
In the study of biology and ecology, understanding the different biomes of our planet is crucial. Biomes are large regions characterized by a specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. Exploring these unique environments provides valuable insights into the Earth’s diversity and helps us understand the delicate balance of life on our planet.
One way to help students grasp the concept of biomes is through the use of biomes worksheets. These worksheets typically include questions and activities that require students to identify and describe various biomes, as well as the adaptations of plants and animals living in those biomes. By completing these worksheets, students can develop a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of organisms and their environments.
The answer key for biomes worksheets serves as a valuable tool for both students and educators. It allows students to self-assess their understanding and correct any misconceptions they may have. Furthermore, the answer key can guide teachers in facilitating classroom discussions and addressing common challenges or misconceptions that students may encounter while studying biomes.
By providing a comprehensive biomes worksheet answer key, educators can ensure that students have the necessary support and resources to fully grasp the complex concepts associated with the Earth’s diverse biomes. Ultimately, this understanding can deepen students’ appreciation for the beauty and intricacy of our planet’s ecosystems, as well as their role in preserving and protecting them for future generations.
Biomes Worksheet Answer Key
In this article, we will provide the answer key to the Biomes Worksheet. This worksheet is designed to test your knowledge and understanding of different biomes around the world. It includes questions about the characteristics, flora, and fauna of each biome, as well as their importance to the environment. By using this answer key, you can check your answers and assess your understanding of the material.
Answer Key:
- Question 1: What is a biome?
- Question 2: Name three major types of biomes.
- Question 3: What are the characteristics of a desert biome?
- Question 4: What are the characteristics of a forest biome?
- Question 5: What are the characteristics of a grassland biome?
- Question 6: Why are biomes important?
Answer: A biome is a large ecological area characterized by its distinct climate, vegetation, and animal life.
Answer: The three major types of biomes are deserts, forests, and grasslands.
Answer: Desert biomes are characterized by low rainfall, high temperatures, and sparse vegetation.
Answer: Forest biomes are characterized by high rainfall, dense vegetation, and a wide variety of animal species.
Answer: Grassland biomes are characterized by moderate rainfall, grasses as the dominant vegetation, and a mix of grazing animals.
Answer: Biomes are important because they provide habitats for plants and animals, regulate climate, and contribute to the overall health of the planet.
By reviewing and understanding the answers to these questions, you can enhance your knowledge and comprehension of different biomes. It is important to remember that each biome has its own unique characteristics and plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the Earth’s ecosystems.
What Are Biomes?
Biomes refer to large ecological areas that are characterized by distinct climate, vegetation, and animal species. They are essentially different types of ecosystems that exist on Earth. Biomes are determined by factors such as temperature, precipitation, and soil type, which influence the types of plants and animals that can survive in a particular area.
There are several major types of biomes, including forests, grasslands, deserts, tundra, and aquatic biomes. Each biome has its own unique set of characteristics and supports a specific range of plant and animal life. For example, forests are characterized by dense trees and vegetation and are home to a variety of animal species, while deserts have sparse vegetation and are adapted to arid conditions.
Forest Biomes
Forest biomes are one of the most diverse and abundant biomes on Earth. They can be classified into different types, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests. Tropical rainforests, such as the Amazon rainforest, are known for their high biodiversity and dense vegetation, while temperate forests, like those found in North America and Europe, experience distinct seasons. Boreal forests, also known as taiga, are characterized by coniferous trees and are found in high-latitude regions.
Grassland Biomes
Grassland biomes are characterized by vast areas of grasses and few or scattered trees. They can be further divided into tropical grasslands, also known as savannas, and temperate grasslands. Savannas are found in regions with a warm climate and a distinct dry and wet season, while temperate grasslands, such as the prairies in North America, experience harsh winters and hot summers.
Desert Biomes
Desert biomes are extremely dry and receive very little precipitation. They can be hot or cold, depending on their location. Deserts are characterized by sparse vegetation, such as cacti and succulents, and have adapted to survive in arid conditions. Examples of deserts include the Sahara Desert in Africa and the Mojave Desert in North America.
