As the AP Statistics exam approaches, it is important to be well-prepared for each section of the test. Test 8A is no exception, as it covers a range of topics that require a solid understanding of statistical concepts and analysis. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to help students effectively prepare for Test 8A.
Test 8A focuses on various statistical concepts, including hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and experimental design. It requires students to apply these concepts to real-world scenarios and draw conclusions based on the data provided. It is crucial for students to have a strong grasp of these concepts and be able to apply them confidently during the test.
One of the key areas covered in Test 8A is hypothesis testing. Students are expected to understand the logic behind hypothesis testing, interpret p-values, and make informed decisions based on statistical significance. Additionally, confidence intervals play a significant role in this section, as students need to calculate and interpret confidence intervals for population parameters.
Another important focus of Test 8A is experimental design. Students are expected to design and analyze experiments, identify potential sources of bias, and determine the most appropriate statistical techniques to use. It is crucial for students to familiarize themselves with different experimental designs, such as completely randomized designs and block designs, and understand the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Ap Statistics Test 8a: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to the comprehensive guide for Ap Statistics Test 8a! This test is designed to assess your understanding and application of statistical concepts covered in this unit. In order to succeed on this test, it is important to review key topics and practice solving different types of problems.
Overview of Test Content
- Data analysis: This section focuses on methods for analyzing and interpreting data, including measures of center, spread, and position, as well as graphical representations of data.
- Probability: This section covers basic probability concepts, including calculating probabilities for different events and understanding the laws of probability.
- Inference: This section involves making inferences and drawing conclusions based on sampled data, including hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
Test Preparation Tips
- Review class notes and textbook readings: Go over your class notes and textbook readings to refresh your memory on key concepts and formulas.
- Practice solving problems: Find practice problems in your textbook or online resources and work through them to reinforce your understanding of concepts and improve your problem-solving skills.
- Seek help if needed: If you are struggling with any specific topics, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher or classmates for help. They can provide additional explanations or resources to clarify any confusion.
- Create a study schedule: Plan out your study time leading up to the test to ensure you cover all the necessary material. Break it down into smaller, manageable chunks to make studying more efficient.
- Take practice tests: Complete practice tests to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter on the actual test. This will also help you manage your time effectively during the test.
Test-taking Strategies
- Read the instructions carefully: Make sure you understand what is being asked before attempting to answer the questions.
- Show your work: Clearly show your work and the steps you take to arrive at your answers. This will help you receive partial credit if you make a mistake.
- Manage your time: Keep an eye on the time and allocate it wisely among the different sections of the test. Don’t spend too much time on a single question.
- Eliminate incorrect choices: If you are unsure of an answer, try to eliminate any obviously incorrect choices to increase your chances of selecting the correct answer.
- Stay calm and focused: Test anxiety can hinder your performance, so take deep breaths and stay focused on the task at hand. Trust in your preparation and abilities.
Remember, thorough preparation and practice are key to success on Ap Statistics Test 8a. Good luck!
Understanding the Basics of Test 8a
In AP Statistics, Test 8a is an important assessment that evaluates students’ understanding of various statistical concepts and techniques. It covers a range of topics, including probability, random variables, confidence intervals, and hypothesis testing. As students prepare for this test, it is crucial to have a solid grasp of the basics.
One key concept that students must understand for Test 8a is probability. Probability is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur. Students must be able to calculate probabilities using various methods, such as the multiplication rule and the addition rule. They should also be familiar with terms like independent events, dependent events, and conditional probability.
Another important topic on Test 8a is random variables. A random variable is a variable that takes on different values based on the outcome of a random experiment. Students need to understand the difference between discrete and continuous random variables, as well as how to calculate expected values and standard deviations for both types.
Confidence intervals and hypothesis testing are also covered on Test 8a. A confidence interval is a range of values within which an unknown population parameter is estimated to lie. Students must be able to calculate confidence intervals for means and proportions using the appropriate formulas. Hypothesis testing involves making decisions about the truth of a claim based on sample data. Students should be familiar with the steps involved in hypothesis testing and understand terms like null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, and p-value.
Overall, Test 8a in AP Statistics assesses students’ understanding of probability, random variables, confidence intervals, and hypothesis testing. By reviewing and practicing these basic concepts, students will be well-prepared for success on the test.
