The ASTM Standard for Charpy Impact Test is a widely accepted method used to determine the resistance and toughness of materials to sudden impact loading. The test is especially important in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and aerospace, where the ability of a material to withstand sudden impact is critical.
ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, and services. The Charpy Impact Test, designated as ASTM E23, is one of the many standards developed by the organization.
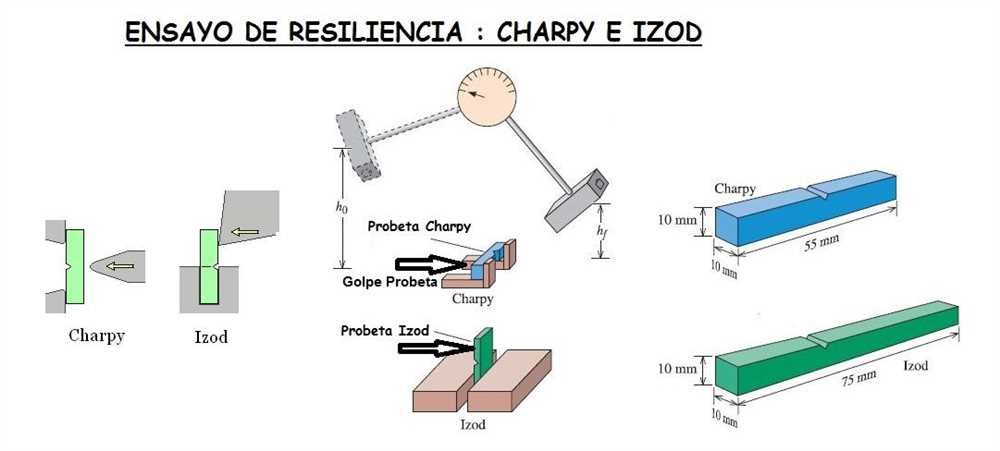
The Charpy Impact Test involves striking a notched specimen with a pendulum swing to measure the amount of energy absorbed by the material during fracture. The test helps determine the material’s resistance to brittle fracture and its ability to absorb energy before failure. The result is usually presented as the energy absorbed in joules or foot-pounds.
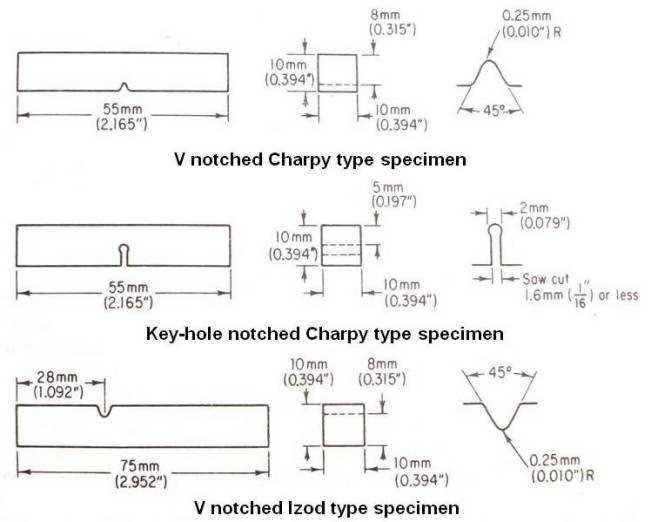
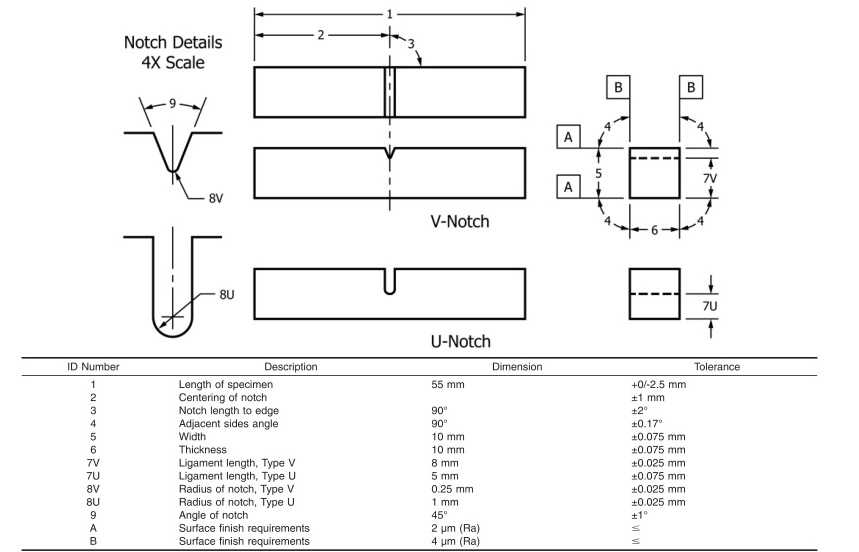
The ASTM Standard for Charpy Impact Test provides guidelines for specimen preparation, testing procedures, and reporting of results. It specifies the requirements for the dimensions and tolerances of the specimen, the angle of the V-shaped notch, and the size and weight of the pendulum. The standard also defines the test temperature and the method of measuring and recording the energy absorbed.