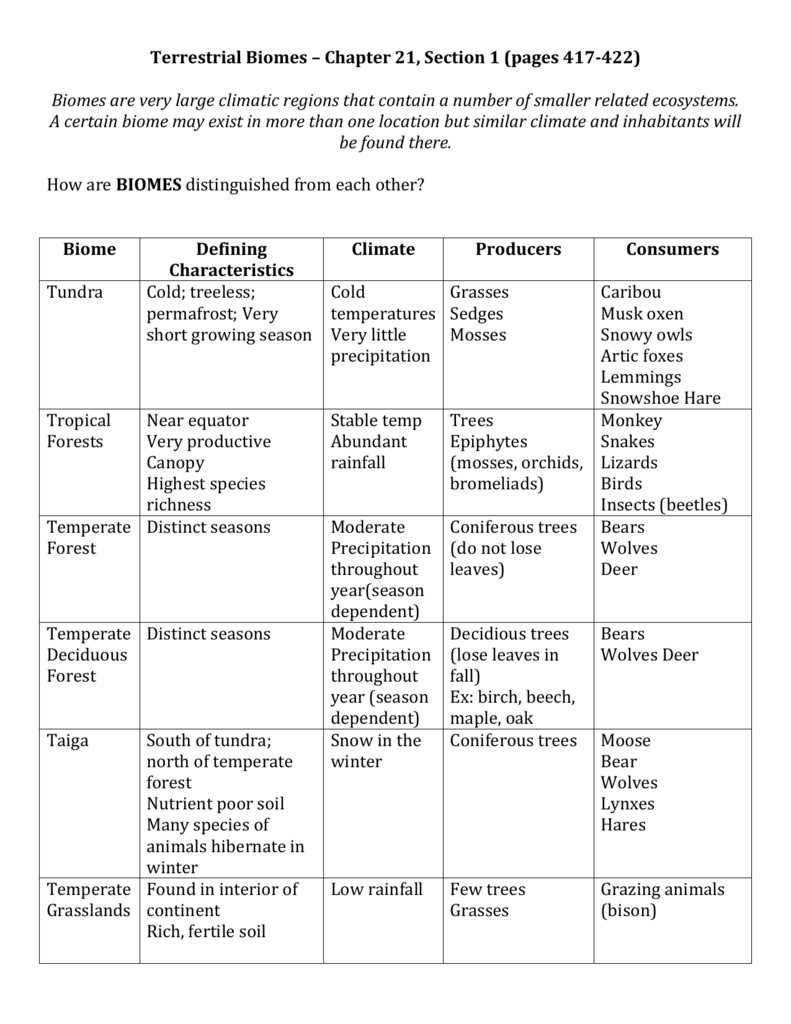
Tundra Biomes
Tundra biomes are found in high-latitude regions, such as the Arctic and Antarctica. They are extremely cold and have a short growing season. Tundra vegetation consists of low-growing plants, lichens, and mosses, and animal life is adapted to survive in the harsh conditions. The tundra biome plays a crucial role in regulating global climate and is home to unique species, such as the polar bear and Arctic fox.
Aquatic Biomes
Aquatic biomes encompass both freshwater and marine ecosystems. Freshwater biomes include rivers, lakes, and wetlands, while marine biomes include oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries. These biomes support a diverse array of aquatic organisms, including fish, marine mammals, coral, and algae. They are influenced by factors such as temperature, salinity, and nutrient availability.
Why Are Biomes Important?
Biomes are essential for maintaining the balance of our planet’s ecosystems. They play a crucial role in supporting a wide range of plant and animal species, ensuring biodiversity and ecological stability. Biomes provide habitats for countless organisms, allowing them to thrive and contribute to the overall health of the planet.
Biodiversity: Biomes are home to a vast array of plant and animal species. Each biome has its unique characteristics, which are adapted to specific environmental conditions. This diversity of species is vital for the overall health of the planet as it ensures that various ecological roles are filled and ecosystems remain stable. The loss of a biome can lead to the extinction of numerous species and disrupt the delicate balance of nature.
Climate Regulation: Biomes play a significant role in regulating global climate patterns. Forest biomes, such as tropical rainforests, act as carbon sinks, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This helps to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas levels. Additionally, biomes influence local weather conditions, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns, through their unique vegetation and geographic features.
Resource Availability: Biomes provide valuable resources for human societies. Forests, for example, are a source of timber, while grasslands support agriculture and provide grazing land for livestock. Freshwater biomes supply water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. The sustainable management of these resources is crucial to ensure their availability for future generations.
Research and Education: Biomes are living laboratories for scientists to study and understand the complex interactions between organisms and their environment. Research conducted in biomes contributes to scientific knowledge and helps inform conservation efforts. Biomes also offer educational opportunities to learn about the diversity and interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Types of Biomes
A biome is a large geographical area characterized by specific climate conditions, plant and animal life, and ecosystems. There are several different types of biomes found around the world, each with its own unique characteristics.
1. Rainforest: Rainforests are found in tropical regions and receive high amounts of rainfall throughout the year. They are known for their dense vegetation, diverse animal species, and tall canopy trees. Some of the world’s most iconic rainforests are located in the Amazon basin and the Congo basin.
2. Desert: Deserts are arid regions characterized by extremely low rainfall and high temperatures. They typically have sparse vegetation and are home to specialized desert-adapted plants and animals. Examples of deserts include the Sahara Desert in Africa and the Mojave Desert in the United States.
3. Tundra: Tundra is a cold and treeless biome found in the Arctic and some high-altitude regions. It is characterized by low temperatures, permafrost, and short, cool summers. Vegetation in the tundra consists mainly of mosses, lichens, and small shrubs. Animals such as reindeer and Arctic foxes are well-adapted to survive in this harsh environment.
4. Grassland: Grasslands are characterized by vast expanses of grasses and herbaceous plants, with few trees. They are found in both tropical and temperate regions and can be further classified as savannas, prairies, or steppes depending on their specific characteristics. Grasslands are home to a diverse range of animal species, including grazing mammals such as bison and zebra.
