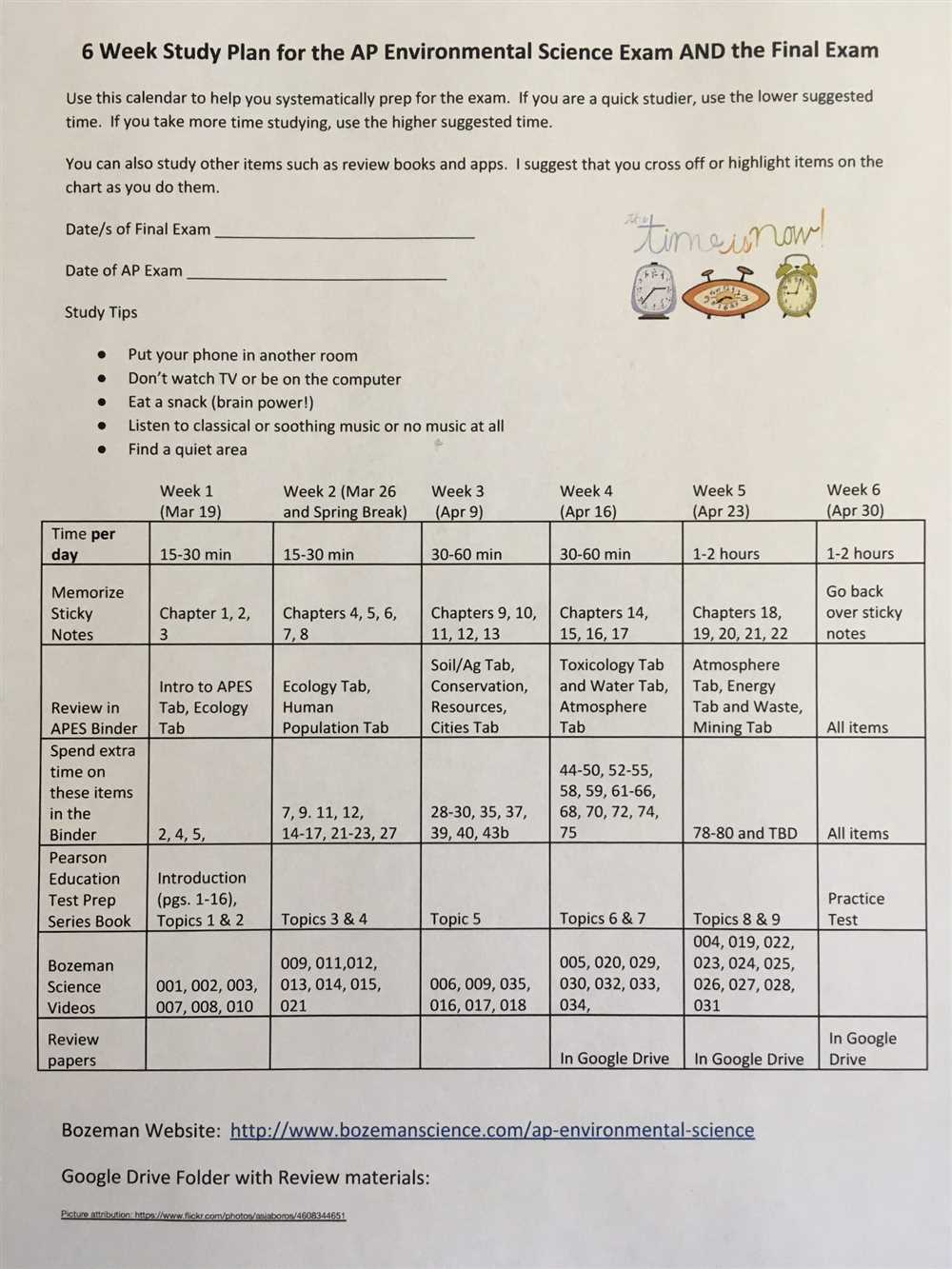
AP Environmental Science is a college-level course designed to give students an understanding of the interrelationships of the natural world, the scientific principles that govern it, and the environmental problems we face today. Unit 4 focuses on land and water use, and it includes free-response questions (FRQs) that test students’ ability to apply their knowledge and critical thinking skills.
