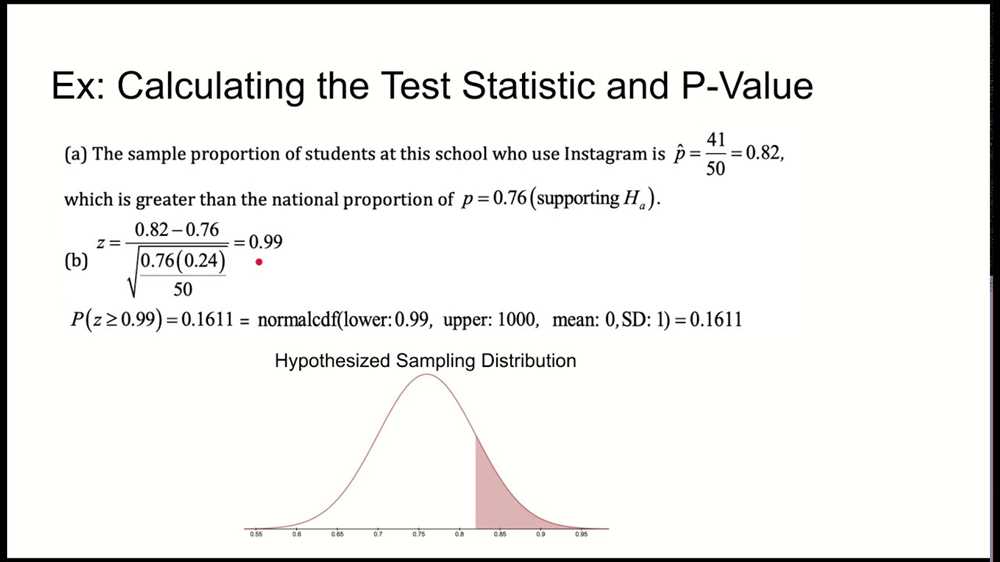
In AP Statistics, Chapter 12 introduces the concept of hypothesis testing. This is a critical topic in statistics because it allows us to make decisions and draw conclusions about population parameters based on sample data. Hypothesis testing helps us determine whether there is enough evidence to support or reject a claim about a population.
The chapter covers different aspects of hypothesis testing, including the formulation of null and alternative hypotheses, determining the appropriate test statistic and its distribution, and calculating p-values. It also delves into the concept of Type I and Type II errors, as well as the significance level and power of a test.
The Chapter 12 test in AP Statistics is designed to assess students’ understanding and application of these concepts. It may include multiple-choice questions, free-response questions, and problem-solving tasks. The test will require students to analyze data, interpret results, and make informed conclusions based on the principles of hypothesis testing.
Overview and Objectives
Welcome to the overview and objectives section of the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test! In this chapter, we will delve into the fascinating world of inference for categorical data. We will explore various tools and techniques that will enable us to make informed conclusions about populations based on sample data.
This chapter focuses on two main objectives: understanding and applying hypothesis tests for proportions and tests for independence. Through these objectives, we aim to develop a deeper understanding of how to analyze categorical data, draw conclusions, and make inferences about populations.
Hypothesis Tests for Proportions
Hypothesis tests for proportions allow us to determine if there is sufficient evidence to support a claim regarding the value of a population proportion. We will learn how to set up null and alternative hypotheses, calculate test statistics, and interpret p-values to draw conclusions. Additionally, we will explore the concept of confidence intervals and how they can be used in conjunction with hypothesis tests.
Tests for Independence
Tests for independence help us examine whether two categorical variables are related or independent of each other. Through chi-square tests, we will assess if there is evidence to support a relationship between variables and examine the strength and direction of that relationship. We will also delve into contingency tables and odds ratios to better understand the association between variables.
By the end of this chapter, you will have a solid foundation in conducting hypothesis tests for proportions and tests for independence. Armed with these statistical tools, you will be able to make informed decisions and draw valid conclusions about categorical data.
Understanding the AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test Format
When preparing for the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test, it is important to have a clear understanding of the test format. The test typically consists of multiple-choice and free-response questions that assess your knowledge and understanding of the concepts covered in this chapter.
The multiple-choice section of the test will require you to analyze and interpret different types of data, such as scatterplots, histograms, and boxplots. You may be asked to identify the appropriate statistical test or method to solve a given problem, or to interpret the results of a statistical analysis. It is crucial to practice answering these types of questions in order to familiarize yourself with the format and improve your problem-solving skills.
