Blood glucose data analysis plays a crucial role in managing diabetes and understanding the impact of various factors on blood sugar levels. It involves analyzing the patterns and trends in blood glucose data to determine the effectiveness of treatment plans and make informed decisions regarding diet, exercise, and medication.
Interpreting blood glucose data can be a complex task, as it requires considering multiple variables, such as time of day, meals, physical activity, and stress levels. With the help of advanced technology and software tools, healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes can analyze blood glucose data more efficiently and accurately.
The key to blood glucose data analysis lies in identifying and understanding the patterns revealed by the data. This includes recognizing recurring high or low blood sugar levels at certain times of the day, identifying the impact of specific foods on blood glucose levels, and determining the effectiveness of medication or insulin doses.
By analyzing blood glucose data, healthcare professionals can provide personalized and targeted recommendations to individuals with diabetes. This may involve adjusting medication dosages, modifying dietary plans, or emphasizing certain types of physical activity. Blood glucose data analysis serves as a valuable tool in optimizing diabetes management and improving overall health outcomes for those living with the condition.
Blood Glucose Data Analysis Answer Key
Blood glucose data analysis is a critical aspect of managing diabetes and monitoring overall health. By analyzing blood glucose levels, individuals, healthcare professionals, and researchers can gain valuable insights into a person’s metabolic health and make informed decisions regarding medication, diet, and lifestyle changes.
There are several key factors to consider when analyzing blood glucose data. One of the first steps is to identify patterns and trends in the data. This can be done by graphing the blood glucose readings over time and looking for consistent highs or lows, spikes, or fluctuations. This information can help identify potential triggers or causes for the blood glucose changes and guide adjustments to treatment plans.
Monitoring the fasting blood glucose levels is another important aspect of data analysis. Fasting blood glucose refers to the blood glucose level measured after a period of fasting, usually overnight. This measurement provides insights into how the body manages glucose levels during periods of inactivity and can be an indicator of insulin resistance or impaired glucose metabolism.
The blood glucose data should also be evaluated in the context of other factors that can affect blood sugar levels, such as meals, physical activity, stress, and medication. By keeping track of these variables and correlating them with blood glucose readings, individuals can gain a better understanding of how these factors impact their blood sugar levels and make necessary adjustments to their daily routines.
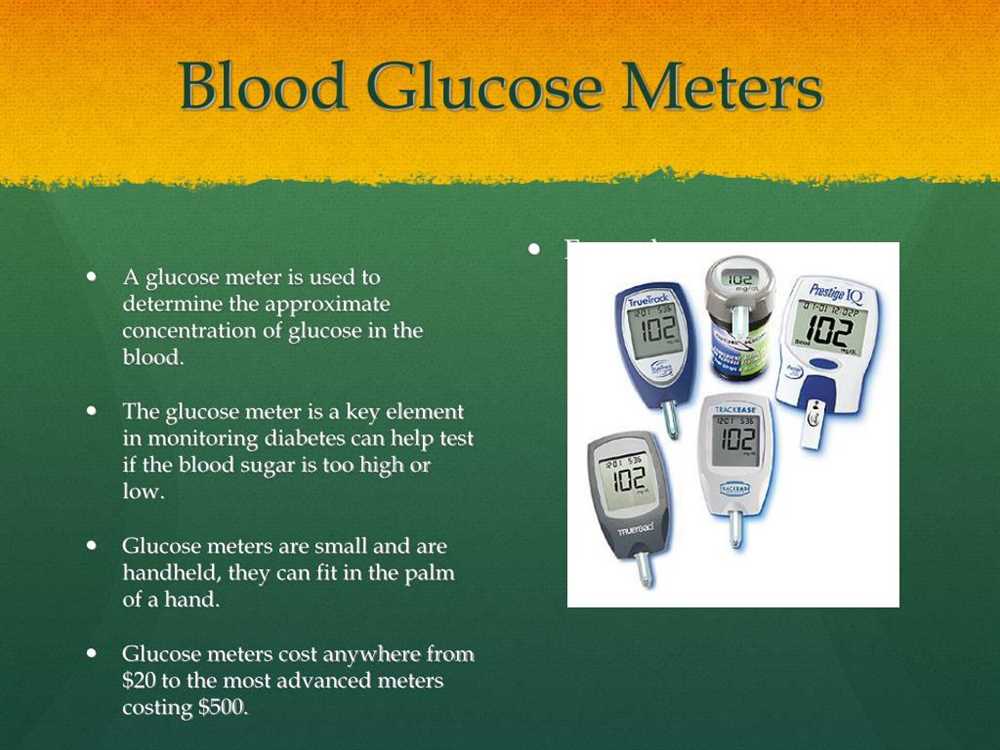
An essential tool in blood glucose data analysis is a glucose meter, which allows individuals to measure their blood glucose levels at home and keep a record of the readings. These readings can then be entered into software or apps that provide data visualization and analysis features. These tools not only help individuals track their blood glucose levels but also enable them to share the data with their healthcare team for more comprehensive analysis and guidance.
