Tuskless elephants are a unique phenomenon observed in certain populations of elephants, where individuals are born without tusks or with very small tusks. This characteristic has sparked significant interest among researchers and conservationists, who are eager to understand the reasons behind this trait and its implications for elephant populations.
One possible explanation for the occurrence of tuskless elephants is a form of natural selection. In regions where elephants face intense pressure from illegal ivory poaching, individuals with smaller or no tusks may have a greater chance of survival. This is because tusks are highly valuable and sought after by poachers, and elephants with larger tusks are more likely to be targeted. As a result, over time, the genes for tusklessness may become more prevalent in the population.
However, this is not the only factor at play. Research has also shown that the occurrence of tusklessness can be influenced by environmental factors, such as the availability of suitable forage. In areas where food is scarce or of poor quality, elephants with smaller tusks may have a competitive advantage, as they require less energy to forage and can access resources that are out of reach for individuals with larger tusks. This creates a selective pressure that favors the development of tusklessness.
To better understand the genetic and environmental factors influencing tusklessness in elephants, researchers have been studying populations where the phenomenon is particularly prevalent. These studies involve collecting data on elephant demographics, genetics, and habitat characteristics. By analyzing this data, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms behind tusklessness and develop effective conservation strategies to protect these unique populations.
The Significance of Tuskless Elephants
Tuskless elephants have been a subject of great interest and significance in the field of wildlife conservation. The absence of tusks in certain elephant populations has raised questions about the factors contributing to this phenomenon and its potential impacts on ecosystems.
Evolutionary Adaptation: One of the main reasons behind tuskless elephants is considered to be natural selective pressure. Over time, elephants without tusks have evolved as a response to hunting pressures. This adaptation allows them to escape human poachers who primarily target elephants for their ivory tusks.
Gender Imbalance: Tusklessness is observed to be more prevalent in female elephants compared to males. This is likely due to the fact that tuskless females have a reproductive advantage. Female elephants with no tusks tend to have a higher chance of survival and reproduction, leading to the perpetuation of the tuskless trait in the population.
Ecological Consequences: The presence or absence of tusks in elephants can have profound ecological consequences. Tusks play a significant role in various behaviors, such as digging, foraging, and defending against predators. The lack of tusks can potentially alter these behaviors and disrupt the balance within ecosystems. Moreover, elephants also play a crucial role in shaping their habitats through their feeding and movement patterns, and any changes in their behavior can have cascading effects on other species and the ecosystem as a whole.
Conservation Implications: Understanding the dynamics of tuskless elephants is essential for effective conservation strategies. By studying the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to tusklessness, researchers can gain insights into the broader impacts of human activities on wildlife populations. Additionally, protecting tuskless elephants and their habitats can contribute to biodiversity conservation and the preservation of natural ecosystems.
- Further research is needed to investigate the specific genetic and environmental factors that influence the prevalence of tuskless elephants in different populations.
- Conservation efforts should focus on raising awareness about the importance of protecting all elephant individuals, regardless of their tusk status.
- Efficient anti-poaching measures should be implemented to reduce the demand for ivory and alleviate the pressures on elephant populations.
- Conservation organizations and governments should work together to establish and manage protected areas that provide suitable habitats for tuskless elephants and other wildlife.
In conclusion, tuskless elephants have significant implications for both the scientific community and conservation efforts. By studying and conserving these unique animals, we can gain valuable insights into evolutionary adaptation, ecological dynamics, and the broader impacts of anthropogenic activities on wildlife populations.
Methodology for Analyzing Data on Tuskless Elephants Answer Key
The methodology for analyzing data on tuskless elephants involves several key steps. First, researchers gather data on elephant populations, specifically focusing on the presence or absence of tusks in individual elephants. This data can be collected through direct observations, photographic evidence, or genetic analysis.
Once the data is collected, researchers can begin analyzing it to determine the prevalence and distribution of tuskless elephants in a given population or region. This analysis typically involves statistical methods such as calculating proportions, conducting chi-square tests, or performing logistic regression to identify any underlying patterns or associations.
Researchers may also explore potential factors that could contribute to the presence of tuskless elephants. This could include examining environmental factors, such as habitat degradation or poaching pressure, as well as genetic factors that may be influencing the development of tusks in elephants.
