
Understanding the structure and function of cell organelles is an essential part of studying biology. A cell organelle is a specialized structure within a cell that performs specific functions. To help students grasp the concept of cell organelles, teachers often provide them with coloring worksheets that require identifying and coloring different organelles.
This article provides an answer key for the Cell Organelles Coloring Worksheet PDF, which allows students to check their answers and learn from any mistakes. The worksheet typically includes various types of organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Each organelle has a specific function that contributes to the overall functioning and survival of the cell.
The answer key helps students identify and correctly color each organelle based on its function and appearance. By completing this worksheet and referring to the answer key, students can reinforce their understanding of cell organelles and their importance in cellular processes. This interactive activity also engages students creatively and helps them remember the names and functions of different organelles through a visual approach.
Cell Organelles Coloring Worksheet PDF Answer Key

In biology, the study of cells is essential to understanding how living organisms function. Cells are the building blocks of life, and each cell is composed of various organelles, or specialized structures, that perform specific functions. To help students learn about these organelles, teachers often use worksheets and activities. One popular worksheet is the Cell Organelles Coloring Worksheet, which allows students to color and label different organelles.
The Cell Organelles Coloring Worksheet often comes with an answer key, providing students with the correct labeling and coloring for each organelle. The answer key is a helpful tool for students to check their work and ensure they are accurately identifying and coloring each organelle. This way, students can gain a better understanding of the different organelles and their functions.
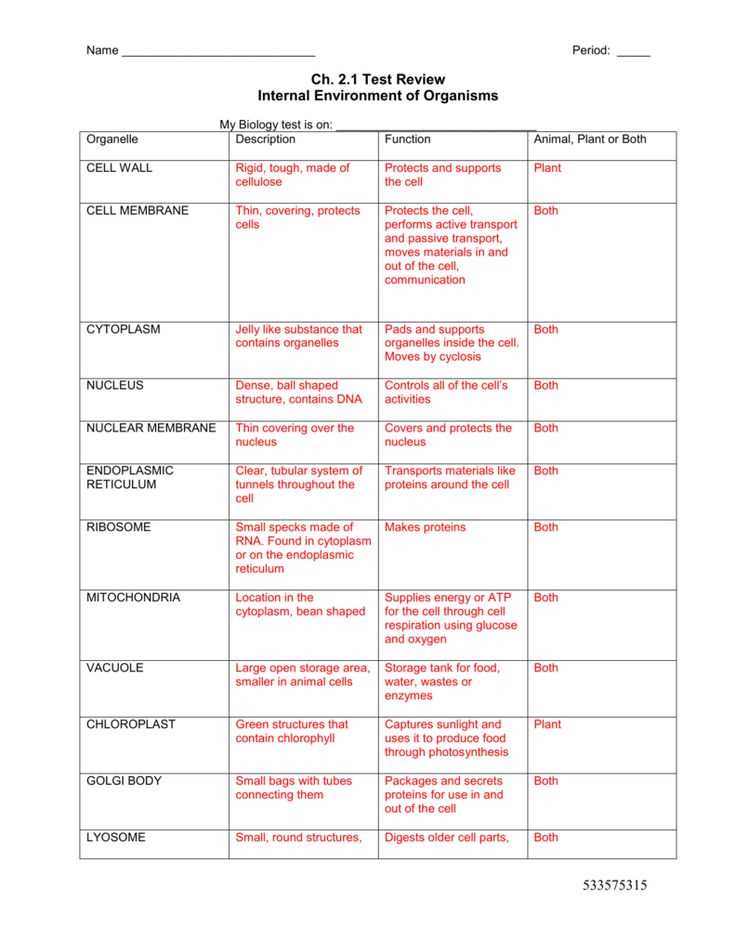
The answer key for the Cell Organelles Coloring Worksheet typically includes a list of organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Each organelle is accompanied by a description of its function and an illustration or diagram indicating its location within the cell. Students can refer to the answer key as they color and label their own worksheet, ensuring they are correctly identifying each organelle.