In summary, blood glucose data analysis plays a crucial role in diabetes management and overall health monitoring. By analyzing patterns and trends, monitoring fasting blood glucose levels, considering other influencing factors, and utilizing glucose meters and data analysis tools, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment plans and achieve better control of their blood glucose levels.
Overview of Blood Glucose Data Analysis
Blood glucose data analysis involves the systematic examination of blood glucose levels to gain insights into an individual’s overall health, monitor the effectiveness of diabetes management, and identify trends that may impact treatment decisions. This analysis is a crucial component of diabetes care and can provide valuable information to healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes.
1. Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels: The primary goal of blood glucose data analysis is to monitor and track blood glucose levels over time. Regular monitoring helps individuals with diabetes understand how their lifestyle choices, medication, and other factors affect their blood sugar levels. By analyzing this data, patterns and trends can be identified to optimize diabetes management and prevent complications.
2. Identifying Trends and Patterns: Blood glucose data analysis allows for the identification of trends and patterns in blood sugar levels. This can include variations in blood glucose levels throughout the day, recurring high or low blood sugar episodes, and the impact of specific meals or activities on blood glucose. Identifying these trends can help individuals adjust their diabetes management plan accordingly.
3. Assessing Treatment Effectiveness: Analyzing blood glucose data can help healthcare professionals assess the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies. By comparing blood glucose data before and after implementing treatment interventions such as medication changes or lifestyle modifications, healthcare professionals can determine if the treatment plan is achieving the desired outcomes and make necessary adjustments.
4. Predicting Potential Issues: Blood glucose data analysis can also serve as a tool for predicting potential issues or complications. By identifying trends such as frequent high or low blood sugar episodes, healthcare professionals can intervene early and prevent further complications or fine-tune the treatment plan to avoid recurring issues.
5. Educating and Empowering Individuals with Diabetes: Blood glucose data analysis provides individuals with diabetes valuable information about their condition and empowers them to take an active role in their diabetes management. By understanding their blood glucose data and the factors that affect it, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, medication, and overall lifestyle to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Importance of Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes as it provides valuable information about their blood sugar levels. By monitoring their blood glucose levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, medication, and lifestyle choices in order to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Blood glucose monitoring allows individuals with diabetes to track how their body responds to different foods, physical activities, and medications. By regularly monitoring their blood sugar levels, they can identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan. For example, if they notice that their blood sugar spikes after consuming a certain type of food, they can make dietary changes to prevent these spikes in the future.
Monitoring blood glucose levels also helps individuals with diabetes to detect and prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) episodes. By regularly checking their blood sugar levels, they can take appropriate action if their levels are too low or too high. This can help prevent serious complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemic coma.
In addition, blood glucose monitoring provides individuals with diabetes and their healthcare team with important data that can be used to adjust their treatment plan. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of medications, insulin dosage, and other interventions and make necessary changes to improve blood sugar control. It also helps individuals with diabetes to take an active role in managing their condition and empowers them to make informed decisions about their health.
Overall, blood glucose monitoring is an essential tool for individuals with diabetes to manage their condition effectively and prevent complications. It helps them understand how their body responds to different factors and empowers them to make necessary adjustments to their lifestyle and treatment plan. By regularly monitoring their blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control and improve their overall quality of life.
Key Measurements for Blood Glucose Analysis
Glycemic Index (GI)
Glycemic index is a measurement that indicates how quickly a particular food increases blood glucose levels. It ranks carbohydrate-containing foods on a scale of 0 to 100, with higher values indicating a faster increase in blood glucose. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause blood sugar spikes, while foods with a low glycemic index are digested more slowly, resulting in a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Analyzing the glycemic index of different foods can be helpful in managing blood glucose levels and making informed food choices.
