As students progress through their Advanced Placement Chemistry course, they inevitably encounter Unit 2, a crucial part of the curriculum that covers a wide range of topics, including atomic structure, periodic trends, and chemical bonding. This unit forms the foundation for understanding many fundamental concepts in chemistry, making it essential for students to thoroughly comprehend and master the material.
The Ap Chem Unit 2 test serves as a comprehensive assessment of students’ knowledge and understanding of these key topics. This examination evaluates students’ abilities to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, solve complex problems, and exhibit critical thinking skills. It is designed to challenge students and push their understanding beyond the surface level, encouraging them to think analytically and synthesize information.
To successfully prepare for the Ap Chem Unit 2 test, students must engage in focused study and review. This may involve revisiting class notes, textbooks, and online resources to reinforce their understanding of key concepts. Additionally, practicing with sample questions and taking practice exams can help students familiarize themselves with the format and types of questions they may encounter on the actual test.
In conclusion, the Ap Chem Unit 2 test is a significant milestone for students in their AP Chemistry journey. Mastering the material covered in this unit is essential for success in future units, as well as for understanding more advanced topics in chemistry. By dedicating time and effort to thorough preparation and review, students can confidently approach this test and demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of atomic structure, periodic trends, and chemical bonding.
What to Expect on the AP Chem Unit 2 Test

The AP Chem Unit 2 test covers a variety of topics, including chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and gas laws. It is important to be well-prepared for this exam, as it requires a solid understanding of these concepts and the ability to apply them to different scenarios.
One key topic that will be tested is chemical reactions. You can expect to see questions that require you to balance equations, predict products, and determine the quantities of reactants and products. Make sure to review the different types of reactions, such as synthesis, decomposition, combustion, and redox reactions.
- Another important area to focus on is stoichiometry. This involves calculating the quantities of substances in a chemical reaction. You may be asked to determine the limiting reactant, calculate the percent yield, or convert between moles, mass, and volume. Practice these types of problems to become comfortable with the calculations.
- Gas laws are also a significant part of this unit. Be prepared to apply Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law, Gay-Lussac’s Law, and the combined gas law to solve problems. Understand the relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and moles in a gas sample.
- Other topics that may appear on the test include solutions, including molarity and dilution calculations, and thermodynamics, including entropy and enthalpy changes. Review these concepts and practice relevant problems to ensure a thorough understanding.
When preparing for the AP Chem Unit 2 test, it is important to not only have a strong grasp of the material but also to practice applying the concepts to different scenarios. Work through practice problems, review class notes and textbooks, and consider seeking additional resources such as study guides or online tutorials. With thorough preparation and understanding of the topics, you can approach the test with confidence.
Overview of the AP Chem Unit 2 Test
The AP Chem Unit 2 Test focuses on chemical reactions and stoichiometry. This unit builds on the foundational knowledge of atoms, molecules, and the periodic table from Unit 1. Students are expected to understand the different types of chemical reactions, including combination, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement reactions.
One key concept in Unit 2 is stoichiometry, which deals with the quantitative relationships between chemical substances in a reaction. Students should be able to calculate the amount of reactants consumed and products formed using balanced chemical equations. Additionally, they should understand how to perform mole-to-mole, mole-to-mass, and mass-to-mass stoichiometric calculations.
The AP Chem Unit 2 Test may include questions that require students to identify the limiting reactant, calculate percent yield, and interpret reaction data. Students should also have a solid understanding of the concept of molarity and be able to solve problems related to dilutions and solution stoichiometry.
Overall, the AP Chem Unit 2 Test assesses students’ understanding of chemical reactions and their ability to apply stoichiometric principles. It requires both conceptual knowledge and problem-solving skills. To be successful on the test, students should review the different types of reactions, practice balancing chemical equations, and become proficient in stoichiometric calculations.
Important Topics Covered in Unit 2
In this unit, students will cover a variety of important topics in AP Chemistry. These topics will build upon the foundational knowledge gained in Unit 1 and provide a deeper understanding of chemical concepts and principles. Some of the key topics covered in Unit 2 include:
- Gases: Students will learn about the properties and behavior of gases, including gas laws, gas pressure, and the ideal gas law. They will also explore the concept of partial pressure and its application in gas mixtures.