By using the Cell Organelles Coloring Worksheet PDF and its answer key, students can engage in a hands-on activity that reinforces their understanding of cell organelles. This worksheet allows them to visually represent the different organelles and their functions, helping them to remember and comprehend these important concepts. The answer key serves as a valuable resource for students, providing them with guidance and feedback as they complete the worksheet.
Overall, the Cell Organelles Coloring Worksheet PDF Answer Key is a valuable tool for biology teachers and students alike. It offers an interactive and visual way for students to learn about cell organelles and reinforces their understanding of these structures. By using the answer key, students can ensure accuracy and receive immediate feedback on their work. This worksheet and its answer key can greatly enhance the learning experience and promote a deeper understanding of cell biology.
Importance of Cell Organelles
Cell organelles play a crucial role in the functioning and survival of cells. Each organelle has its specific function, and together they work harmoniously to maintain the overall integrity and functionality of the cell.
Nucleus: The nucleus is often referred to as the control center of the cell. It houses the cell’s genetic material, DNA, and is responsible for regulating cellular activities such as growth, reproduction, and protein synthesis. It plays a vital role in transmitting genetic information to the next generation.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranous tubules and sacs that are involved in the synthesis, folding, and transport of proteins and lipids. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cell homeostasis and detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is responsible for processing, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for transportation. It acts as the cell’s post office, ensuring that these molecules are correctly sorted and sent to their final destination both inside and outside the cell.
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are the recycling centers of the cell. They contain enzymes that break down waste materials, damaged organelles, and cellular debris. By breaking down and recycling these materials, lysosomes play a crucial role in maintaining cellular health and preventing the accumulation of toxic substances.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. They are responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process called cellular respiration. This energy is essential for the functioning and survival of the cell.
Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are unique to plant cells and are responsible for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight and converts it into chemical energy. Through photosynthesis, chloroplasts produce glucose and oxygen, which are vital for the growth and survival of plants.
Overall, cell organelles are essential for the proper functioning and survival of cells. They work together in a coordinated manner to carry out various cellular processes, ensuring the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and enabling cells to perform their specific functions in multicellular organisms.
Understanding Cell Organelles
Cells are the basic units of life, and within each cell there are various organelles that perform specific functions. These organelles are like tiny organs within a cell, each with its own unique structure and purpose. Understanding cell organelles is essential for understanding how cells function and carry out their roles in living organisms.
One of the most important organelles in a cell is the nucleus. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, which carries all the genetic information necessary for the cell’s growth, development, and reproduction. The nucleus is like the control center of the cell, coordinating all the cell’s activities and regulating gene expression.
Another important organelle is the mitochondria. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell because they generate energy in the form of ATP through a process called cellular respiration. This energy is essential for the cell to carry out its various functions. Mitochondria also have their own DNA, separate from the DNA in the nucleus.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is another organelle that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. It is a network of membrane-bound tubes and sacs that extends throughout the cell. The rough ER is covered in ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis, while the smooth ER is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification processes.
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle involved in the processing, packaging, and sorting of proteins and lipids. It receives proteins and lipids from the ER, modifies them, and packages them into vesicles for transport to their final destinations within or outside the cell. The Golgi apparatus is like the cell’s post office, ensuring that molecules are properly sorted and delivered to the correct locations.
In conclusion, understanding cell organelles is crucial for understanding how cells function and carry out their roles in living organisms. Each organelle has its own unique structure and purpose, and together they work in harmony to ensure the survival and proper functioning of the cell. By studying and coloring cell organelles, we can better comprehend the complex and fascinating world of cells and their organelles.
Key Features of the Coloring Worksheet
The Cell organelles coloring worksheet is designed to help students learn and understand the different structures and functions of cell organelles. This worksheet is a valuable educational tool that combines coloring and labeling to engage students in a hands-on learning experience.