HbA1c Level
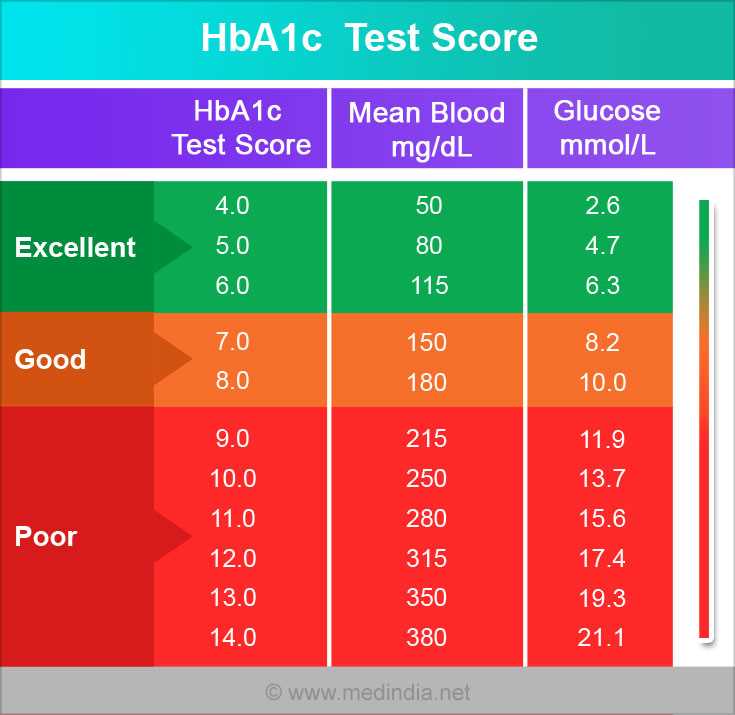
HbA1c level, also known as glycated hemoglobin, is a measurement of average blood glucose levels over a period of 2-3 months. It provides an indication of long-term blood glucose control and is commonly used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. The HbA1c level is expressed as a percentage and is considered a reliable marker for assessing overall glycemic control. It is recommended that individuals with diabetes aim for a target HbA1c level of less than 7% to reduce the risk of complications.
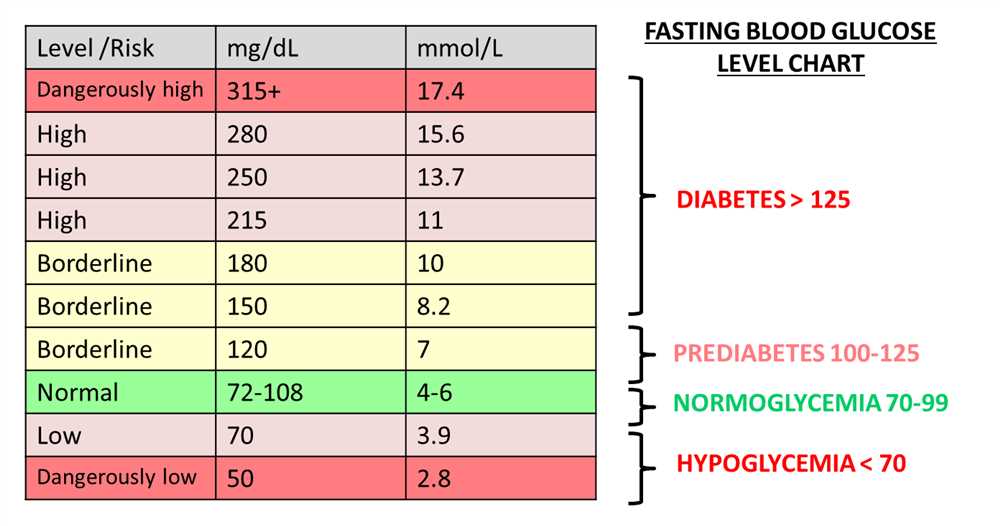
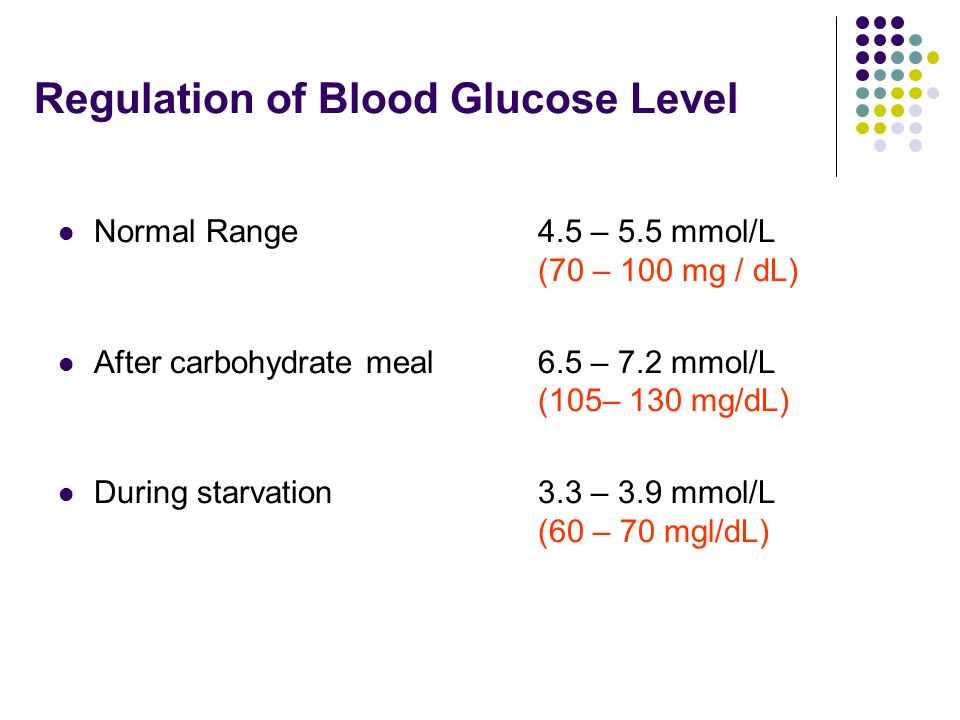
- Fasting Blood Glucose: Fasting blood glucose is the measurement of blood sugar levels after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. It is commonly used as a screening test for diabetes and can indicate the body’s ability to regulate blood glucose levels in the absence of food intake. Normal fasting blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 100 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.6 mmol/L).
- Postprandial Blood Glucose: Postprandial blood glucose refers to the measurement of blood sugar levels after a meal. It reflects the body’s ability to process and utilize glucose from food. Elevated postprandial blood glucose levels may indicate impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes. Optimal postprandial glucose levels are generally less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after a meal.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Continuous glucose monitoring is a method of measuring blood glucose levels in real-time throughout the day and night. It involves wearing a small sensor under the skin that continuously tracks glucose levels and provides data on trends and patterns. CGM can provide valuable insights into blood glucose fluctuations and help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about insulin dosing, medication, and lifestyle modifications.
By monitoring and analyzing these key measurements, individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes can gain a better understanding of their blood glucose levels and make necessary adjustments to achieve optimal glycemic control.
Understanding Blood Glucose Patterns
A crucial part of managing diabetes is understanding blood glucose patterns. Blood glucose levels can fluctuate throughout the day, and it is essential to identify patterns and trends to make informed decisions about medication, nutrition, and lifestyle choices.