In addition to these quantitative analyses, qualitative methods may also be employed to gain a deeper understanding of the reasons behind the existence of tuskless elephants. This could involve conducting interviews or surveys with local communities, conservationists, or wildlife experts to gather their perspectives on tuskless elephants and their potential implications.
Overall, the methodology for analyzing data on tuskless elephants is interdisciplinary, combining both quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a comprehensive understanding of the prevalence, distribution, and potential causes of tusklessness in elephant populations.
Data Collection Techniques
Data collection is a crucial step in the process of analyzing data on tuskless elephants. Collecting accurate and reliable data is essential for making informed decisions and drawing meaningful conclusions. There are several techniques that can be used to collect data on tuskless elephants, each with its own advantages and limitations.
One technique commonly used in data collection is direct observation. This involves physically observing tuskless elephants in their natural habitat or in a controlled environment, and recording their behavior, characteristics, and any other relevant information. Direct observation allows researchers to gather real-time data and provides an opportunity to study the animals’ natural behavior. However, it can be time-consuming and may require specialized equipment or access to restricted areas.
Another technique is the use of remote sensing technology, such as satellite imagery and drones. These technologies allow researchers to collect data on a larger scale and from areas that may be difficult to access. Satellite imagery can provide information on the distribution and population density of tuskless elephants, as well as changes in their habitat over time. Drones can be used to capture aerial photographs or videos, providing detailed information on the animals’ behavior, movement patterns, and habitat preferences. However, the use of remote sensing technology may be limited by factors such as cost, technical expertise, and privacy regulations.
Interviews and surveys are also commonly used data collection techniques in studying tuskless elephants. Researchers can conduct interviews with local communities, wildlife experts, and other stakeholders to gather information on the presence and behavior of tuskless elephants in specific areas. Surveys can be distributed to gather quantitative data on the prevalence of tuskless elephants and the factors that contribute to their occurrence. These techniques allow researchers to gather information from a wide range of sources and perspectives. However, interviews and surveys may be subject to bias and may require careful design and analysis to ensure the validity of the data collected.
In summary, data collection techniques in analyzing tuskless elephants include direct observation, remote sensing technology, and interviews/surveys. Each technique has its own strengths and limitations, and researchers need to carefully consider which technique or combination of techniques is most appropriate for their specific research objectives. By employing a variety of data collection techniques, researchers can ensure a comprehensive and accurate analysis of data on tuskless elephants.
Key Findings from Analyzing Data on Tuskless Elephants
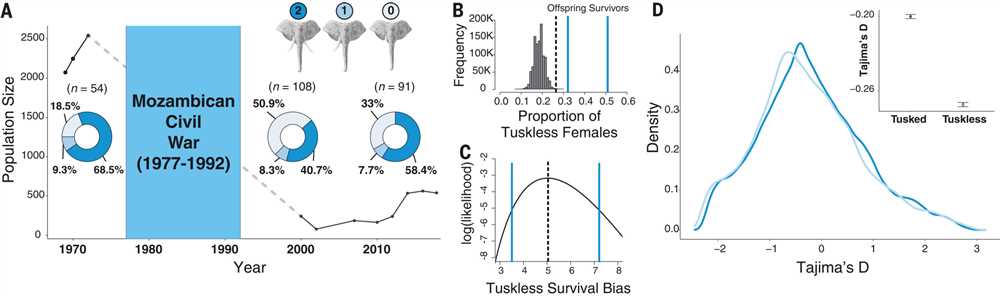
Tusklessness is a fascinating trait observed in some elephant populations. By analyzing data collected from various research studies, several key findings have emerged about tuskless elephants.
1. High occurrence of tuskless elephants
One of the most important findings is the high occurrence of tuskless elephants in certain populations. In some regions, up to 38% of females and 2% of males are tuskless. This is significantly higher than previously thought, highlighting the need for further research to understand the reasons behind this phenomenon.
2. Maternal inheritance of tusklessness
Another notable finding is the strong evidence of maternal inheritance of tusklessness. Through genetic analysis, researchers have discovered that tuskless females more likely have tuskless daughters, suggesting a genetic link between generations. This supports the theory that tusklessness is a heritable trait and not solely due to environmental factors.
