Are you ready to embark on an exciting journey to explore the world’s richest and most biologically diverse areas? In this webquest, you will uncover the answers to some of the most intriguing questions about biodiversity hotspots. Prepare to dive into the depths of these unique regions and discover the incredible wealth of species that call them home.
Biodiversity hotspots are areas that support an exceptional concentration of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. These hotspots are not only a haven for wildlife, but they also play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our planet’s ecosystems. By protecting and conserving these areas, we can safeguard the incredible variety of life on Earth.
In this webquest, you will navigate through a series of questions and challenges to unlock the answers to the biodiversity hotspots puzzle. From understanding the criteria that define a hotspot to exploring the different regions that make up these biodiversity hotspots, you will gain a deep understanding of the importance of preserving these unique ecosystems. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready for an adventure that will open your eyes to the wonders of our planet’s most precious natural treasures!
Biodiversity Hotspots Webquest Answer Key
In this answer key, we will explore the concept of biodiversity hotspots and their importance in conservation efforts. Biodiversity hotspots refer to areas that contain a high level of species richness and are also under threat from human activities. These hotspots are crucial for the preservation of global biodiversity and play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance.
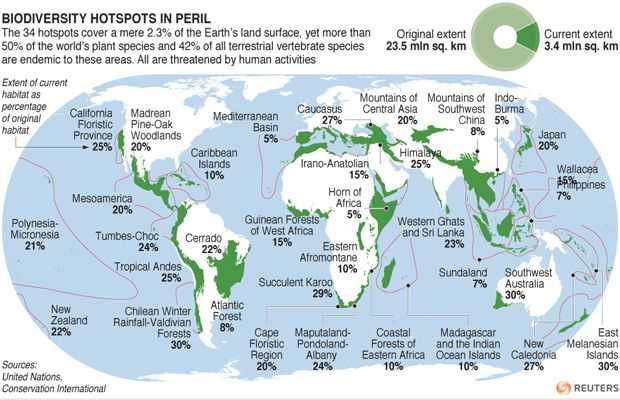
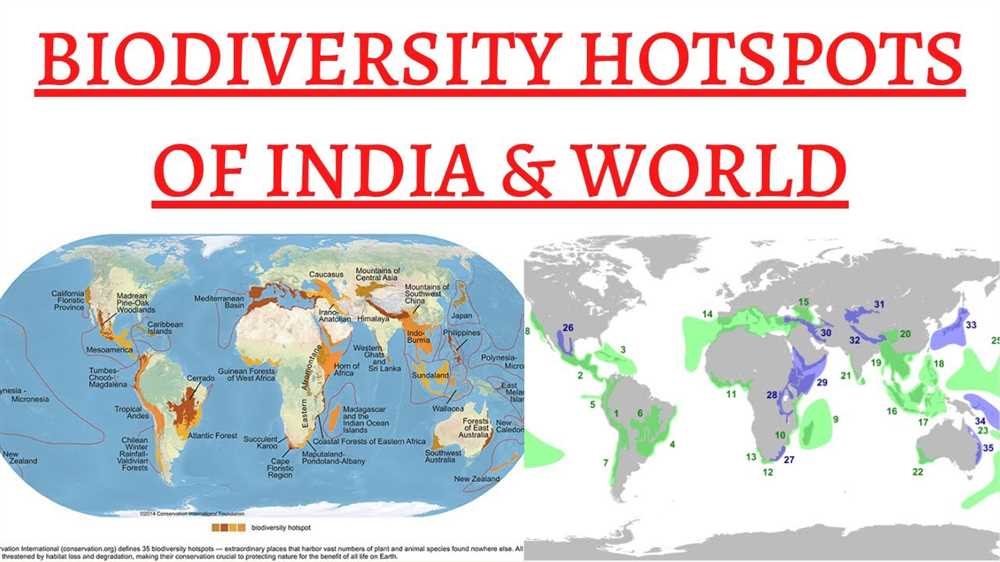
One of the key questions in the webquest asked about the number of biodiversity hotspots worldwide. The answer is that there are currently 36 recognized biodiversity hotspots around the world. These hotspots are spread across various continents, including areas in South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. Each hotspot has its unique set of species, many of which are found nowhere else on the planet.