- Thermochemistry: Thermochemistry deals with the study of heat transfer during chemical reactions. Students will explore key concepts such as enthalpy, heat capacity, and calorimetry. They will also learn about endothermic and exothermic reactions and how to calculate heat transfer in various scenarios.
- Atomic Structure: This topic focuses on the structure of atoms, including the arrangement of subatomic particles and the organization of electrons in energy levels and orbitals. Students will also learn about atomic models, including the Bohr model and quantum mechanical model.
- Periodic Trends: Understanding periodic trends is crucial in predicting the properties of elements based on their position in the periodic table. Students will explore trends such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. They will also learn about the periodicity of these trends across different periods and groups.
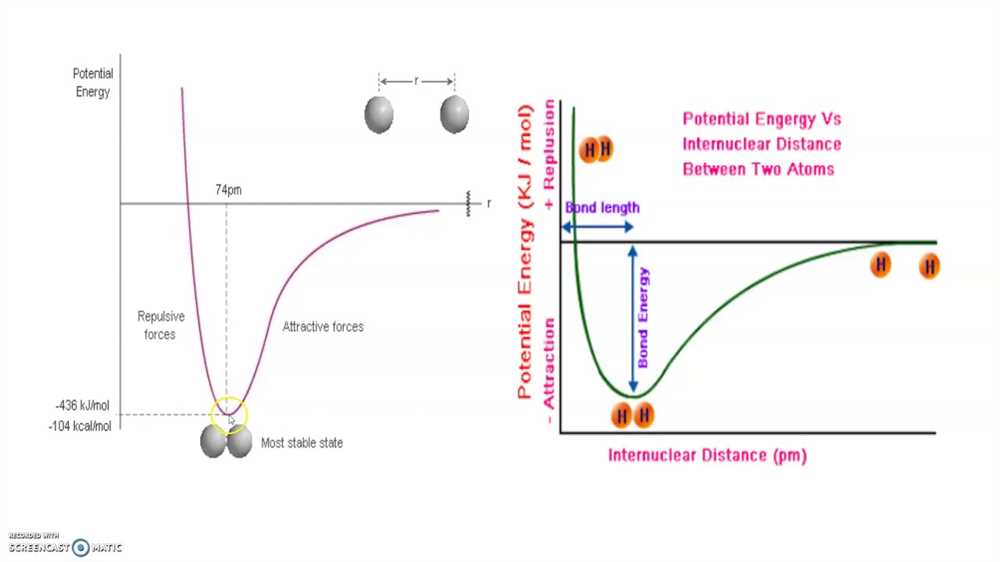
- Chemical Bonding: Chemical bonding is essential in understanding how atoms combine to form molecules and compounds. Students will learn about different types of chemical bonds, including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. They will also explore Lewis structures, molecular geometry, and bond polarity.
These are just a few of the important topics covered in Unit 2 of AP Chemistry. Mastering these concepts will provide a solid foundation for further exploration of advanced chemical principles and applications.
Format of the AP Chem Unit 2 Test

The AP Chemistry Unit 2 Test is designed to assess your understanding of chemical bonding and molecular structure. This section of the exam is worth 25% of your overall score and consists of a mix of multiple-choice questions and free-response questions. It is important to familiarize yourself with the format of the test in order to effectively prepare and perform well.
The multiple-choice portion of the exam consists of 60 questions, each with four answer choices. These questions assess your knowledge of concepts such as Lewis structures, molecular geometry, intermolecular forces, and bonding theories. It is essential to thoroughly review these topics and practice answering multiple-choice questions to develop your test-taking skills.
The free-response section of the exam consists of three questions: one long question and two shorter questions. These questions require you to apply your understanding of chemical bonding and molecular structure to solve problems and explain concepts. The long question typically involves a scenario where you are asked to analyze a given molecule or compound, while the shorter questions may require you to draw Lewis structures or identify intermolecular forces.
