
The carbon cycle is a vital process that keeps the Earth’s atmospheric carbon dioxide levels in balance. Understanding this cycle is crucial for understanding the impacts of human activities on the environment and climate change. The Carbon Cycle Gizmo is a valuable tool designed to help students explore and understand the different components and processes of the carbon cycle.
Activity C of the Carbon Cycle Gizmo answer key focuses on the impact of deforestation on the carbon cycle. Deforestation, the clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, or urban development, has become a significant concern due to its contribution to increased carbon dioxide levels and climate change. The Carbon Cycle Gizmo enables students to simulate and analyze the effects of deforestation on the carbon cycle through interactive activities and visualizations.
By engaging with Activity C of the Carbon Cycle Gizmo, students can understand how deforestation results in increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. They can explore how the removal of trees disrupts the process of photosynthesis, leading to a decrease in the absorption of carbon dioxide. Additionally, students can also examine the impact of deforestation on other components of the carbon cycle, such as the release of carbon from decomposing plants and soil.
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo provides students with an interactive and immersive learning experience, allowing them to manipulate variables and observe the direct impact of deforestation on carbon dioxide levels. By actively participating in the simulation, students can develop a deeper understanding of the carbon cycle and the consequences of deforestation, empowering them to make informed decisions about environmental preservation and conservation.
Explanation of the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the process through which carbon moves between various reservoirs in the Earth’s biosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and hydrosphere. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere, which is essential for regulating Earth’s climate.
One of the key reservoirs of carbon in the carbon cycle is the atmosphere, where carbon exists primarily in the form of CO2. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants and other autotrophs take in CO2 from the atmosphere and convert it into organic compounds, such as sugars and carbohydrates. This process removes CO2 from the atmosphere and stores carbon in living organisms.
Another important reservoir of carbon is the ocean. The ocean acts as a sink for atmospheric CO2, as it absorbs a significant amount of carbon from the atmosphere. This process, known as oceanic carbon uptake, helps to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere and mitigate the greenhouse effect. Additionally, marine organisms play a role in the carbon cycle by converting CO2 into calcium carbonate, a process known as biological carbon sequestration.
The carbon cycle also includes processes such as respiration, decomposition, and combustion, which release carbon back into the atmosphere. When organisms respire, they release CO2 as a byproduct, contributing to the carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere. Decomposition of organic matter, whether through natural decay or human activities, also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Combustion of fossil fuels and other organic materials releases carbon in the form of CO2, contributing to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions.
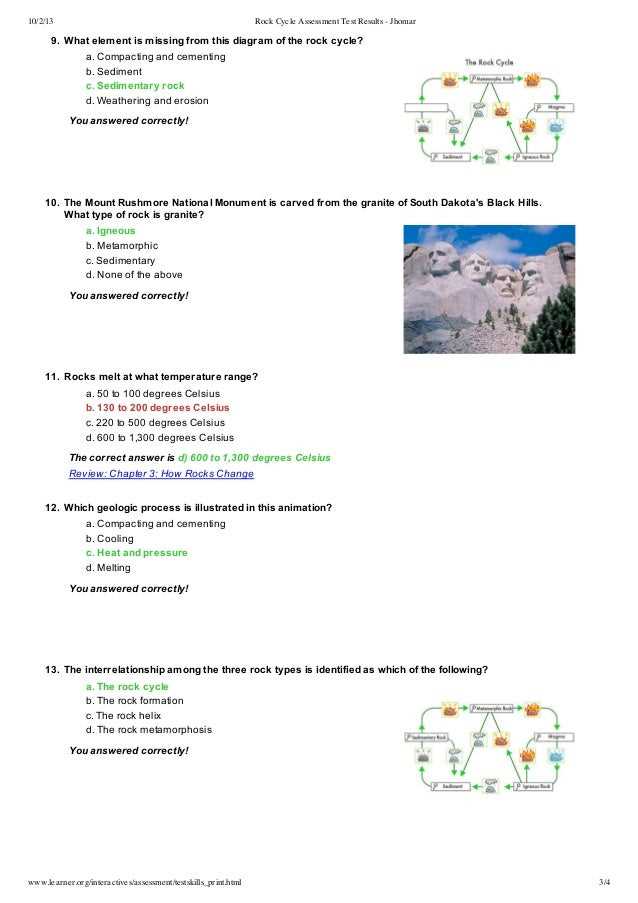
In summary, the carbon cycle is a complex process that involves the exchange of carbon between various reservoirs in the Earth’s systems. Understanding and managing the carbon cycle is crucial for addressing climate change and ensuring the long-term sustainability of our planet.
What is the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon compounds are exchanged and transformed in the biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. It is a natural cycle that involves the movement of carbon atoms between different components of the Earth’s system. Carbon is an essential element for life on Earth and plays a crucial role in maintaining the planet’s climate and ecosystems.