Tips for Preparation and Study Guides
Preparing for the AP Statistics Test 8A can be a daunting task, but with the right strategies and study guides, it can become manageable and even enjoyable. Here are some tips to help you succeed:
- Start early: Don’t wait until the last minute to begin studying. The AP Statistics Test covers a wide range of topics, so give yourself enough time to review and practice.
- Create a study plan: Organize your study time by creating a detailed study plan. Allocate specific time slots for each topic and make sure to stick to it.
- Focus on the most important topics: While it’s important to have a general understanding of all the topics, focus more on the areas that are heavily tested. Look at past exams and review the questions that come up most frequently.
- Practice with sample questions: Take advantage of practice exams and sample questions to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you may encounter on the actual test. This will also help you identify areas where you need to improve.
- Use study guides and review books: Invest in a good study guide or review book that is specifically designed for the AP Statistics Test. These resources often provide comprehensive explanations of concepts, practice questions, and helpful tips.
- Form a study group: Consider forming or joining a study group with classmates who are also preparing for the test. Collaborative learning can help you gain different perspectives and reinforce your understanding of the material.
- Ask for help: If you’re struggling with a particular concept or topic, don’t hesitate to seek help from your teacher, classmates, or online resources. There are plenty of resources available, such as online forums and tutoring services, that can provide additional support.
By following these tips and utilizing study guides and resources, you’ll be well-prepared for the AP Statistics Test 8A and increase your chances of earning a high score. Remember to stay focused, stay motivated, and stay confident in your abilities!
Overview of the Topics Covered in Test 8a
The Ap statistics test 8a covers various topics that are crucial in understanding and analyzing data. This test encompasses a wide range of concepts, including experimental design, probability, and statistical inference. Mastery of these topics is essential for anyone looking to make informed decisions and draw valid conclusions based on data.
One of the main areas covered in test 8a is experimental design. This includes understanding the principles behind randomization and control groups, as well as the different types of experimental designs such as completely randomized designs and matched pairs designs. It also delves into the importance of sample size and how it can impact the validity of experimental results.
Probability is another significant topic covered in the test. Students will explore the fundamental principles of probability, including calculating probabilities using the addition and multiplication rules, as well as understanding concepts such as independence and conditional probability. The test will also assess students’ ability to apply these principles to solve real-world problems.
Statistical inference is perhaps one of the most crucial topics covered in test 8a. It involves making inferences and drawing conclusions about a population based on sample data. This includes understanding the concept of sampling distributions, estimating population parameters, and conducting hypothesis tests. Students will also learn about confidence intervals and how they can be used to estimate unknown population parameters.
In summary, test 8a of the Ap statistics curriculum covers essential concepts in experimental design, probability, and statistical inference. These topics lay the groundwork for understanding and interpreting data accurately, and they are fundamental in various fields, including business, science, and social sciences.
How to Interpret and Analyze Data
Interpreting and analyzing data is an essential skill in the field of statistics. It allows us to make informed decisions and draw meaningful conclusions from the information available. To effectively interpret and analyze data, there are several steps and techniques that can be followed:
1. Define the research question: Before analyzing any data, it is important to clearly define the research question or objective. This will help guide the analysis and ensure that the right variables are considered for interpretation.
2. Collect relevant data: Once the research question is defined, the next step is to collect the relevant data. This may involve conducting surveys, experiments, or gathering existing data from various sources. It is crucial to ensure that the data collected is reliable and representative of the population of interest.
3. Organize and summarize the data: After collecting the data, it is important to organize and summarize it in a meaningful way. This can be done through tables, charts, and graphs. Summarizing the data allows us to get a quick overview and identify any patterns or trends that may exist.
4. Apply appropriate statistical techniques: Depending on the nature of the data and the research question, different statistical techniques may be applied. This could include measures of central tendency, such as mean or median, or measures of dispersion, such as standard deviation or range. The choice of statistical techniques will help us gain deeper insights into the data and answer the research question effectively.
5. Interpret the results: Once the data has been analyzed using statistical techniques, it is time to interpret the results. This involves drawing conclusions and making inferences based on the findings. It is important to consider any limitations or potential sources of bias in the data, as well as the statistical significance of the results.
6. Communicate the findings: Finally, the interpretation of the data should be effectively communicated to others. This can be done through written reports, presentations, or visualizations. Clear and concise communication of the findings is crucial to ensure that the information is understood and can be used for decision-making purposes.
In summary, interpreting and analyzing data requires careful consideration of the research question, collection of relevant data, organization and summarization of the data, application of appropriate statistical techniques, interpretation of the results, and effective communication of the findings. By following these steps and techniques, we can make meaningful use of data to gain insights and make informed decisions.