In this article, we will provide answers to the FRQs in Unit 4 of the AP Environmental Science exam. These questions typically ask students to analyze and interpret data, describe environmental issues, and propose potential solutions. By understanding the key concepts and topics covered in Unit 4, students will be better prepared to tackle the FRQs and demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter.
Some of the topics covered in this unit include land use planning, urbanization, agriculture, water resources, and the environmental impacts of human activities. By studying these topics and practicing with FRQs, students can develop the skills and knowledge needed to successfully complete the AP Environmental Science exam.
Understanding the Unit 4 Free Response Questions
The Unit 4 Free Response Questions in AP Environmental Science are designed to assess students’ understanding of key concepts and their ability to apply them to real-world scenarios. These questions require students to demonstrate their knowledge of ecosystem dynamics, biodiversity, and the impact of human activities on the environment.
One of the key themes in Unit 4 is the concept of carrying capacity. Carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that a given environment can sustainably support. Understanding carrying capacity is crucial for evaluating the long-term viability of an ecosystem and predicting the effects of human activities on ecosystem dynamics. Students may be asked to analyze a hypothetical situation or examine real data to determine carrying capacity and its implications.
Another important topic in Unit 4 is biodiversity and its significance. Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. Students may be asked to explain the importance of biodiversity for ecosystem stability and resilience, as well as the potential consequences of biodiversity loss. They may also be required to propose strategies for conserving biodiversity and mitigating the negative impacts of human activities, such as habitat destruction and pollution.
Furthermore, the Unit 4 Free Response Questions often explore the relationship between human activities and environmental sustainability. Students may be asked to analyze the impact of specific human activities, such as deforestation, overfishing, or the use of pesticides, on ecosystem health and various ecosystem services. They may also be challenged to propose sustainable solutions and evaluate their potential effectiveness in addressing environmental issues.
In summary, the Unit 4 Free Response Questions in AP Environmental Science assess students’ understanding of carrying capacity, biodiversity, and the impact of human activities on the environment. By analyzing hypothetical scenarios and real-world data, students must demonstrate their ability to apply these concepts to evaluate ecosystem dynamics and propose sustainable solutions for biodiversity conservation and environmental sustainability.
Importance of Unit 4 FRQ Answers
The Unit 4 FRQ answers in the AP Environmental Science exam are crucial for students as they provide an opportunity to demonstrate their understanding of the material covered in this unit. FRQs, or free-response questions, are designed to assess students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as well as their ability to apply the concepts they have learned in a real-world context.
By answering the FRQs in Unit 4, students are able to showcase their knowledge of topics such as population dynamics, human population growth, and the impacts of human activities on the environment. These topics are essential in understanding the complexities of environmental science and how human actions can have significant consequences on ecosystems and natural resources.
Furthermore, the FRQs allow students to demonstrate their ability to analyze and interpret data, as well as develop and support a coherent argument. This is particularly important in Unit 4, as students are often required to analyze population data, calculate growth rates, and assess the factors influencing population dynamics. Being able to effectively communicate their interpretations and findings through clear and logical written responses is a crucial skill for success in the AP Environmental Science exam.
Overall, the Unit 4 FRQ answers play a significant role in determining a student’s understanding of the topics covered in this unit and their ability to apply their knowledge in a real-world context. The FRQs provide students with an opportunity to demonstrate their critical thinking, problem-solving, and data analysis skills, all of which are essential in the field of environmental science. Therefore, it is important for students to thoroughly prepare for the Unit 4 FRQs and ensure that they are able to effectively communicate their understanding and analysis of the topics covered.