The carbon cycle begins with carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere, which is absorbed by plants during the process of photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis, plants convert CO2 into organic compounds, such as sugars, which are used for growth and energy. These organic compounds are then passed on to other organisms in the food chain. When living organisms respire or decompose, carbon is released back into the atmosphere as CO2.
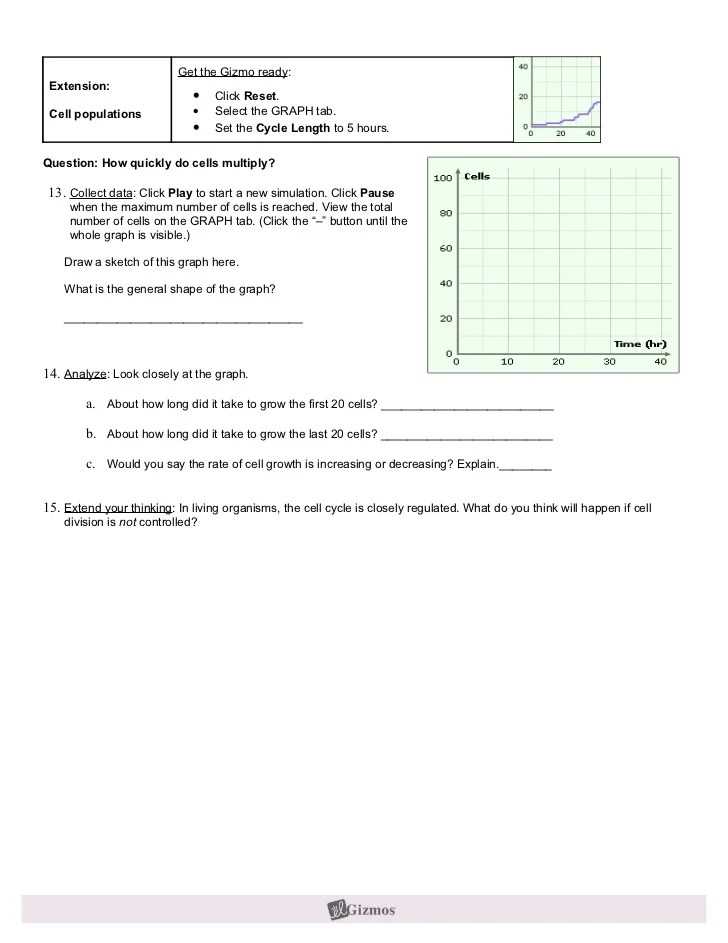
In addition to photosynthesis and respiration, there are other important processes in the carbon cycle. Carbon dioxide can also dissolve in water, forming carbonic acid, which can be utilized by marine organisms to build their shells and skeletons. Over time, these shells and skeletons can become buried in sediments and eventually form rocks, such as limestone, which store carbon for millions of years.
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly altered the carbon cycle by releasing large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This excess carbon dioxide contributes to the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change. Understanding the carbon cycle is essential for comprehending the impact of human activities on the environment and developing strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Importance of the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is an essential process that plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that traps heat and contributes to global warming. Therefore, understanding the carbon cycle and its importance is imperative for addressing climate change and ensuring the long-term sustainability of our planet.
One key aspect of the carbon cycle is the uptake of carbon dioxide by plants through photosynthesis. During this process, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, convert it into carbohydrates, and release oxygen as a byproduct. This not only helps to reduce the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere but also provides us with the oxygen we need to breathe. Without the carbon cycle, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere would increase significantly, leading to detrimental effects on climate and human health.
The carbon cycle also plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s temperature. The cycle acts as a natural thermostat, controlling the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. When carbon dioxide levels rise, more heat is trapped, causing the Earth’s temperature to increase. However, thanks to the carbon cycle, excess carbon dioxide is absorbed by oceans and forests, preventing an exponential increase in temperature. By understanding and managing the carbon cycle, we can effectively mitigate climate change and prevent the catastrophic consequences associated with global warming.
Furthermore, the carbon cycle is intricately linked to other biogeochemical cycles, such as the nitrogen and phosphorus cycles. These cycles interact with each other, influencing the availability of nutrients for plants and the overall productivity of ecosystems. For example, carbon is stored in the form of organic matter in soil, providing nutrients for plants and promoting their growth. Additionally, the decomposition of organic matter releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, completing the carbon cycle. Understanding the interconnectedness of these cycles is vital for maintaining healthy and balanced ecosystems.
In conclusion, the carbon cycle is of utmost importance for the overall sustainability and well-being of our planet. It regulates the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, regulates the Earth’s temperature, and influences the productivity of ecosystems. By comprehending and managing the carbon cycle, we can actively contribute to mitigating climate change, protecting biodiversity, and ensuring a habitable environment for future generations.
Understanding the Carbon Cycle Gizmo
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo is a powerful interactive tool that allows students to explore and understand the complex processes of the carbon cycle. This educational tool is designed to help students grasp the interconnectedness of various components and learn how carbon moves through different reservoirs in the environment.
