If you are studying biomes and need a comprehensive resource to test your knowledge, a biomes worksheet is an invaluable tool. This worksheet provides a series of questions and activities that cover various biomes, allowing you to assess your understanding of key concepts and characteristics. In order to check your answers and ensure accuracy, an answer key is provided in a PDF format.
The biomes worksheet PDF answer key serves as a guide to help you review your responses and compare them with the correct answers. It allows you to evaluate your understanding of the different biomes, their climates, flora and fauna, and the various adaptations of organisms within each biome. This answer key can provide additional explanations and insights into the topics covered in the worksheet.
By utilizing the biomes worksheet PDF answer key, you can identify any areas where you may need further study or review. It allows you to gauge your progress and reinforce your learning by providing you with immediate feedback on your answers. Whether you are a student preparing for an exam or a teacher looking for a resource to assess your students’ comprehension, the biomes worksheet answer key can be a valuable tool for effective learning and evaluation.
Biomes Worksheet PDF Answer Key
A biomes worksheet PDF answer key is a valuable resource for both students and teachers. This answer key provides the correct answers to the questions and activities in the biomes worksheet, allowing students to check their work and learn from their mistakes. It also helps teachers to quickly assess the understanding and progress of their students.
The biomes worksheet PDF answer key typically includes answers to questions about the different types of biomes, their characteristics, and the plants and animals that inhabit them. It may also provide explanations and additional information to help students understand the concepts better. With this answer key, students can compare their answers to the correct ones, identify any misconceptions or errors, and make corrections as needed.
Key topics covered in a biomes worksheet PDF answer key:
- The definition and characteristics of biomes
- The major biomes of the world, such as tundra, taiga, grassland, desert, and tropical rainforest
- The factors that determine the distribution of biomes, including climate, latitude, and altitude
- The adaptations of plants and animals to different biomes
- The importance of biodiversity and the threats to biomes
Using a biomes worksheet PDF answer key can improve students’ understanding of biomes and their associated concepts. By comparing their answers to the correct ones, students can identify areas where they need to improve and seek further clarification if necessary. This answer key also allows teachers to provide feedback and guidance to their students, helping them to develop a deeper understanding of the topic.
In conclusion, a biomes worksheet PDF answer key is an essential resource for students and teachers studying biomes. It provides the correct answers to the questions and activities in the worksheet, allowing students to check their work and learn from their mistakes. This answer key also helps teachers assess their students’ understanding and guide them in their learning journey.
What are Biomes?
Biomes are distinct regions of the Earth that are characterized by their specific climates, vegetation, and animal life. They are large-scale ecological communities that cover vast areas of land or water. Biomes are determined by factors such as temperature, precipitation, altitude, and soil composition, which influence the types of plants and animals that can thrive in that particular environment.
There are several major types of biomes found on Earth, including deserts, grasslands, forests, tundra, and aquatic ecosystems such as oceans, rivers, and lakes. Each biome has its own unique set of characteristics and species adapted to the specific conditions found within that region. For example, deserts are characterized by low rainfall, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation, while forests are characterized by high levels of rainfall, moderate temperatures, and dense vegetation.
Within each biome, there are often distinct ecosystems with their own specific organisms and interactions. For example, within a forest biome, there may be different types of forests such as deciduous forests or coniferous forests, each with their own set of plant and animal species. Biomes and ecosystems play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the Earth’s ecosystems and providing habitats for a wide variety of species.
Key characteristics of biomes include:
- Climate: Temperature and precipitation patterns
- Vegetation: Types of plants that dominate the area
- Animal life: Types of animals that inhabit the biome
- Soil composition: The types of soil found in the biome
- Geographic location: Biomes are found in specific regions of the Earth
Understanding biomes is important for understanding the Earth’s biodiversity, as well as for conservation and ecological restoration efforts. By studying and preserving biomes, scientists can gain insights into the complex interactions between organisms and their environment and work towards maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Importance of Biomes
Biomes play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting a diverse range of plant and animal life. These distinct ecological regions are characterized by their unique climate, soil, and vegetation, and each biome has a specific set of organisms that have adapted to survive and thrive in its conditions.
One of the key reasons why biomes are important is their contribution to the Earth’s overall biodiversity. Biomes provide a habitat for countless species, from microscopic organisms to large mammals, and serve as interconnected ecosystems where different organisms rely on each other for food, shelter, and other resources. The preservation and conservation of biomes are essential to ensure the survival of these species and protect the delicate balance of nature.