3. Impact of ivory poaching
Interestingly, the data analysis has revealed a correlation between the prevalence of tuskless elephants and the intensity of ivory poaching. In areas with high poaching pressure, the percentage of tuskless individuals tends to be higher. This suggests that selective hunting for ivory may be influencing the genetic makeup of elephant populations and favoring the survival of tuskless individuals.
4. Ecological implications

The findings also shed light on the ecological implications of tusklessness. Tuskless elephants have been observed to exhibit different behaviors and social dynamics compared to their tusked counterparts. They may rely more on other sensory abilities and adapt their feeding strategies to compensate for the lack of tusks. Understanding these behavioral differences can provide valuable insights into how elephant populations respond to selective pressures and adapt to changing environments.
In conclusion, analyzing data on tuskless elephants has revealed significant findings regarding their occurrence, genetic inheritance, relationship with ivory poaching, and ecological implications. These insights contribute to our understanding of this unique trait and its impact on elephant populations, highlighting the importance of further research in this field.
Percentage of Tuskless Elephants Among Different Populations

The percentage of tuskless elephants varies among different populations across Africa. Tusklessness is a genetic trait that can be inherited, and the prevalence of tusklessness can be influenced by various factors such as habitat, hunting pressure, and elephant conservation efforts. Understanding the distribution of tuskless elephants is important for conservation planning and management strategies.
African Savanna elephant populations
Studies have shown that the percentage of tuskless elephants in African Savanna elephant populations range from 2% to 60%. This wide variation can be attributed to different ecological and anthropogenic factors. In areas where elephant populations have been heavily poached for ivory, the tuskless trait has been selected for, as tusked elephants are more vulnerable to poaching. Additionally, in areas with dense forests or thick vegetation, tusked elephants may have a disadvantage when it comes to foraging or navigating through dense vegetation, leading to a higher prevalence of tusklessness.
African Forest elephant populations
African Forest elephants, which inhabit the dense rainforests of Central and West Africa, have a higher percentage of tuskless individuals compared to African Savanna elephants. Studies have shown that tusklessness among African Forest elephants can range from 30% to 60%. This higher prevalence of tusklessness can be attributed to the challenging forest environment, where large tusks may hinder an elephant’s movement through the dense vegetation. Furthermore, the habitat fragmentation and hunting pressure in forested areas may also contribute to the higher percentage of tuskless individuals.
Conservation implications
The percentage of tuskless elephants among different populations has important implications for elephant conservation efforts. The loss of tusks can have both positive and negative effects on individual elephants. On one hand, tuskless elephants may be less susceptible to poaching, providing them with a survival advantage in areas with high hunting pressure. On the other hand, tusks play a crucial role in feeding, self-defense, and social interactions. Understanding the factors that influence tusklessness and monitoring its prevalence can help conservationists develop targeted management strategies to ensure the long-term survival of elephants and their habitats.
Factors Affecting Tusklessness in Elephants
Tusklessness, the lack of tusks in elephants, has been a topic of interest for researchers and conservationists for many years. Several factors contribute to this phenomenon, including genetic inheritance, habitat conditions, and human activities.
Genetic Inheritance: One of the primary factors that influence tusklessness in elephants is genetic inheritance. Tusk development is controlled by a single gene, and elephants with two copies of the recessive gene, one inherited from each parent, will be tuskless. This genetic variation results in a higher occurrence of tuskless individuals in certain populations.
Habitat Conditions: The availability of resources and the specific environment in which elephants live also play a role in tusklessness. In areas with limited food sources or dense vegetation, elephants may have less need for tusks to forage or defend themselves. As a result, tuskless individuals have a higher likelihood of surviving in these habitats, leading to an increased prevalence of tusklessness over time.
Human Activities: Another significant factor affecting tusklessness is human activities, notably poaching. In regions where elephants are targeted for their ivory, individuals with larger tusks become primary targets. Consequently, tuskless elephants have a higher chance of survival and reproduction, passing on their tuskless trait to future generations. The selective pressure exerted by human hunting practices has contributed to the increase in tusklessness in certain elephant populations.
In conclusion, tusklessness in elephants is influenced by a combination of genetic inheritance, habitat conditions, and human activities. These factors interact to shape the prevalence of tusklessness in different elephant populations. Understanding these factors is crucial for conservation efforts and the overall management of elephant populations worldwide.