5. Forest: Forest biomes are characterized by dense tree coverage and are found in various climate zones around the world. Different types of forests include temperate forests, boreal forests, and tropical forests. Forests support a wide array of plant and animal species, and they play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate.
6. Marine: The marine biome includes all the bodies of water on Earth, such as oceans, seas, and coral reefs. It is home to an incredibly diverse range of marine species, from large whales and sharks to tiny plankton. Marine biomes are essential for maintaining the planet’s overall ecosystem balance and provide numerous resources for human societies.
These are just a few examples of the different types of biomes that exist worldwide. Each biome has its own unique characteristics and plays a vital role in the overall health of our planet’s ecosystems.
Tundra Biome
The tundra biome is one of the coldest and harshest biomes on Earth. It is characterized by extremely cold temperatures, strong winds, and a lack of trees. The word “tundra” comes from the Finnish word for barren or treeless land. This biome is found in the northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia.
The tundra biome is known for its unique and fragile ecosystem. The soil in the tundra is permanently frozen, which is called permafrost. This makes it difficult for plants to establish deep root systems, resulting in a relatively low plant diversity. However, the tundra is home to a variety of specialized plant species, such as mosses, lichens, and low-growing shrubs, that are adapted to the cold and harsh conditions.
The animal life in the tundra biome is also well adapted to the extreme climate. Animals such as arctic foxes, caribou, and polar bears have thick fur and special adaptations that allow them to survive in the cold. The tundra is an important breeding ground for many bird species, including Arctic terns and snow buntings. In the summer, migratory birds fly to the tundra to take advantage of the abundance of food and nesting opportunities.
The tundra biome is facing significant challenges due to climate change. Rising temperatures and melting permafrost are causing changes to the ecosystem, including shifts in plant and animal populations. It is crucial to protect and conserve this unique biome to ensure the survival of its delicate ecosystem and the species that depend on it.
Taiga Biome
The taiga biome, also known as the boreal forest, is the largest land biome on Earth. It spans across the northern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia, covering an area of approximately 17 million square kilometers. The taiga biome is characterized by its cold and long winters, as well as its short and cool summers. It experiences a wide range of temperatures, from -65 degrees Celsius in the winter to 30 degrees Celsius in the summer.
The taiga biome is dominated by coniferous trees, such as pine, spruce, and fir. These trees have adapted to the harsh environment by having needle-like leaves that reduce water loss and can withstand the weight of heavy snowfall. The taiga biome also has a relatively low biodiversity compared to other biomes, with fewer species of plants and animals.
Despite its harsh conditions, the taiga biome is home to a variety of wildlife. Many species, such as moose, wolves, and bears, have adapted to survive in the cold climate and are well suited to hunting and foraging in the taiga. The taiga biome also serves as an important habitat for migratory birds and provides nesting grounds for many species.
Key Features of the Taiga Biome:
- Cold and long winters
- Short and cool summers
- Dominated by coniferous trees
- Low biodiversity
- Home to wildlife such as moose, wolves, and bears
- Important habitat for migratory birds
In conclusion, the taiga biome is a unique and challenging environment characterized by its cold climate and coniferous forests. Despite its harsh conditions, it supports a diverse range of wildlife and plays a crucial role in the global ecosystem.
Grassland Biome
The grassland biome, also known as prairies or savannas, is characterized by vast stretches of grasses and wildflowers, with few or no trees. This biome is found on every continent except Antarctica and covers about 25% of the Earth’s land surface. Grasslands are typically located in the interior regions of continents, away from large bodies of water.
One key feature of grasslands is their rich and fertile soil, which is perfect for growing crops. As a result, many grassland areas have been converted into agricultural lands for farming. These grasslands are essential for food production and play a crucial role in providing food security for many countries around the world.
Climate: Grasslands have a unique climate with hot summers and cold winters. They receive moderate rainfall, typically between 25-75 cm per year. The lack of trees allows for strong winds to blow across the grasslands, making the region prone to wildfires.
Plant life: Grasses are the dominant plant species in the grassland biome. They have adapted to the frequent fires and grazing by large herbivores. Some common grass species include buffalo grass, blue grama, and big bluestem. Wildflowers also thrive in grasslands, adding vibrant colors to the landscape.
Animal life: Grasslands are home to a diverse array of animal species. Large herbivores such as bison, wildebeest, and gazelles graze on the grasses, while predators like lions, wolves, and coyotes hunt for food. Birds such as hawks and eagles soar above the grasslands to hunt for small mammals and insects. Insects, reptiles, and rodents also make up a significant portion of the grassland’s animal population.
Environmental threats: Grassland biomes face several environmental threats, including overgrazing, habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species. Human activities such as agriculture, urban development, and mining have contributed to the degradation of grassland ecosystems. It is crucial to implement sustainable land management practices to ensure the preservation of these important biomes.
Conclusion: Grasslands are vital ecosystems that provide habitat for a variety of plant and animal species. They also offer valuable resources for human societies, such as food production and grazing lands. Protecting and conserving grassland biomes is essential for maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the sustainability of our planet.