The use of the ASTM Standard for Charpy Impact Test ensures that the testing is conducted consistently and accurately across different laboratories and industries. This allows for reliable and comparable results, which are essential for making informed decisions regarding material selection and design. By following the standard, manufacturers can ensure the quality and performance of their products, while researchers can evaluate the impact resistance of new materials.
Importance of Charpy Impact Test in Material Testing
Charpy Impact Test is an important test conducted on materials to evaluate their toughness and resistance to sudden impact. This test measures the amount of energy absorbed by a specimen when it is subjected to an impact force under specific conditions. The results obtained from this test can provide valuable information about the material’s ability to withstand sudden shock or impact in various industries, such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
The Charpy Impact Test follows the ASTM Standard (American Society for Testing and Materials), which provides guidelines and procedures for conducting the test accurately and consistently. This standard ensures that the test results are reliable and can be compared across different laboratories and testing facilities.
The Charpy Impact Test is particularly important in material testing because it helps determine the brittle or ductile nature of a material. Materials with high impact strength are less likely to fracture or fail under sudden impact, making them suitable for applications where safety and durability are paramount, such as in structural components or equipment parts.
Furthermore, the Charpy Impact Test is useful for assessing the quality and reliability of materials used in various industries. It can help identify any defects or weaknesses in the material’s structure, as well as any potential problems that may arise during its use. This information allows manufacturers to make informed decisions about material selection, design modifications, and quality control measures to ensure the overall safety and performance of their products.
In summary, the Charpy Impact Test plays a crucial role in material testing by providing valuable insights into the toughness and resistance of a material to sudden impacts. It helps ensure the safety and reliability of various products and components, making it an essential test in the field of material science and engineering.
Overview of ASTM Standard for Charpy Impact Test
The Charpy Impact Test is a commonly used measurement technique to determine the impact toughness of materials. It assesses the energy absorbed by a material when struck by a pendulum hammer. This test is widely used in various industries, including construction, aerospace, and automotive, to evaluate the durability and resilience of materials.
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) has established a standard specification, namely ASTM E23, for conducting the Charpy Impact Test. This standard provides detailed guidelines for test setup, specimen preparation, and test procedure to ensure consistency and accuracy of results.
Test Setup: According to the ASTM E23 standard, the test specimen should have specific dimensions and should be carefully machined to ensure accurate results. The specimen is held in a special clamp, and the pendulum hammer is positioned at a specific height to strike the specimen. The testing apparatus must be properly calibrated and maintained to ensure accurate measurements.
Test Procedure: The Charpy Impact Test is conducted by releasing the pendulum hammer from a certain height to strike the center of the specimen. The energy absorbed and the resulting fracture behavior are recorded. The test is typically repeated multiple times to obtain an average value and assess the consistency of the material’s impact toughness.
Reporting Results: Following the test, the energy absorbed by the specimen, called the impact energy, is measured and reported in joules or foot-pounds. The fracture behavior is also evaluated, including the appearance of the fracture surface, the presence of any cracks or other defects, and the extent of the deformation. These results can provide valuable information on the material’s resistance to impact loading.
In conclusion, the ASTM Standard for Charpy Impact Test provides a comprehensive framework for conducting and reporting the test. Adhering to this standard ensures consistency and reliability of test results, thereby facilitating material selection and design in various industries.
ASTM E23 – Standard Test Methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of Metallic Materials
The ASTM E23 standard provides guidelines for conducting notched bar impact testing of metallic materials. This test method is widely used for measuring the impact resistance and toughness of metals. It involves subjecting a notched specimen to a sudden load, typically with a pendulum or falling weight, and measuring the amount of energy absorbed by the specimen. This energy absorption is an indicator of the material’s ability to withstand sudden impact and can be used to evaluate its suitability for various applications.
The ASTM E23 standard includes several different test methods, each tailored to specific types of metallic materials and testing conditions. These methods specify the type of specimen to be used, the dimensions of the notch, the test temperature, and the impact velocity, among other parameters. The standard also provides guidelines for specimen preparation and testing procedures to ensure accurate and reliable results.