Key Concepts in Probability and Sampling
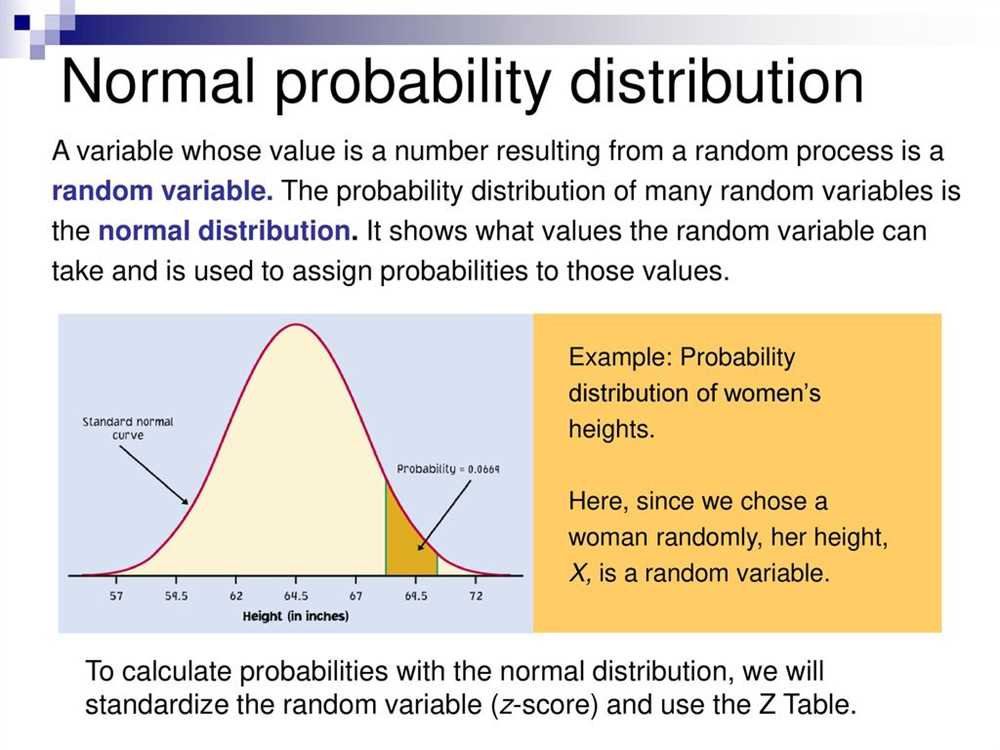
In the field of statistics, understanding the key concepts of probability and sampling is essential for analyzing data and making accurate predictions. Probability refers to the likelihood of an event occurring, while sampling involves selecting a subset of individuals or units from a larger population for analysis.
Probability: Probability plays a crucial role in statistics as it helps us quantify and measure uncertainty in various situations. It is represented as a value between 0 and 1, with 0 representing an impossible event and 1 representing a certain event. The probability of an event occurring can be determined using mathematical calculations and can be influenced by various factors such as random variables, independence, and conditional probability.
Sampling: Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of individuals or units from a larger population to gather information and make inferences about the population as a whole. There are various sampling methods, including random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. Random sampling involves randomly selecting individuals from a population, while stratified sampling involves dividing the population into homogeneous groups and selecting individuals from each group. Cluster sampling involves dividing the population into clusters and randomly selecting clusters to sample.
Main Concepts:
- Random Variables: Random variables are variables whose values depend on the outcome of a random event. They can be discrete or continuous and are often used to model real-world phenomena.
- Independence: Independence refers to the lack of a relationship between two events. If two events are independent, the occurrence of one event does not affect the probability of the other event occurring.
- Conditional Probability: Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It is calculated by dividing the probability of the joint occurrence of the two events by the probability of the given event.
- Sampling Distribution: A sampling distribution is a probability distribution that describes the likelihood of obtaining a particular sample statistic from a population.
- Sampling Error: Sampling error refers to the discrepancy between the sample statistic and the true population parameter it represents. It is an unavoidable part of sampling and can be reduced through larger sample sizes and careful sampling techniques.
Understanding these key concepts in probability and sampling is essential for conducting statistical analyses and interpreting data accurately. By applying these concepts, statisticians can make informed decisions, draw valid conclusions, and make reliable predictions.