Overview of Unit 4 Topics
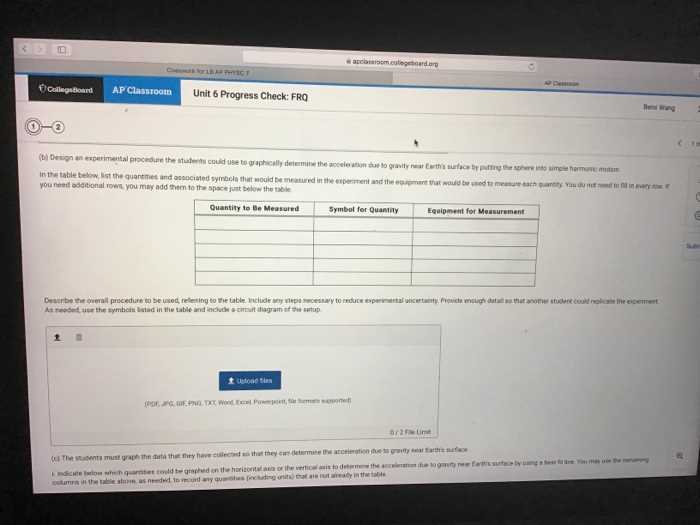
In Unit 4, we will be exploring several important topics related to environmental science. These topics include biodiversity, ecosystem services, and habitat fragmentation, as well as the causes and consequences of species extinction.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms in a given area. It is an important measure of the health and resilience of an ecosystem. We will discuss the different levels of biodiversity, including genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecosystem diversity. Additionally, we will examine the factors that can result in biodiversity loss, such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change.
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from natural ecosystems. These services include things like clean air and water, soil fertility, and the regulation of climate and disease. We will explore the various types of ecosystem services and discuss the ways in which they are being degraded or lost as a result of human activities.
Habitat fragmentation occurs when large, continuous habitats are divided into smaller, isolated patches. This can have significant negative impacts on wildlife, as it restricts their ability to move and find resources. We will examine the causes of habitat fragmentation, such as urbanization and the construction of roads, and discuss its ecological consequences.
Lastly, we will study the causes and consequences of species extinction. We will discuss natural factors that can lead to extinctions, as well as the human activities that are driving species to extinction at an unprecedented rate. We will also explore the ecological and economic consequences of species loss, and consider strategies for conservation and restoration.
Through our study of these topics, we will gain a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between humans and the environment, and the importance of preserving biodiversity and ecosystem services for a sustainable future.
Exploring Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Ecosystems and biodiversity are essential components of our planet’s natural resources and support the survival of all living organisms. Studying and understanding these complex systems is crucial for addressing environmental challenges and conservation efforts.
Biodiversity refers to the variety and abundance of different species in an ecosystem. It is an indicator of the health and stability of an ecosystem. High levels of biodiversity contribute to ecological resilience, as different species have the ability to adapt and provide important ecosystem services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control.
When exploring ecosystems and biodiversity, scientists analyze the interactions between species and their environment. They study the physical and biological factors that influence population dynamics, distribution patterns, and ecosystem functioning. Understanding these relationships helps identify potential threats and develop effective conservation strategies.
To assess the biodiversity of an ecosystem, scientists use various methods such as field surveys, genetic analysis, and remote sensing technologies. These tools allow them to collect data on species composition, abundance, habitat suitability, and ecosystem health. By monitoring biodiversity over time, scientists can detect changes and evaluate the effectiveness of conservation measures.
Protecting and conserving ecosystems and biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the balance of our planet’s ecosystems and ensuring the sustainable use of natural resources. This requires collaborative efforts from governments, organizations, and individuals worldwide. By promoting sustainable practices, implementing protected areas, and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity, we can contribute to the preservation of our planet’s precious ecosystems.
Understanding Ecological Relationships
Ecological relationships are the interactions between different organisms within an ecosystem. These relationships can be categorized into different types such as predator-prey, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Understanding these relationships is crucial for understanding the dynamics of ecosystems and how they function.
Predator-prey relationships: In a predator-prey relationship, one organism (predator) hunts and consumes another organism (prey). This relationship is a key driving force in controlling population sizes and maintaining balance within an ecosystem. For example, wolves (predators) hunting deer (prey) helps control the deer population while also providing a food source for the wolves.
Mutualism: Mutualism is a type of relationship where both organisms benefit. This type of relationship is often seen in interactions between species such as pollinators and flowering plants. Bees, for example, collect nectar from flowers and in the process, they transfer pollen, allowing plants to reproduce. In return, bees obtain food from the nectar.
Commensalism: Commensalism is a relationship where one organism benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited. An example of commensalism is when certain birds build their nests in trees. The birds benefit from the protection and support of the tree branches, while the tree is unaffected by the bird’s presence.
