
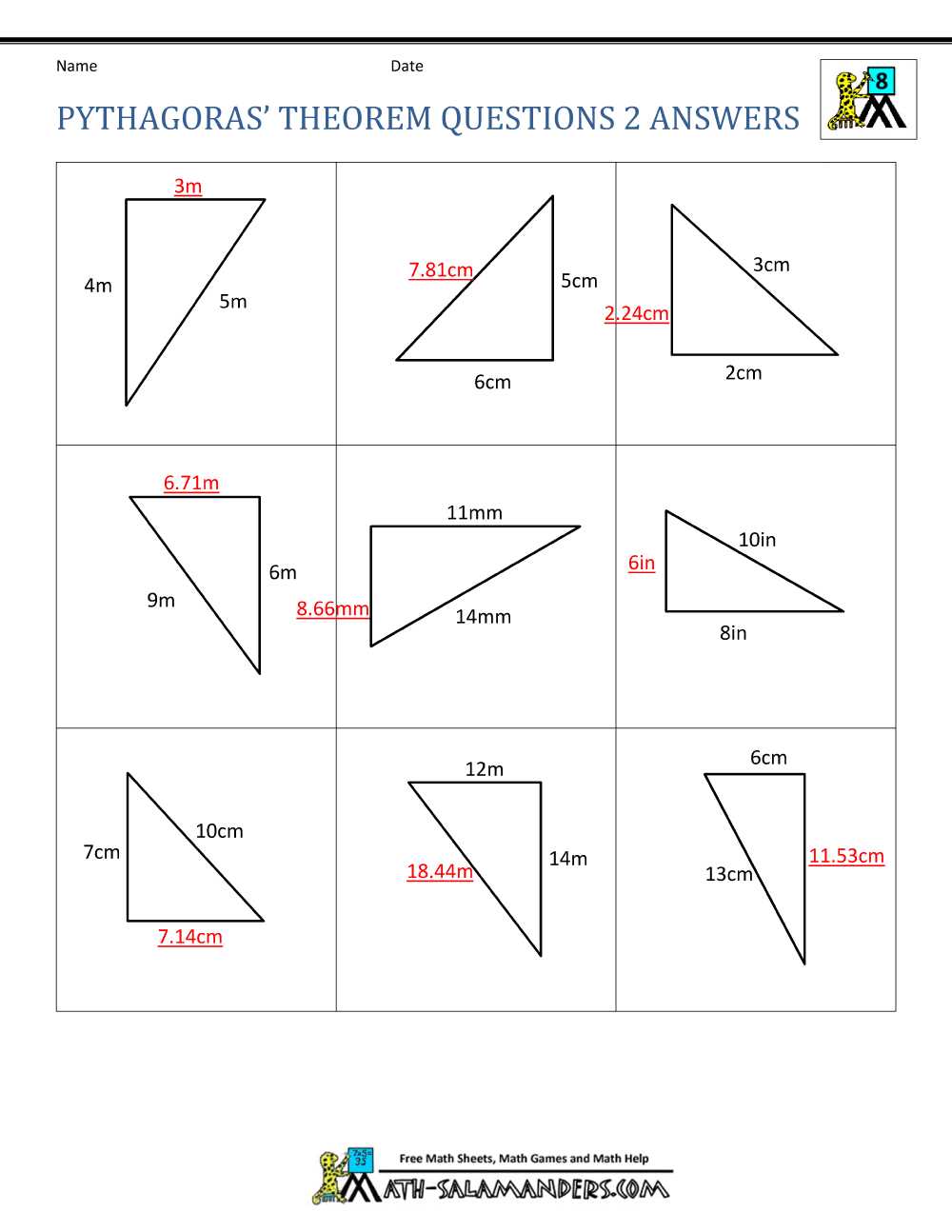
Cell biology is a fascinating field that explores the structure, function, and behavior of cells, the building blocks of life. Understanding cell theory is essential for comprehending the intricate workings of living organisms. One valuable resource that facilitates the learning process is the Cell Theory Worksheet PDF, which provides comprehensive answers to questions and exercises related to cell theory.
