work with hazardous materials to receive appropriate training and education. This includes understanding the properties of the materials being handled, the potential hazards they present, and the proper procedures for storage, handling, and emergency response. Regular training and refresher courses should be provided to ensure that individuals are up to date with the latest safety practices and regulations.
By following these guidelines and implementing proper storage and handling procedures, the risks associated with hazardous materials can be minimized, protecting the well-being of workers, the community, and the environment as a whole.