The constitution is the foundation on which a country’s laws and governance are built. It serves as a guiding document that outlines the rights and responsibilities of citizens and the powers and limitations of the government. Understanding the anatomy of a constitution, including its structure and key components, is crucial in comprehending the legal framework of a nation.
One of the key elements of a constitution is its preamble, which provides an introduction and sets the tone for the document. It often includes statements about the purpose and principles of the constitution, expressing the ideals and aspirations of the nation. The preamble serves as a concise summary of the constitution’s main objectives and values.
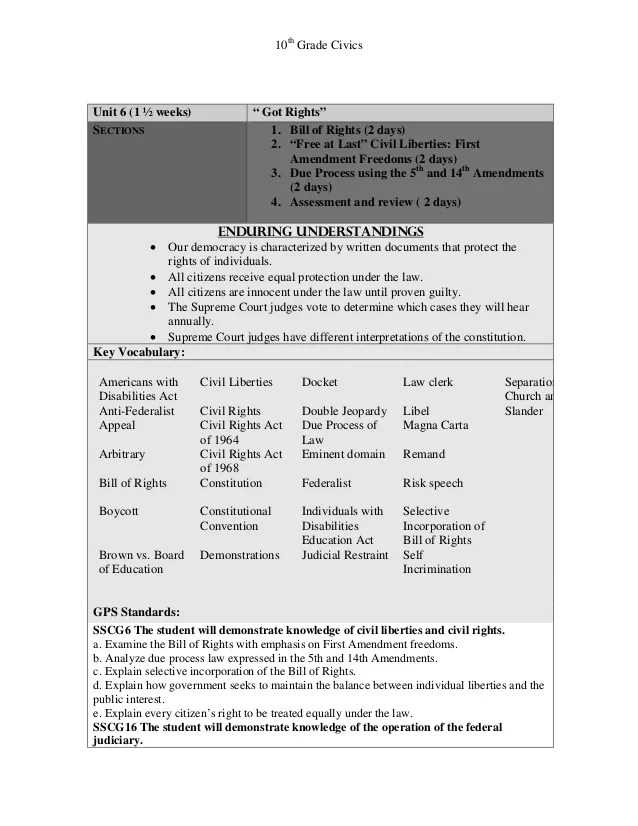
Another important component of a constitution is the bill of rights, which outlines the fundamental freedoms and protections granted to individuals. These rights often include freedom of speech, religion, and assembly, as well as the right to a fair trial and protection against unreasonable searches and seizures. The bill of rights ensures that citizens have certain fundamental liberties that are protected by the constitution.
Anatomy of Constitution Answer Key
The Anatomy of Constitution Answer Key provides a comprehensive understanding of the various components and principles that make up a constitution. It serves as a guide to understanding the structure, functions, and powers of a constitution, as well as the rights and responsibilities of citizens within the framework of the constitution. By examining the Answer Key, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the key elements that shape and define a constitution.
The Answer Key typically includes answers and explanations to questions related to the constitution, such as the purpose of a constitution, the process for its amendment, the separation of powers, and the rights and freedoms protected by the constitution. It also provides clarity on the roles and responsibilities of the different branches of government, such as the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and their interrelationship.
Key Components of the Answer Key
- Preamble: The Answer Key explains the significance of the preamble in introducing the objectives and goals of the constitution.
- Fundamental Rights: It provides a detailed analysis of the fundamental rights guaranteed by the constitution, including freedom of speech, religion, and assembly.
- Separation of Powers: The Answer Key outlines the concept of separation of powers and how it ensures a system of checks and balances in the government.
- Amendment Process: It describes the procedure for amending the constitution, highlighting the importance of a flexible and adaptable constitution.
- Federalism: The Answer Key explains the principles of federalism and how power is divided between the central government and state governments.
- Judicial Review: It explores the concept of judicial review and the role of the judiciary in interpreting and applying the constitution.
By using the Anatomy of Constitution Answer Key, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances of a constitution. It serves as a valuable resource for students, scholars, and anyone interested in understanding the structure and principles that govern a country’s legal framework and protect the rights and liberties of its citizens.