The Cell Theory Worksheet PDF answers offer a detailed explanation of the key principles of cell theory. These principles include the idea that all living organisms are composed of cells, that cells are the basic unit of structure and function in organisms, and that cells arise from pre-existing cells through cell division. By studying the answers provided in the worksheet, students can gain a solid understanding of these fundamental concepts.
The Cell Theory Worksheet PDF answers cover a wide range of topics within cell biology. Students can explore questions related to cell structures and organelles, cell types and their functions, and the processes that occur within cells. By examining these answers, students can reinforce their knowledge and identify any areas that may require further study or clarification.
Whether you are a student studying cell biology or a teacher looking for valuable resources to supplement your lessons, the Cell Theory Worksheet PDF answers are an invaluable tool. With their detailed explanations and comprehensive coverage of cell theory topics, these answers provide a valuable resource for learning and reinforcing the fundamentals of cell biology.
Cell Theory Worksheet PDF Answers: Basic Concepts
The cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that describes the basic structure and function of cells. It states that all living organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living organisms, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This theory was developed in the 19th century by scientists such as Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. Understanding the cell theory is crucial for comprehending the workings of living organisms.
The cell theory worksheet provides a series of questions that test your understanding of the cell theory and its principles. By answering these questions, you can assess your knowledge and identify any areas where further study may be required. The worksheet typically includes questions about the three main parts of the cell theory, the key experiments and scientists that contributed to its development, and the importance of the cell theory in modern biology.
Some of the basic concepts covered in the cell theory worksheet include:
- The three main parts of the cell theory: all living organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
- The contribution of Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in formulating the cell theory.
- The importance of the microscope in the discovery and understanding of cells.
- The experiments conducted by Rudolf Virchow that supported the cell theory.
- The significance of the cell theory in the study of diseases, genetics, and cell biology.
By reviewing the cell theory worksheet and its answers in PDF format, you can solidify your understanding of these basic concepts and gain a deeper insight into the fundamental principles of biology. This knowledge will not only enhance your performance in biology-related exams and assignments but also equip you with a solid foundation for further studies in the field of life sciences.
Understanding the cell theory and its importance in biology

The cell theory is one of the fundamental principles in biology that explains the structure and function of living organisms. It states that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms, and cells arise from pre-existing cells. This theory was proposed by Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in the mid-19th century and has since become a cornerstone of modern biology.
According to the cell theory, cells are the building blocks of life and are responsible for carrying out all the essential functions of living organisms. They are microscopic structures that vary in size, shape, and function depending on the organism they make up. Cells can range from simple prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, to complex eukaryotic cells found in plants and animals.
The cell theory plays a crucial role in biology as it provides a framework for understanding the organization and functioning of living organisms. It allows scientists to study cells at a microscopic level and explore their structure, organelles, and biochemical processes. By understanding how cells work, researchers can gain insights into diseases, develop new treatments, and even engineer cells for various purposes.
Furthermore, the cell theory helps explain the process of reproduction and growth in organisms. By understanding how cells divide and differentiate, scientists can comprehend the development of an organism from a single cell to a complex multicellular organism. This knowledge has significant implications in fields such as developmental biology, regenerative medicine, and genetics.
In conclusion, the cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that provides an essential framework for understanding the structure, function, and organization of living organisms. It allows scientists to study cells at a microscopic level, explore their biochemical processes, and gain insights into diseases and development. Without the cell theory, our understanding of biology would be severely limited, and many advancements in medicine and biotechnology would not be possible.
Cell Structure and Function: Key Components
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It is composed of several key components that work together to carry out various biological processes. These components include the plasma membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles.
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the internal and external environment. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, allowing for selective permeability. The plasma membrane also contains proteins that facilitate cell signaling and communication.
The nucleus is often referred to as the “control center” of the cell. It contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA, which carries the instructions for cellular functions and heredity. Within the nucleus, you can find the nucleolus, which is responsible for the production of ribosomes.
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles. It is where many metabolic reactions occur and serves as a medium for transporting molecules throughout the cell. The cytoplasm also contains various structures, such as the cytoskeleton, which provides structural support and enables cell movement.
Organelles are specialized structures within the cell that perform specific functions. Some important organelles include the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein and lipid synthesis, while the Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins. Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, producing energy through cellular respiration, and chloroplasts are found in plant cells and are responsible for photosynthesis.