In addition to the multiple-choice questions, the free-response section of the test will require you to demonstrate your ability to apply statistical concepts and principles to real-world scenarios. You may be asked to design and conduct a statistical study, analyze and interpret data, or communicate the results of a statistical analysis. It is important to practice answering these types of questions in order to develop your critical thinking and communication skills.
To effectively prepare for the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test, it is recommended to review the key concepts covered in this chapter, such as correlation, regression, and statistical inference. Additionally, practicing with sample questions and past exams can help you become familiar with the types of questions that may be asked and improve your overall performance on the test. By understanding the test format and dedicating time to thorough preparation, you can increase your chances of success on the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test.
Components and scoring
In the AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test, students will encounter questions that assess their understanding of statistical concepts and their ability to apply statistical methods. The test typically consists of multiple-choice questions, free-response questions, and/or investigative tasks. This variety of question types allows students to demonstrate both their procedural and conceptual knowledge.
The multiple-choice questions in the AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test are designed to assess students’ ability to interpret and analyze statistical information. These questions may require students to interpret graphs, tables, or statistical output, and make conclusions or predictions based on the given data. The multiple-choice questions are scored using a rubric that assigns specific points for correct answers and deductions for incorrect or omitted responses.
The free-response questions in the test require students to demonstrate a deeper understanding of statistical concepts and methods. These questions often ask students to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios, design and conduct experiments or surveys, analyze and interpret data, and communicate their findings effectively. The scoring of free-response questions involves a rubric that assesses both the accuracy and clarity of the responses. Points are awarded for correct calculations, appropriate use of statistical techniques, and effective communication of the results.
The investigative tasks in the AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test provide students with an opportunity to demonstrate their ability to design and conduct statistical investigations. These tasks often involve multiple steps, including formulating a research question, planning and implementing data collection methods, analyzing the data, and drawing conclusions based on statistical evidence. The scoring of investigative tasks considers the soundness of the statistical investigation, the accuracy of the analysis, and the clarity of the conclusions. Points are allocated for each step of the investigation, with additional points awarded for demonstrating creativity and insight.
Overall, the AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test assesses students’ understanding of statistical concepts, their ability to apply statistical methods, and their skills in interpreting and communicating statistical information. The scoring process ensures that students are rewarded for their knowledge, critical thinking, and effective communication skills, providing them with valuable feedback on their statistical proficiency.
Key Concepts and Topics Covered in AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test

In this AP Statistics Chapter 12 test, students will focus on key concepts related to linear regression and correlation. The test will assess their understanding of the relationship between two quantitative variables, as well as their ability to interpret and draw conclusions from various statistical measures.
Simple Linear Regression: One of the main topics covered in this test is simple linear regression. Students will be expected to understand the concept of a linear relationship between two variables and how to fit a regression line to the data. They should also be able to interpret the slope and intercept of the regression line in the context of the problem.
Correlation: Another important concept covered in this chapter is correlation. Students will learn how to calculate and interpret the correlation coefficient, which measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. They should also understand the limitations of correlation and be able to distinguish between causation and correlation.
Residuals: The concept of residuals will also be assessed in this test. Students should understand that residuals represent the vertical distance between each data point and the regression line. They should be able to calculate and interpret residuals, as well as use them to assess the fit of the regression line.
Inference for Regression: This chapter also covers inference for regression, including hypothesis tests and confidence intervals. Students should be able to perform these inferential procedures and interpret the results in the context of the problem. They should also be able to apply the appropriate statistical procedures when given a sample regression output.
Model Assumptions and Residual Analysis: Students will need to demonstrate their understanding of the assumptions underlying linear regression and how to assess these assumptions using residual analysis. They should be able to identify and address violations of these assumptions, such as nonlinearity and heteroscedasticity.
In summary, the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test will assess students’ knowledge and skills related to linear regression and correlation. Understanding the concepts of simple linear regression, correlation, residuals, inference for regression, and model assumptions will be key to success on this test.
Exploring Confidence Intervals and Significance Tests
In statistics, confidence intervals and significance tests are important tools used to make inferences about population parameters based on sample data. These techniques provide a way to estimate the true value of a population parameter and assess the likelihood of a statistical difference between groups.
Confidence intervals are used to estimate an unknown population parameter, such as a population mean or proportion. They provide a range of possible values within which the true population parameter is likely to fall. The confidence level determines the percentage of times that the true parameter would be expected to fall within the interval, based on repeated sampling.