Parasitism: Parasitism is a relationship where one organism (parasite) benefits at the expense of the other organism (host). Parasites live and obtain nutrients from the host organism, often resulting in harm or even death for the host. An example of parasitism is a tick feeding on a dog. The tick benefits from the dog’s blood while the dog may suffer from anemia or other diseases transmitted by the tick.
These different ecological relationships play important roles in shaping the structure and functioning of ecosystems. By studying and understanding these relationships, scientists can gain insights into the intricate web of interactions that exist in nature and how they impact the overall health and stability of ecosystems.
Analyzing Population Dynamics

Population dynamics refers to the study of how populations change over time, including the factors that influence birth rates, death rates, and migration. An understanding of population dynamics is essential for analyzing and predicting the impacts of population growth on the environment and society.
Population growth: One key aspect of population dynamics is population growth. This refers to the increase in the number of individuals in a population over time. Population growth can be influenced by factors such as birth rates, death rates, and net migration.
Birth rates: Birth rates are the number of live births per 1,000 individuals in a population per year. Factors that influence birth rates include access to healthcare, education, cultural and social norms, and availability of family planning services. High birth rates can lead to rapid population growth, which can put pressure on resources and the environment.
Death rates: Death rates are the number of deaths per 1,000 individuals in a population per year. Factors that influence death rates include access to healthcare, sanitation, nutrition, and prevalence of diseases. High death rates can lead to population decline, while low death rates can contribute to population growth.
Migration: Migration refers to the movement of individuals into and out of a population. Immigration refers to individuals moving into a population, while emigration refers to individuals leaving a population. Migration can influence population dynamics by changing the size and composition of a population. Factors that influence migration include economic opportunities, political stability, and environmental conditions.
Population density: Population density is the number of individuals per unit of area or volume. It is an important factor in determining the availability of resources, the level of competition for resources, and the potential impacts on the environment. High population densities can lead to increased resource consumption, habitat destruction, and pollution.
Understanding population dynamics: Analyzing population dynamics requires an understanding of the interplay between birth rates, death rates, and migration. It also requires considering factors such as age structure, sex ratio, and population density. By studying population dynamics, scientists can better predict the future impacts of population growth on the environment and society, and develop strategies to manage and mitigate these impacts.
Tips for Answering Unit 4 FRQs
Unit 4 FRQs in AP Environmental Science require a comprehensive understanding of the topic and the ability to apply that knowledge to real-world scenarios. These tips will help you approach the FRQs effectively and maximize your chances of earning a high score.
1. Understand the Question Format: Familiarize yourself with the different question formats that may appear in Unit 4 FRQs. These can include data analysis, experimental design, and scenario-based questions. Knowing what to expect will help you structure your answers appropriately.
2. Read the Question Carefully: Take the time to read each question carefully, ensuring that you understand what is being asked. Identify the key information and any specific instructions or requirements given in the question prompt.
3. Plan Your Answer: Before diving into your response, take a few minutes to plan your answer. Organize your thoughts and create an outline of the main points you want to address. This will help you structure your response and ensure that you include all the necessary information.
4. Use Relevant Content Knowledge: Draw on your knowledge of environmental science concepts and principles to support your answer. Use specific examples, data, and evidence to strengthen your points and demonstrate a deep understanding of the topic.
5. Be Concise and Clear: Write your answers in a concise and clear manner. Avoid unnecessary repetition or rambling. Stick to the main points and provide a clear and logical argument or explanation.
6. Use Proper Terminology: Use appropriate environmental science terminology and vocabulary to demonstrate your understanding of the subject matter. This will also help you communicate your ideas effectively to the reader.
7. Show Your Work: When applicable, show your work or calculations to support your answer. This can include data analysis, calculations, or experimental design. Make sure to explain your methodology and reasoning behind your approach.
8. Time Management: Manage your time effectively during the exam. Allocate an appropriate amount of time to each question, ensuring that you have enough time to fully answer each one. If you are running out of time, prioritize the most important points and move on.
9. Proofread Your Answer: Before submitting your answer, take a few moments to proofread and revise your response. Check for any spelling or grammatical errors, and make sure your answer is coherent and makes sense.
By following these tips, you can approach Unit 4 FRQs with confidence and increase your chances of success. Remember to practice applying your knowledge to different scenarios and familiarize yourself with past FRQs to further improve your skills.