Biomes also play a vital role in maintaining the Earth’s climate and regulating the water cycle. Forests, for example, act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to reduce the effects of climate change. Additionally, biomes such as wetlands and mangroves act as natural water filters, purifying and regulating water supplies.
Understanding the various biomes and their characteristics is crucial for scientists and researchers in fields such as ecology, biology, and environmental science. Studying biomes helps us gain insights into how different organisms adapt to their environments, how they interact with each other, and how they respond to environmental changes. This knowledge is invaluable in developing strategies for sustainable resource management, conservation efforts, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
In conclusion, biomes are of utmost importance for the functioning of our planet. They provide habitats for diverse species, regulate climate and water cycles, and serve as valuable sources of knowledge for scientific research. Protecting and preserving biomes is not only essential for the survival of countless organisms but also for the overall health and sustainability of our planet.
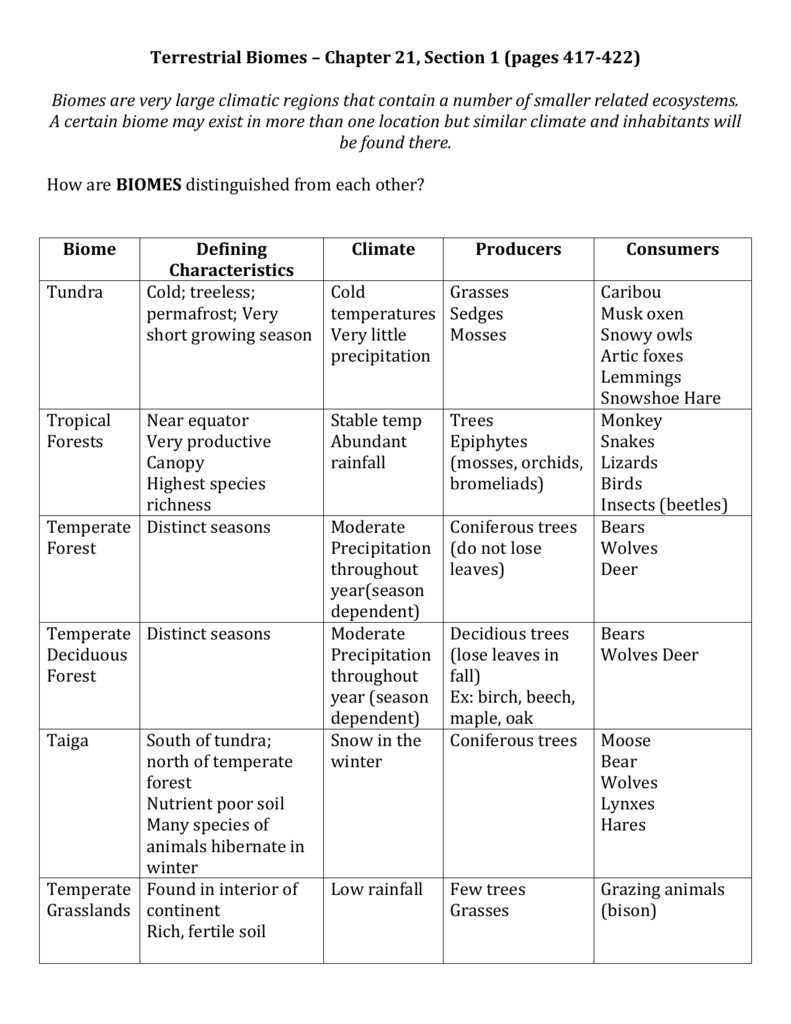
Types of Biomes
Biomes are large geographic areas that are characterized by their unique climate, flora, and fauna. There are several different types of biomes found on Earth, each with its own distinct features. These biomes include:
- Tropical Rainforest: This biome is characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year. It is home to an incredible diversity of plant and animal species, including colorful birds, monkeys, and orchids.
- Desert: Deserts are dry and arid biomes, with little to no rainfall. They are known for their extreme temperatures and lack of vegetation. However, deserts are home to unique species that have adapted to survive in these harsh conditions, such as cacti and camels.
- Tundra: Tundra biomes are found in the cold regions of the world, such as the Arctic and Antarctic. They have low temperatures and very short growing seasons. Tundra vegetation mainly consists of mosses, lichens, and small shrubs. Animals in the tundra, such as polar bears and reindeer, have thick fur and other adaptations to survive the cold.
- Grassland: Grasslands are characterized by vast expanses of grasses, with few or no trees. They are found in both tropical and temperate regions and have a moderate amount of rainfall. Animals commonly found in grasslands include bison, zebras, and prairie dogs.