For example, a 95% confidence interval for the mean annual income of a population might be $40,000 to $50,000. This means that if we were to take many random samples from this population, we would expect that 95% of the resulting confidence intervals would contain the true mean annual income.
Significance tests are used to determine whether there is a statistically significant difference between two groups or whether a relationship exists between two variables. These tests involve comparing sample statistics to hypothesized population parameters or comparing sample means or proportions between groups.
For example, a significance test can be used to determine whether there is evidence to suggest that the mean IQ scores of males and females differ. By collecting data from random samples of males and females and conducting a hypothesis test, we can assess whether any observed differences in the sample means are statistically significant or just due to random chance.
In conclusion, confidence intervals and significance tests are valuable tools in statistics that help researchers make inferences about population parameters and assess the statistical significance of observed differences or relationships. These techniques allow for more accurate interpretations of sample data and provide a framework for making informed decisions based on statistical evidence.
Preparing for the AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test
As you approach the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test, it is important to prepare effectively in order to maximize your chances of success. Chapter 12 covers the concepts of inference for proportions, including confidence intervals and hypothesis tests. To ensure you are well-prepared, it is crucial to review the key topics and practice applying them to various scenarios.
1. Understand the concepts:
- Review the formulas and concepts related to inference for proportions. Make sure you understand the difference between confidence intervals and hypothesis tests.
- Pay close attention to the conditions required for performing inference for proportions, such as the randomization condition, independence condition, and success-failure condition.
- Practice interpreting confidence intervals and hypothesis tests in the context of real-world scenarios, as this will be a key component of the test.
2. Review and practice problems:
- Go through the chapter exercises and practice problems to reinforce your understanding of the concepts. Make sure to understand the steps involved in solving each problem and be able to explain your reasoning.
- Work on additional practice problems from online sources or review books to get more exposure to different types of questions.
- Consider forming a study group or partnering with a classmate to review the material and solve problems together. This can provide an opportunity for discussion and clarification of any confusing topics.
3. Utilize resources:
- Make use of any resources provided by your teacher, such as review guides or study materials.
- Refer to your textbook or online resources for additional practice problems, explanations, and examples.
- Take advantage of online tutorials or instructional videos that cover the topics in Chapter 12. This can be a helpful supplemental resource to reinforce your understanding.
By following these steps and putting in the necessary effort, you will be well-prepared for the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test. Remember to allocate enough time for studying and practice, and don’t hesitate to seek help if you encounter any difficulties. With the right preparation and mindset, you can confidently approach the test and perform your best.
Study Tips and Resources for AP Statistics Chapter 12 Test
Preparing for the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test requires a combination of understanding the concepts and practicing problem-solving. Here are some study tips and resources to help you excel in your preparation:
1. Understand the Key Concepts:
Before diving into practice problems, make sure you have a solid understanding of the key concepts covered in Chapter 12. Review the textbook or lecture notes to ensure you can explain concepts such as hypothesis testing, p-values, Type I and Type II errors, and confidence intervals.
2. Practice with Sample Problems:
Working through sample problems is crucial for mastering the material. Look for practice problems in your textbook or online resources that focus on hypothesis testing and confidence intervals. Make sure to solve problems that cover both one-sample and two-sample scenarios to ensure a comprehensive understanding.
3. Utilize Study Guides:
Study guides are valuable resources that can help you organize and consolidate the information. Look for comprehensive study guides specifically tailored to AP Statistics Chapter 12 topics. These guides often provide summaries, key formulas, and practice questions to reinforce your learning.
4. Collaborate with Peers:
Discussing the material with classmates can provide new perspectives and help solidify your understanding. Consider forming study groups or participating in online forums to engage in discussions and exchange insights and tips for approaching Chapter 12 problems. Explaining concepts to others can also reinforce your own understanding.
5. Seek Additional Resources:
If you need more help, don’t hesitate to explore additional resources. Online tutorials, videos, and interactive quizzes can provide alternative explanations and visual aids to enhance your understanding. Check out websites and platforms that offer AP Statistics resources, such as Khan Academy or College Board.
By following these study tips and utilizing available resources, you can effectively prepare for the AP Statistics Chapter 12 test and improve your chances of success. Remember to allocate sufficient time for review and practice, and don’t hesitate to reach out for help when needed.