The Gizmo provides a virtual simulation of the carbon cycle, enabling students to manipulate variables and observe the effects on carbon levels in different reservoirs. By engaging with this hands-on activity, students can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the carbon cycle and the impact of human activities on carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere.
Exploring the Gizmo

When using the Carbon Cycle Gizmo, students can start by examining the initial carbon levels in the atmosphere, vegetation, soil, and the ocean. They can then adjust variables such as photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion to see how these processes affect carbon levels in each reservoir. By analyzing the changes in carbon levels, students can make connections between the different components of the carbon cycle and understand the importance of maintaining a balance.
- Photosynthesis: This process allows plants to absorb carbon dioxide and convert it into oxygen and carbohydrates. By increasing or decreasing the rate of photosynthesis, students can observe the impact on carbon levels in vegetation and the atmosphere.
- Respiration: Respiration by plants and animals releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Students can manipulate the respiration rate to see how it affects carbon levels in the atmosphere and vegetation.
- Decomposition: Decomposition of dead plants and animals also releases carbon dioxide. By adjusting the decomposition rate, students can explore how carbon levels change in the soil and atmosphere.
- Combustion: Combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, contributes significantly to carbon dioxide emissions. Students can experiment with different combustion rates to observe the impact on carbon levels in the atmosphere and the ocean.
Overall, the Carbon Cycle Gizmo provides an engaging and interactive learning experience for students to grasp the complexity of the carbon cycle. By exploring different variables and observing the resulting changes, students can develop a deeper understanding of this crucial process and its relevance to environmental sustainability.
Purpose of the Carbon Cycle Gizmo
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo is designed to help students understand the process and importance of the carbon cycle. Through interactive simulations and visualizations, the Gizmo allows students to explore how carbon moves through different parts of the Earth’s system, such as the atmosphere, oceans, and living organisms.
The Gizmo provides students with a hands-on learning experience, allowing them to manipulate variables and observe the impact of these changes on the carbon cycle. By engaging in this virtual exploration, students can develop a deeper understanding of how human activities, such as burning fossil fuels or deforestation, affect the balance of carbon in the atmosphere.
Key features of the Carbon Cycle Gizmo include:

- Interactive simulations: Students can adjust variables, such as carbon emissions or ocean absorption, to see how these changes impact the carbon cycle.
- Data visualization: The Gizmo provides visualizations, such as graphs and charts, to help students analyze and interpret data related to the carbon cycle.
- Real-world connections: The Gizmo includes real-world examples and scenarios to help students understand the relevance and significance of the carbon cycle in everyday life.
- Educational resources: The Gizmo comes with educational resources, including lesson plans and activities, to support teachers in incorporating the Gizmo into their instruction.
Overall, the purpose of the Carbon Cycle Gizmo is to enhance students’ understanding of the carbon cycle and its importance in maintaining Earth’s climate and ecosystems. By engaging in interactive simulations and exploring real-world examples, students can develop critical thinking skills and a deeper appreciation for the impact of human activities on the carbon cycle.
Key features of the carbon cycle gizmo
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows users to explore the key features of the carbon cycle. It provides a visual representation of how carbon is exchanged between different reservoirs on Earth and helps users understand the processes that drive this cycle.
One of the key features of the Carbon Cycle Gizmo is the ability to manipulate different factors and observe their effects on the carbon cycle. Users can adjust the rate of carbon emissions, the rate of photosynthesis, and the rate of carbon absorption by the ocean. This allows for a hands-on exploration of how human activities and natural processes impact the carbon cycle.
Carbon Reservoirs
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo provides a clear visualization of the different carbon reservoirs on Earth. These include the atmosphere, plants, animals, soil, and the ocean. Each reservoir is represented by a bar graph that shows the amount of carbon stored in that reservoir at any given time. Users can click on each reservoir to view detailed information about its carbon content and how it is affected by the carbon cycle.
Furthermore, the Carbon Cycle Gizmo allows users to track the movement of carbon between different reservoirs. They can observe how carbon is transferred from the atmosphere to plants through photosynthesis, how it is released back into the atmosphere through respiration, and how it is absorbed by the ocean or stored in the soil. This interactive feature helps users visualize the interconnectedness of the carbon cycle and understand the importance of maintaining a balance between carbon emissions and absorption.
Impact of Human Activities
The Carbon Cycle Gizmo also highlights how human activities can disrupt the natural balance of the carbon cycle. Users can increase the rate of carbon emissions from various sources, such as burning fossil fuels or deforestation, and observe the consequences on the carbon cycle. They can see how these increased emissions lead to a buildup of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming.
Overall, the Carbon Cycle Gizmo is an invaluable tool for understanding the key features of the carbon cycle. Its interactive nature and visual representations make it easy for users to grasp complex concepts and see the impact of different factors on the carbon cycle. By exploring this simulation, users can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of carbon balance and the role humans play in influencing this crucial natural process.