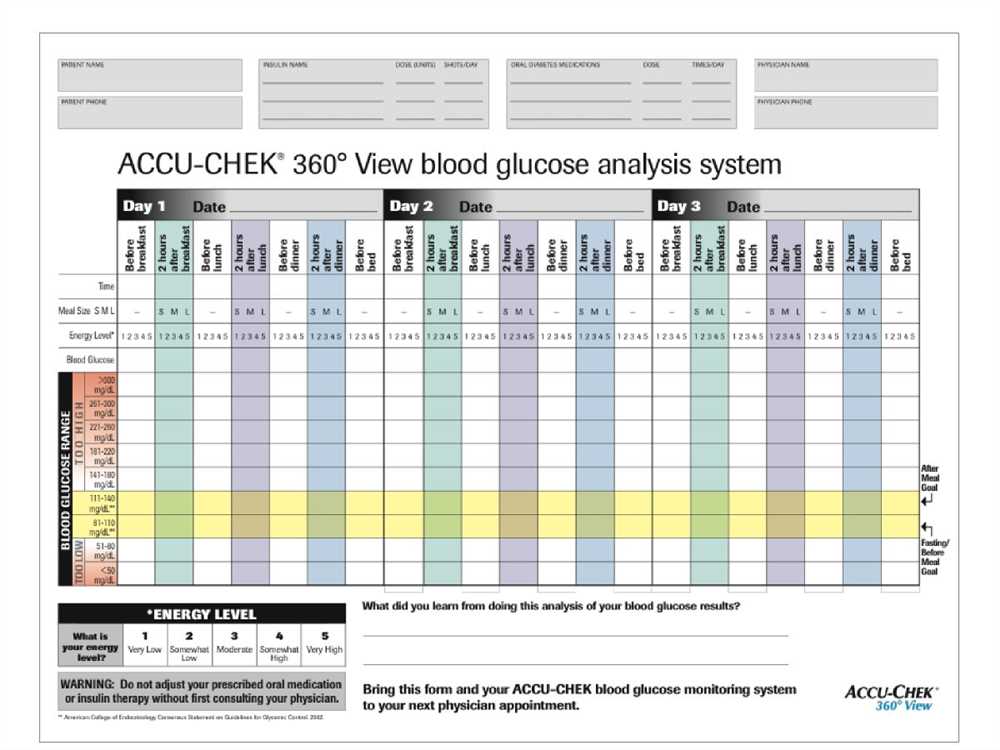
One way to analyze blood glucose patterns is to track daily glucose levels using a blood glucose meter. By regularly monitoring levels and keeping a record, individuals can start to identify patterns and understand how different factors, such as food, exercise, stress, and medication, affect their blood sugar. This information can then be used to make adjustments in medication dosage or timing, improve meal planning, and identify potential triggers for high or low blood sugar.
When analyzing blood glucose data, it is essential to look for patterns such as consistently higher or lower levels at certain times of the day. This could indicate a need for adjustments in medication or lifestyle choices. Additionally, spikes or drops in blood glucose levels after meals or exercise can provide insights into how different foods or activities affect individual blood sugar levels.
A helpful tool for understanding blood glucose patterns is a chart or graph that visually represents the data. This can make it easier to identify trends over time, spot outliers, and track progress towards blood sugar goals. An organized record of blood glucose data can also be beneficial for healthcare providers, as it provides a comprehensive overview of an individual’s blood glucose management and aids in making treatment decisions.
In conclusion, understanding blood glucose patterns is crucial for effective diabetes management. By monitoring blood glucose levels, identifying patterns, and making informed adjustments, individuals can optimize their treatment plans and make better choices to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Analyzing Blood Glucose Trends
When analyzing blood glucose trends, it is important to carefully examine the data and look for patterns and variations. This can provide valuable insights into a person’s overall blood glucose control and help identify any potential issues or trends that may need to be addressed.
Understanding the Data: Blood glucose data typically includes information on blood glucose levels measured at various times throughout the day. This data can be collected through self-monitoring or continuous glucose monitoring devices. It is important to pay attention to the units of measurement used, as different countries may use different systems (such as mg/dL or mmol/L).
One key aspect of analyzing blood glucose trends is looking at the overall pattern of fluctuations in blood glucose levels. This involves identifying the highest and lowest blood glucose levels and examining how they relate to each other over a specific time period. This can help determine if there are any regular patterns or trends, such as consistently high or low blood glucose levels at certain times of the day.
For example, if a person consistently experiences high blood glucose levels after meals, this may indicate issues with insulin resistance or ineffective medication management. On the other hand, consistently low blood glucose levels during the night may suggest the need for adjustments in medication or dietary intake.
Another important factor to consider when analyzing blood glucose trends is the variability in blood glucose levels. Variability refers to how much blood glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day. High variability can indicate unstable blood glucose control and may lead to increased risk of complications over time.
Tracking blood glucose trends over an extended period of time can help identify long-term trends and offer insights into the effectiveness of treatment plans. For example, if blood glucose levels consistently remain within a target range, this may indicate successful diabetes management. On the other hand, if there are frequent spikes or drops in blood glucose levels, this may suggest that adjustments need to be made to the treatment plan.
Overall, analyzing blood glucose trends is a valuable tool in understanding and managing diabetes. By carefully examining the data and identifying patterns and variations, individuals and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about treatment options and make necessary adjustments to improve blood glucose control. Regular monitoring and analysis of blood glucose trends can help prevent complications and improve overall quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.