When preparing for the AP Chemistry Unit 2 Test, it is important to practice both multiple-choice and free-response questions. Reviewing key concepts, practicing problem-solving, and seeking clarification on any areas of confusion will help you feel more confident and prepared on test day. Familiarizing yourself with the format of the exam will enable you to effectively manage your time and showcase your knowledge in a clear and concise manner.
Tips for Studying for the AP Chem Unit 2 Test
Preparing for the AP Chem Unit 2 Test requires a solid understanding of the key concepts and skills covered in the unit. Here are a few tips to help you study effectively:
- Review class notes: Go over your class notes and make sure you understand all the information covered in class. Pay attention to any examples or explanations provided by your teacher.
- Read the textbook: Read the relevant chapters in your chemistry textbook to reinforce your understanding of the topics. Take notes and make sure you can explain the main ideas in your own words.
- Practice problem-solving: Chemistry involves a lot of problem-solving, so it’s important to practice solving various types of problems. Use your textbook or online resources to find practice questions and try to solve them on your own. If you get stuck, seek help from your teacher or classmates.
- Review past assignments and quizzes: Go through your past assignments and quizzes to identify any areas where you may need additional practice or review. Focus on understanding your mistakes and learning from them.
- Create a study schedule: Plan out your study time leading up to the test. Break down your studying into smaller, manageable chunks and allocate specific time slots for each topic or concept. This will help you stay organized and ensure you cover all the necessary material.
- Form a study group: Consider forming a study group with classmates who are also preparing for the test. Collaborating with others can help you clarify any doubts, discuss challenging concepts, and learn from each other.
Remember, studying for the AP Chem Unit 2 Test requires consistent effort and practice. Work on understanding the concepts, reviewing the material regularly, and seeking help when needed. With dedication and proper preparation, you can perform well on the test and achieve your desired score.
Key Concepts in Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are fundamental processes that occur in nature and play a crucial role in our everyday lives. Understanding key concepts in chemical reactions is essential for studying chemistry and applying it to various fields such as medicine, industry, and environmental science.
Chemical Equations: Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equations, which show the reactants on the left side and the products on the right side. Balancing the equation is necessary to ensure that the number of atoms on both sides is equal, as atoms cannot be created or destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Types of Reactions: Chemical reactions can be categorized into different types based on the changes that occur. Some common types include synthesis (combination), decomposition, combustion, single replacement, and double replacement reactions. Each type of reaction has its own characteristics and can be identified by analyzing the reactants and products.
Reaction Rates: The rate of a chemical reaction is the speed at which reactants are converted into products. Several factors can influence the reaction rate, such as temperature, concentration of reactants, surface area, and the presence of catalysts. Understanding reaction rates is crucial for optimizing industrial processes and designing efficient chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry: Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationship between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. It involves calculating the amount of reactants needed or the amount of products produced based on the balanced chemical equation. Stoichiometry is essential for determining the theoretical yield of a reaction and analyzing the efficiency of chemical processes.
Energy Changes: Chemical reactions involve energy changes, which can be either exothermic or endothermic. Exothermic reactions release energy to the surroundings, usually in the form of heat, while endothermic reactions absorb energy from the surroundings. Understanding energy changes in chemical reactions is important for determining the feasibility of a reaction and its impact on the environment.
Reaction Mechanisms: Reaction mechanisms explain the step-by-step process by which a chemical reaction occurs. They involve intermediate species and elementary steps that lead to the formation of products. Understanding reaction mechanisms is crucial for predicting reaction outcomes, designing new reactions, and improving existing processes.
Chemical Kinetics: Chemical kinetics is the study of the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence them. It involves measuring the rate of reaction and determining the rate law, which relates the rate of reaction to the concentrations of the reactants. Chemical kinetics provides insights into the mechanism of reactions and helps in understanding the factors that control reaction rates.
Equilibrium: Chemical equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time. Understanding chemical equilibrium is essential for studying reversible reactions, calculating equilibrium constants, and predicting the direction of a reaction under different conditions.
In conclusion, key concepts in chemical reactions include understanding chemical equations, types of reactions, reaction rates, stoichiometry, energy changes, reaction mechanisms, chemical kinetics, and equilibrium. Mastery of these concepts is crucial for further studies in chemistry and their practical application in various fields.