One common application of the ASTM E23 standard is in the testing of steels, where impact toughness is an important material property. For example, the Charpy V-notch test, specified in ASTM E23 method A, is widely used to assess the impact resistance of steel. This test involves striking a notched specimen with a pendulum and measuring the energy absorbed as the specimen breaks. The result is reported as the impact energy, in joules, required to fracture the specimen.
By following the guidelines outlined in the ASTM E23 standard, manufacturers and researchers can obtain consistent and comparable results when testing the impact properties of metallic materials. These results can then be used to evaluate material performance, optimize material selection, and ensure the safety and reliability of various metal components and structures in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and manufacturing.
ASTM A370 – Standard Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
The ASTM A370 standard specifies the test methods and definitions for mechanical testing of steel products. This standard is widely used in the steel industry to ensure the quality and performance of steel materials. It provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for conducting various mechanical tests, including tension, bend, elongation, and impact tests.
One of the key aspects of the ASTM A370 standard is the Charpy impact test, which measures the resistance of a material to sudden impact or shock. This test is particularly important in assessing the toughness and ductility of steel products, as it simulates real-world scenarios where materials may experience sudden, high-stress impact loads. The ASTM A370 standard provides detailed procedures for conducting Charpy impact tests, including the preparation of specimens, the configuration of the test apparatus, and the interpretation of results.
In addition to the Charpy impact test, the ASTM A370 standard also covers other mechanical tests such as tension and bend tests. These tests evaluate the strength, elasticity, and flexibility of steel materials, ensuring that they meet the required specifications and performance standards. The standard specifies the equipment, procedures, and calculations for conducting these tests, allowing for accurate and reliable results.
Overall, the ASTM A370 standard plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and performance of steel products. By providing standardized test methods and definitions, it allows for consistent assessment and comparison of different steel materials. Manufacturers and users of steel products can rely on the ASTM A370 standard to validate the mechanical properties of steel materials, ensuring their suitability for various applications and environments.
ASTM D6110 – Standard Test Methods for Determining the Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched Specimens of Plastics
The ASTM D6110 standard test methods provide a standardized procedure for determining the Charpy impact resistance of notched specimens of plastics. This testing method is widely used in the plastics industry to evaluate the toughness and durability of plastic materials under impact loading conditions. The test measures the amount of energy absorbed by the specimen during a single, sharp blow from a pendulum hammer.
The Charpy impact test is commonly used to assess the performance of plastic materials, as it simulates real-world situations where materials may experience sudden impact or shock loading. The results of the test can be used to compare the impact resistance of different plastic materials, and to evaluate the effect of changes in material composition or processing conditions on the material’s impact behavior.
The ASTM D6110 standard describes two different test methods for conducting the Charpy impact test on notched specimens of plastics: Method A, which uses a simple supported beam configuration, and Method B, which uses a cantilever beam configuration. Both methods involve striking a notched specimen with a pendulum hammer, and measuring the energy absorbed by the specimen as it fractures. The difference between the two methods lies in the configuration of the specimen and the positioning of the notch.
The test results obtained using the ASTM D6110 standard can be used to make informed decisions about the suitability of a plastic material for specific applications, such as in automotive, construction, or packaging industries. By evaluating the impact resistance of plastics, manufacturers can ensure that their products are able to withstand the forces they may encounter in real-world scenarios, and meet the required safety and performance standards.
ASTM E208 – Standard Test Method for Conducting Drop-Weight Test to Determine Nil-Ductility Transition Temperature of Ferritic Steels
The ASTM E208 standard test method provides guidelines for conducting a drop-weight test to determine the nil-ductility transition temperature (NDTT) of ferritic steels. The NDTT is an important parameter in evaluating the toughness and fracture behavior of these steels, especially under low temperatures. This test method is applicable to a wide range of ferritic steels, including those used in pressure vessels, piping, and structural components.
The drop-weight test involves subjecting a notched specimen to an impact load at progressively lower temperatures until it fractures. The test measures the energy absorbed by the specimen and the corresponding temperature at which the fracture occurs. This data is then used to determine the NDTT, which represents the temperature below which the ferritic steel loses its ability to deform plastically and becomes susceptible to brittle fracture.
To conduct the drop-weight test according to ASTM E208, a pendulum-type impact testing machine is typically used. The specimen is carefully prepared with a notch according to specific requirements outlined in the standard. The test is carried out by progressively cooling the specimen and subjecting it to an impact load until fracture occurs. The absorbed energy and temperature at fracture are measured, and the NDTT is determined using mathematical equations provided in the standard.
ASTM E208 provides detailed guidance on the necessary equipment, specimen preparation, test procedure, and data analysis for conducting the drop-weight test. It also includes provisions for verifying the accuracy and precision of the test results. Compliance with this standard ensures that the test is conducted consistently and reliably, allowing for accurate determination of the NDTT for ferritic steels.