The webquest also asked about the criteria used to determine a biodiversity hotspot. The answer lies in two main factors: the number of endemic species and the degree of threat to the ecosystems in that area. Endemic species are those that are found exclusively in a specific region or habitat. Threats to ecosystems can come in the form of habitat destruction, climate change, or invasive species. By identifying areas with high species richness and high levels of threat, conservation organizations can prioritize efforts to protect these hotspots and prevent the loss of biodiversity.
Another important question in the webquest focused on the benefits of protecting biodiversity hotspots. The answer is that preserving these hotspots can have far-reaching benefits for both humans and the environment. Biodiversity hotspots act as natural reservoirs of genetic diversity, which can be utilized in various fields such as medicine and agriculture. Additionally, these hotspots play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem services like water purification, pollination, and climate regulation. By safeguarding biodiversity hotspots, we can ensure the continued provision of these essential services for future generations.
In conclusion, biodiversity hotspots are critical areas for conservation efforts due to their high species richness and level of threat. By identifying, protecting, and restoring these hotspots, we can preserve global biodiversity and ensure the sustainable functioning of our ecosystems.
What are Biodiversity Hotspots?
Biodiversity hotspots are regions that exhibit exceptional levels of species richness and endemism. These hotspots are characterized by a high number of plant and animal species that are unique to the area and cannot be found anywhere else in the world. The concept of biodiversity hotspots was first introduced by Norman Myers, an environmentalist and conservation biologist, in 1988. He identified these hotspots as areas that are not only biologically diverse, but also under threat of significant habitat destruction and loss.
In order to qualify as a biodiversity hotspot, an area must meet certain criteria. These criteria include having at least 1,500 endemic plant species, which means species that are found only in that particular area, and having lost at least 70% of its original habitat. Additionally, these areas must be under significant threat, such as deforestation, urbanization, or climate change, to qualify as a hotspot.
Currently, there are 36 recognized biodiversity hotspots around the world. These hotspots cover only 2.4% of the Earth’s land surface but are home to more than half of the world’s plant species and almost 43% of all terrestrial vertebrate species. These regions are of great importance for global biodiversity conservation because they contain species that are not found anywhere else in the world and are at risk of extinction due to human activities. Protecting these hotspots is crucial in order to preserve Earth’s unique and irreplaceable biodiversity.
The Importance of Biodiversity Hotspots
The concept of biodiversity hotspots is crucial for our understanding and conservation of Earth’s rich and diverse ecosystems. Biodiversity hotspots are specific regions that are characterized by an exceptional concentration of endemic species and high levels of habitat loss. These hotspots are like treasure troves of biodiversity, holding a significant portion of the world’s plant and animal species.
One of the main reasons why biodiversity hotspots are important is that they serve as home to numerous species that are found nowhere else on the planet. These endemic species are often highly specialized and adapted to the unique conditions of their local habitats. Preserving these biodiversity hotspots is essential for ensuring the continued existence of these rare and unique species. By protecting these habitats, we are effectively safeguarding the genetic diversity and ecological balance of our planet.
Moreover, biodiversity hotspots play a crucial role in providing various ecosystem services that are vital for human well-being. These services include the provision of clean air and water, regulation of climate, pollination of crops, nutrient cycling, and the development of new medicines. Biodiversity hotspots contribute immensely to the overall resilience and stability of ecosystems, making them more resistant to disturbances such as diseases, invasive species, and climate change.
Unfortunately, many biodiversity hotspots are under threat due to human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, agriculture, and climate change. The rapid loss of these hotspots not only leads to the extinction of numerous species but also disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems and threatens the stability of the planet. Therefore, it is crucial that we take immediate action to conserve and protect these biodiversity hotspots, both for the sake of the unique species they harbor and for the well-being of future generations.