In conclusion, the cell is a complex structure with various components that work together to ensure the proper functioning of living organisms. Understanding the key components of cell structure and function is essential for comprehending cellular processes and their significance in biology.
Exploring the different parts of a cell and their specific functions

The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It consists of various parts, each with its specific function, that work together to carry out the essential processes of life. By understanding the different parts of a cell and their functions, we can gain insight into the intricacies of life itself.
One of the most important parts of a cell is the cell membrane, which acts as a barrier and regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins that help transport molecules across the membrane. The cell membrane also contains receptors that allow the cell to communicate with its environment.
1. Nucleus: The nucleus is often referred to as the control center of the cell. It contains the cell’s DNA, which holds the instructions for building and maintaining the cell. The nucleus also plays a key role in cell division, as it is responsible for the replication and distribution of DNA during cell division.
2. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles. It provides a medium for chemical reactions to occur and supports the organelles within the cell. The cytoplasm contains various molecules and ions that are necessary for cellular metabolism and function.
3. Endoplasmic reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and sacs that are involved in the synthesis, folding, and transport of proteins and lipids. It can be divided into two regions: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes and is involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification of harmful substances.
4. Golgi apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranous sacs that processes, modifies, and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the cell. It receives materials from the ER and sorts, tags, and packages them into vesicles for transport to their final destinations.
These are just a few examples of the many parts of a cell and their specific functions. Each organelle plays a vital role in maintaining the overall function and survival of the cell. By studying and understanding these components, we can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of life at the cellular level.
Cell Theory Worksheet PDF Answers: Cell Types
The study of cells is crucial in understanding the basic building blocks of life. The cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that states that all living organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living organisms, and cells come from pre-existing cells. To further explore and reinforce this concept, a worksheet on cell types is provided with PDF answers to aid in learning and assessment.
The worksheet on cell types presents a variety of questions and scenarios related to different types of cells. Students are challenged to identify and classify different types of cells based on their characteristics and functions. Some of the cell types covered in the worksheet include prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, plant cells, animal cells, and specialized cells such as nerve cells and muscle cells.
With the worksheet PDF answers, students can check their understanding and knowledge of the different cell types. The answers provide detailed explanations and information about each cell type, allowing students to compare their responses and learn from any misconceptions or gaps in their understanding. This reinforces the key concepts of cell theory and helps students develop a solid foundation in cell biology.
Sample Questions and Answers:
- Question 1: What are the main differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
- Answer: Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack a membrane-bound nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a membrane-bound nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are usually single-celled organisms, while eukaryotic cells can be single-celled or multicellular.
- Question 2: How do plant cells differ from animal cells?
- Answer: Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large central vacuoles, while animal cells lack these features. Plant cells also have a more regular shape compared to the varied shapes of animal cells.
- Question 3: What is the function of nerve cells?
- Answer: Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals and messages throughout the body. They play a crucial role in the nervous system and are responsible for communication and coordination.
The cell types worksheet and its accompanying PDF answers provide a valuable resource for students to deepen their understanding of cell theory and explore the various types of cells that make up living organisms. By engaging with the worksheet and reviewing the answers, students can strengthen their knowledge and comprehension of this fundamental concept in biology.
Examining the various types of cells, including prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. They come in various shapes and sizes, and can be classified into two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Understanding the characteristics and differences between these cell types is essential in studying the cell theory.
Prokaryotic cells are simple and primitive in structure, lacking a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They are typically small and found in organisms such as bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotic cells contain a single, circular DNA molecule located in the cytoplasm, along with other essential cellular structures such as ribosomes. These cells have a cell wall and pili, which aid in their survival and reproduction.
Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and evolved. They possess a true nucleus and are found in multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells have numerous membrane-bound organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria. These organelles perform specialized functions within the cell, allowing it to carry out various metabolic processes.
Eukaryotic cells also have a cytoskeleton, which provides structural support and helps in cell movement. They can be further divided into animal cells and plant cells. Animal cells do not have a cell wall but have centrioles, which aid in cell division. Plant cells, on the other hand, have a cell wall made of cellulose and contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells play crucial roles in the functioning of living organisms. By studying and comparing these cell types, scientists can gain a better understanding of the fundamental processes that occur within cells and how they contribute to the overall physiology and development of organisms.