Visual Representation: The worksheet provides students with a visual representation of different cell organelles. Each organelle is labeled, allowing students to easily identify and recognize them. Additionally, the worksheet includes key information to help students understand the function of each organelle.
Interactive Learning: By coloring and labeling the cell organelles, students actively participate in the learning process. This hands-on activity helps students to better retain information and comprehend complex concepts. The act of coloring also encourages creativity and makes learning more enjoyable.
- Color-Coded Key: The worksheet includes a color-coded key that matches different colors to each organelle. This helps students to make visual connections between the organelles and their functions.
- Detailed Diagram: The worksheet features a detailed diagram of a cell, providing students with a comprehensive overview of the different organelles and their placement within the cell.
- Visual Aid for Revision: Once completed, the coloring worksheet can serve as a visual aid for revision. Students can refer back to the worksheet to review the names and functions of different cell organelles.
In conclusion, the Cell organelles coloring worksheet is an effective educational resource that combines coloring, labeling, and key information to enhance students’ understanding of cell organelles. This interactive learning tool provides a visual representation of the organelles and encourages active participation, making it an engaging and effective tool for teaching and revising cell biology.
How to Use the Answer Key
Once you have completed the cell organelles coloring worksheet, it’s time to check your answers using the answer key. The answer key is provided to help you verify if you have correctly identified and colored the different cell organelles. Here are some steps on how to effectively use the answer key:
- Compare your answers: Start by comparing your answers with the ones provided in the answer key. Look for any differences or similarities between your coloring and the key.
- Check for accuracy: Carefully examine each cell organelle you have colored and compare it with the correct answer in the key. Make sure you have accurately identified and colored each organelle.
- Revise if necessary: If you find any mistakes or discrepancies between your answers and the key, take the time to revise and correct your coloring. Use the key as a guide to make any necessary adjustments.
- Clarify doubts: If you come across any organelles or parts of the cell that you are unsure of, refer to the answer key for clarification. It can help you understand the correct identification and color choice.
- Learn from the key: The answer key provides a valuable learning tool. Take the time to study the correct answers and understand why they are accurate. This can help reinforce your knowledge of cell organelles.
Using the answer key can be a helpful way to assess your understanding of cell organelles and ensure that you have correctly identified and colored them in the worksheet. Remember to use the key as a tool for learning and clarification, and make any necessary revisions to improve your accuracy.
Detailed Analysis of Each Organelle
In order to understand the function of each organelle, it is important to delve into the details of their structures and roles within the cell. Here, we will provide a comprehensive analysis of each organelle, highlighting their key features and functions.
Nucleus
The nucleus is often referred to as the “control center” of the cell. It is a spherical-shaped organelle that is enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material, known as DNA, which carries the instructions for the cell’s activities. Within the nucleus, there is also a nucleolus, where ribosomes are synthesized.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” of the cell because they are responsible for generating most of the cell’s energy. These organelles are oval-shaped and have an inner and outer membrane. The inner membrane is folded into structures called cristae, which increase the surface area for cellular respiration. Mitochondria have their own DNA and can replicate independently within the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranes that extends throughout the cell. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes, and smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes. The rough ER is involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins, while the smooth ER is responsible for lipid metabolism and detoxification of drugs.
Golgi Apparatus

The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranous sacs that function as a processing and packaging center for molecules. It receives proteins and lipids from the ER, modifies them, and sorts them into vesicles for transportation to their final destinations. The Golgi apparatus also plays a role in the formation of lysosomes, which are organelles involved in intracellular digestion.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are small organelles filled with digestive enzymes. They have a single membrane and are involved in the breakdown of macromolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Lysosomes function as recycling centers within the cell, removing waste and recycling the components for reuse. They also play a role in programmed cell death, or apoptosis.
Centrioles
Centrioles are cylindrical structures composed of microtubules that are involved in cell division. They are located near the nucleus and are responsible for organizing the spindle fibers during mitosis and meiosis. Centrioles are found in pairs and are most commonly found in animal cells.