- Temperate Forest: Temperate forests have moderate temperatures and a well-defined four-season cycle. They are populated by a variety of deciduous trees, such as oak and maple. Animals in temperate forests include deer, squirrels, and bears.
These are just a few examples of the different types of biomes found on Earth. Each biome has its own unique climate, vegetation, and animal life, making them fascinating and important ecosystems to study and protect.
Desert Biome

The desert biome can be described as a harsh and dry environment with extreme temperatures and limited rainfall. It is characterized by its arid climate, sparse vegetation, and unique adaptations of plants and animals to survive in such conditions.
In the desert biome, temperatures can reach extreme highs during the day and drop significantly at night. This drastic temperature fluctuation poses a challenge for plants and animals to adapt and thrive. Many plants in the desert biome have evolved to have specialized features like deep root systems, small leaves, and thick waxy coatings to conserve water and withstand the arid conditions.
Desert animals also have specific adaptations to survive in this harsh environment. Some animals, like the camel, have developed the ability to store large amounts of water and tolerate high body temperatures. Others, such as the Fennec fox, have large ears that help dissipate heat and regulate their body temperature.
Despite its harsh conditions, the desert biome is home to a surprising variety of life. Many species have developed unique strategies to obtain water and food, such as nocturnal activity to avoid the scorching heat of the day. Some plants and animals in the desert biome even have symbiotic relationships, where they rely on each other for survival.
In conclusion, the desert biome is a challenging yet fascinating ecosystem with its extreme temperatures, limited water supply, and remarkable adaptations of its inhabitants. Exploring and understanding the desert biome can provide valuable insights into the resilience and diversity of life on Earth.
Tropical Rainforest Biome
Tropical rainforests are some of the most diverse and ecologically rich areas on Earth, characterized by high temperatures, heavy precipitation, and lush vegetation. They are found near the equator, in regions such as the Amazon basin in South America, the Congo basin in Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia.
Climate: The climate in tropical rainforests is hot and humid year-round. Average temperatures range from 25 to 30 degrees Celsius (77 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit). The high levels of rainfall, typically more than 2,000 millimeters (78 inches) per year, contribute to the lush vegetation and constant availability of water.
Vegetation: The dense vegetation of the tropical rainforest biome is one of its defining characteristics. It is home to a wide variety of plants, including towering trees that form the canopy layer, smaller trees and shrubs in the understory, and various types of ferns, mosses, and epiphytes. The abundance of plant life provides habitat and food for countless species of animals.
Animal Life: Tropical rainforests are teeming with animal life, from tiny insects to large mammals. They are home to iconic species such as jaguars, toucans, macaws, and monkeys. The incredible biodiversity of the rainforest biome is due to the availability of food and shelter provided by the diverse plant life.
Threats: Unfortunately, tropical rainforests are under threat from deforestation, primarily due to human activities such as logging, mining, and agriculture. This leads to habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity. Conservation efforts and sustainable practices are crucial for preserving this valuable and delicate ecosystem.
Conclusion: The tropical rainforest biome is a unique and vital part of the Earth’s natural environment. Its rich biodiversity and complex ecosystem provide numerous benefits to both wildlife and humans. It is our responsibility to protect and conserve these valuable habitats for future generations.
Temperate Forest Biome
The temperate forest biome is characterized by its moderate climate, with distinct seasons of summer, winter, spring, and fall. It is found in regions with moderate rainfall and temperatures that range between freezing in the winter and warm in the summer. This biome is located in the mid-latitudes of North America, Europe, and Asia.
The temperate forest biome is known for its rich diversity of plant and animal species. The vegetation in this biome includes a variety of deciduous trees, such as oak, maple, ash, and beech. These trees shed their leaves in the winter, adapting to the cold temperatures. Underneath the canopy of trees, there are smaller plants and shrubs that thrive in the shade. The forest floor is covered in a layer of decomposing leaves and organic matter, providing a fertile environment for new plant growth.
The animal life in the temperate forest biome is also abundant. Mammals such as deer, squirrels, rabbits, and bears can be found here. Birds like owls, woodpeckers, and songbirds inhabit the trees, while amphibians and reptiles make their homes in the streams and ponds. This biome is also home to a wide variety of insects, including butterflies, beetles, and spiders.
The temperate forest biome is an essential ecosystem that provides many benefits to humans. It helps regulate the climate, purifies the air, and serves as a natural habitat for countless species. Additionally, these forests are valuable for timber production, providing wood for construction and furniture. However, human activities such as deforestation and urbanization pose significant threats to the temperate forest biome, leading to habitat loss and a decline in biodiversity. It is crucial to protect and conserve this biome to ensure its continued existence for future generations.