Overview of the Constitution
The Constitution of a country serves as the fundamental law that establishes the framework of government and outlines the rights and responsibilities of citizens. It is a written document that defines the structure and powers of the government, as well as the limitations on those powers. In the case of the United States, the Constitution is a cornerstone of democracy and has been a model for many other countries.
Structure: The Constitution is divided into several sections or articles, each addressing different aspects of governance. It begins with a preamble that sets out the purpose and goals of the Constitution. The remainder of the document is organized into articles and amendments, covering topics such as the separation of powers, the establishment of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, and the rights and freedoms of citizens.
Separation of Powers: One of the key principles of the Constitution is the separation of powers, which divides the government into three distinct branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial. This system ensures a system of checks and balances, where each branch has its own unique powers and responsibilities, and can limit and oversee the actions of the other branches.
Amendments: The Constitution also provides a mechanism for change through the amendment process. This allows the document to adapt to the evolving needs of society and to address any shortcomings or injustices. Amendments must be proposed by either Congress or a national convention, and must be ratified by three-fourths of the states to become part of the Constitution.
Protecting Individual Rights: One of the most significant features of the Constitution is its dedication to protecting individual rights and freedoms. The Bill of Rights, which consists of the first ten amendments, guarantees key rights such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly. These rights serve as a safeguard against government intrusion and provide citizens with the ability to voice their opinions and participate in the democratic process.
Conclusion: The Constitution plays a vital role in shaping and defining the government and society of a country. Its structure, principles, and protections provide a solid foundation for democracy and ensure that the rights and freedoms of citizens are upheld. As an essential part of the American identity, the Constitution continues to serve as a guiding document that reflects the values and aspirations of the people.
Structure of the Constitution
The Constitution of a country serves as the foundational document that outlines the structure and principles of its government. It provides the framework for the organization and functioning of the various branches of government, as well as the rights and responsibilities of its citizens. The structure of the Constitution is designed to ensure a system of checks and balances, distribution of power, and protection of individual liberties.
One key aspect of the structure of the Constitution is the division of powers between the federal government and the state governments. This division, known as federalism, allows for a balance of authority and ensures that neither level of government becomes too powerful. The Constitution outlines the specific powers granted to the federal government, such as the authority to regulate commerce and establish a national defense, while reserving all other powers to the states.
The Constitution also establishes three separate branches of government: the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch. This separation of powers ensures that no single branch becomes too dominant and allows for a system of checks and balances. The legislative branch, made up of the Congress, is responsible for making laws. The executive branch, headed by the President, is responsible for enforcing laws. The judicial branch, consisting of the federal courts, interprets the laws and ensures their constitutionality.
Additionally, the Constitution includes a Bill of Rights, which consists of the first ten amendments. These amendments outline the fundamental rights and liberties of individuals, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial. The Bill of Rights serves as a crucial protection against the abuse of power by the government and ensures that citizens’ rights are upheld.
In summary, the structure of the Constitution establishes a system of federalism, separation of powers, and protection of individual rights. It outlines the division of powers between the federal and state governments, establishes three separate branches of government, and includes a Bill of Rights. This structure provides a foundation for a functioning democracy and safeguards the rights and liberties of the people.
Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights is the collective name given to the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. It was originally proposed by James Madison in 1789 and ratified on December 15, 1791. The purpose of the Bill of Rights is to protect individual liberties and limit the power of the government.
The Bill of Rights guarantees various rights and freedoms to the American people. These include the freedom of speech, religion, and the press; the right to bear arms; the protection against unreasonable searches and seizures; the right to a fair trial; and the prohibition of cruel and unusual punishment, among others. These rights are considered fundamental and are protected by law.
Each amendment in the Bill of Rights addresses a specific issue and provides a clear limitation on the government’s power. For example, the First Amendment protects freedom of speech and prohibits the government from interfering with an individual’s right to express themselves. The Second Amendment guarantees the right to bear arms, while the Fourth Amendment protects against unreasonable searches and seizures.