Classification of Biodiversity Hotspots
The classification of biodiversity hotspots is based on certain criteria that determine the level of species richness and endemism within a specific geographic area. These criteria include the number of endemic plant species, the degree of threat faced by the ecosystem, and the level of habitat loss that has occurred. Based on these factors, biodiversity hotspots are identified and categorized for conservation efforts.
One key criterion for classifying biodiversity hotspots is the presence of a large number of endemic plant species. Endemism refers to the occurrence of a species exclusively within a specific geographic area. Hotspots with a high number of endemic plant species are considered to have a unique and irreplaceable natural heritage that needs to be protected. Endemic plant species are often more susceptible to habitat loss and other threats, making their conservation a priority.
Another important factor in classifying biodiversity hotspots is the degree of threat faced by the ecosystem. This includes factors such as deforestation, invasive species, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation of resources. Hotspots with a higher level of threat are deemed to be in urgent need of conservation efforts in order to prevent further biodiversity loss. The identification of these high-threat hotspots helps prioritize conservation actions and allocate resources effectively.
Habitat loss, another crucial criterion, is assessed by looking at the extent of natural habitat that has been transformed or destroyed within a hotspot. Habitats that have experienced significant loss are considered to be under greater threat and are prioritized for conservation efforts. The extent of habitat loss also indicates the level of human impact on the ecosystem and highlights the need for sustainable land use practices.
In conclusion, the classification of biodiversity hotspots takes into account the presence of endemic plant species, the degree of threat, and the level of habitat loss. By identifying and categorizing these hotspots, conservation efforts can be focused on protecting valuable and vulnerable ecosystems, preserving biodiversity, and promoting sustainable practices for the benefit of both wildlife and human populations.
Criteria for Biodiversity Hotspots
There are several criteria used to identify biodiversity hotspots around the world. These criteria help us understand which regions are most important for conservation efforts and have the highest concentration of unique and threatened species.
Species richness
One of the main criteria for designating a region as a biodiversity hotspot is the presence of high species richness. This means that the region is home to a large number of different species. The more species that are found in an area, the more important it is for biodiversity conservation.
Endemism
Endemism is another important factor in identifying biodiversity hotspots. Endemic species are those that are found nowhere else in the world. Regions with high levels of endemism are considered to be of high conservation value because they represent unique evolutionary lineages and are often more susceptible to extinction.
Threatened species
The presence of threatened species is also taken into account when identifying biodiversity hotspots. These are species that are at risk of extinction. Regions that have a high number of threatened species are considered to be priority areas for conservation efforts.
Habitat loss
Habitat loss is a significant threat to biodiversity worldwide. Areas that have experienced significant habitat loss are often designated as biodiversity hotspots. This is because these regions have lost a large portion of their natural habitats and are in urgent need of conservation interventions to protect what remains.
Human impact
The impact of human activities on biodiversity is an important consideration in identifying hotspots. Areas that have been heavily impacted by human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and overexploitation, are often prioritized for conservation efforts to mitigate further damage and protect the remaining biodiversity.
Overall, the criteria for biodiversity hotspots take into account factors such as species richness, endemism, threatened species, habitat loss, and human impact. By identifying and protecting these regions, we can ensure the preservation of unique and irreplaceable biodiversity for future generations.
Biodiversity Hotspots Around the World
Biodiversity hotspots are regions around the world that are characterized by exceptional levels of biodiversity but are also under threat. These areas are considered to be some of the most critical places for conservation efforts due to their unique ecosystems and high concentration of endemic species. There are currently 36 biodiversity hotspots identified globally, each with its own distinct characteristics and conservation challenges.
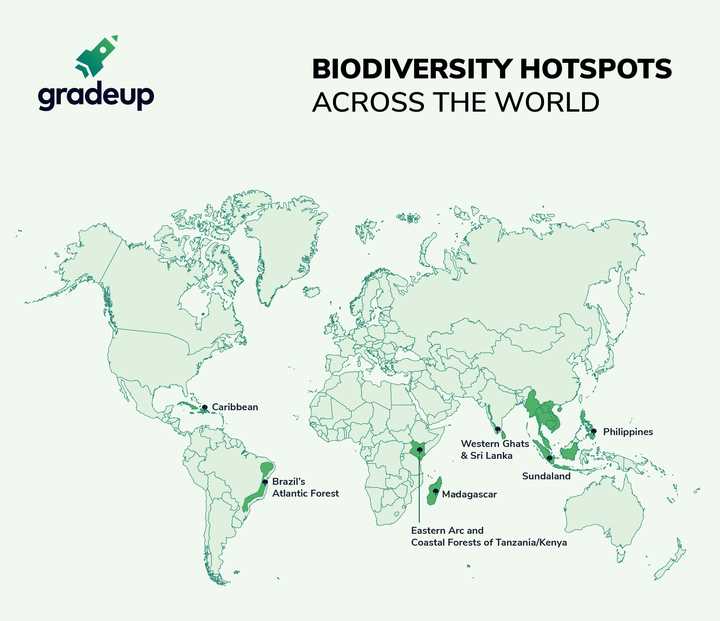
One example of a biodiversity hotspot is the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka hotspot, located in southwestern India and Sri Lanka. This hotspot is known for its rich biodiversity, including a large number of endemic species such as the endangered lion-tailed macaque and the Nilgiri tahr. However, this hotspot is also under threat due to deforestation, pollution, and invasive species, making conservation efforts crucial for its survival.
The Atlantic Forest hotspot in Brazil is another example of a biodiversity hotspot. This hotspot is home to an incredible variety of plant and animal species, including the endangered golden-headed lion tamarin and the iconic jaguar. However, extensive deforestation for agriculture and urbanization has greatly reduced the extent of the Atlantic Forest, threatening many of its unique species. Conservation organizations are working to protect and restore this hotspot to ensure the survival of its biodiversity.
Key Points:
- Biodiversity hotspots are regions with high levels of biodiversity that are under threat.
- There are currently 36 biodiversity hotspots identified globally.
- Each hotspot has its own unique characteristics and conservation challenges.
- The Western Ghats and Sri Lanka hotspot and the Atlantic Forest hotspot are examples of biodiversity hotspots.
- Conservation efforts are necessary to protect the unique species and ecosystems found in these hotspots.
In conclusion, biodiversity hotspots around the world are incredibly important areas for conservation due to their exceptional levels of biodiversity and the threats they face. Protecting these hotspots is crucial for the survival of countless species and the preservation of unique ecosystems. By raising awareness and supporting conservation efforts, we can work towards ensuring that these biodiversity hotspots continue to thrive and contribute to the overall health of our planet.
Threats to Biodiversity Hotspots
Biodiversity hotspots are areas that are rich in biological diversity and contain a large number of unique species. They are considered to be some of the most important areas for conservation efforts. However, these hotspots are facing numerous threats that pose a significant risk to their biodiversity.
One major threat to biodiversity hotspots is habitat loss. Human activities such as deforestation, agriculture, and urban expansion are rapidly destroying natural habitats, leading to the displacement and extinction of many species. This loss of habitat has a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem, as species rely on each other for survival and the disruption of one species can have far-reaching consequences.
Another threat to biodiversity hotspots is climate change. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are altering ecosystems and disrupting the life cycles of many species. This can lead to shifts in species distributions, decreased reproductive success, and increased susceptibility to diseases. The impacts of climate change are particularly pronounced in fragile ecosystems such as coral reefs and polar regions.
Illegal wildlife trade is another major threat to biodiversity hotspots. Many unique and endangered species are targeted for their valuable body parts, such as ivory, fur, or feathers. This trade not only drives species towards extinction but also fuels organized crime and threatens the stability of local communities. Efforts are being made to combat this issue through increased law enforcement and educational campaigns.
In conclusion, biodiversity hotspots are facing a range of threats that jeopardize their rich biological diversity. These threats include habitat loss, climate change, and illegal wildlife trade. It is crucial to raise awareness about these issues and implement effective conservation measures to protect these valuable ecosystems and the species they support.