The Bill of Rights has been a cornerstone of American democracy and has set a precedent for other countries around the world. It reflects the values and principles of the American people, emphasizing individual liberty and the importance of a limited government. The amendments in the Bill of Rights continue to shape and influence the interpretation of the Constitution and play a vital role in safeguarding the rights and freedoms of every American citizen.
- First Amendment: Freedom of speech, religion, and the press
- Second Amendment: Right to bear arms
- Fourth Amendment: Protection against unreasonable searches and seizures
- Eighth Amendment: Prohibition of cruel and unusual punishment
Amendments to the Constitution

The Constitution of the United States is a living document that outlines the fundamental principles and laws that govern the nation. However, it is not a static document, and has been amended multiple times throughout history to adapt to changing times and address the evolving needs of the country. These amendments represent the voices of the people and their desire to shape the government and protect individual rights.
The process of amending the Constitution
Amending the Constitution is not an easy task, and for good reason. It requires a deliberate and thoughtful process to ensure that any proposed changes are well-considered and have widespread support. According to Article V of the Constitution, an amendment can be proposed either by a two-thirds vote in both houses of Congress or by a Constitutional Convention called for by two-thirds of the state legislatures. Once proposed, an amendment must be ratified by three-fourths of the states, either through the state legislatures or through specially called state conventions.
The importance of amendments
Amendments allow the Constitution to adapt to the changing needs and values of society. They have played a critical role in expanding civil rights and liberties, protecting minority rights, and clarifying the scope and limitations of government powers. Some of the most significant amendments include the Bill of Rights, which guarantees fundamental rights such as freedom of speech and religion, and the 19th Amendment, which granted women the right to vote. Each amendment represents a significant milestone in the nation’s history and reflects the ongoing efforts to create a more inclusive and just society.
Ongoing debates and future amendments
The process of amending the Constitution is intentionally challenging to prevent hasty or ill-considered changes. However, this also means that it can be difficult to address pressing issues and adapt to new realities. As society continues to evolve, new debates emerge over issues such as campaign finance, gun control, and voting rights. These debates often spark calls for new amendments, as citizens and lawmakers seek to enshrine their beliefs and values in the supreme law of the land. The process of amending the Constitution ensures that these debates receive careful consideration, and that any changes reflect the will of the people and stand the test of time.
Branches of Government
In the United States, the government is divided into three branches: the executive branch, the legislative branch, and the judicial branch. Each branch has its own unique powers and responsibilities, which work together to maintain a system of checks and balances.
Executive Branch

The executive branch is responsible for enforcing the laws of the country. The President of the United States is the head of the executive branch and is elected by the American people. The President is responsible for making important decisions, such as signing bills into law, appointing judges, and representing the United States on the world stage. The executive branch also includes various departments and agencies that help the President carry out their duties.
Key Phrases: executive branch, President of the United States, enforcing laws, making decisions, signing bills into law, appointing judges, representing the United States
Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. It consists of the Congress, which is made up of two houses: the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress is the law-making body of the United States and has the power to pass bills, declare war, and oversee the budget and finances of the country. Both houses of Congress have their own specific powers and responsibilities, and they work together to ensure that the laws are fair and reflect the needs and values of the American people.
Key Phrases: legislative branch, Congress, Senate, House of Representatives, making laws, passing bills, declaring war, overseeing budget and finances
Judicial Branch
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting and applying the laws. It consists of the Supreme Court, which is the highest court in the United States, and other federal courts. The Supreme Court has the power to review laws and determine whether they are constitutional. The judicial branch plays a crucial role in ensuring that the laws are interpreted and applied fairly and consistently throughout the country.
Key Phrases: judicial branch, Supreme Court, federal courts, interpreting laws, applying laws, reviewing laws, determining constitutionality
In conclusion, the branches of government in the United States work together to maintain a system of checks and balances. The executive branch enforces the laws, the legislative branch makes the laws, and the judicial branch interprets and applies the laws. This division of powers ensures that no single branch becomes too powerful and that the rights and freedoms of the American people are protected.