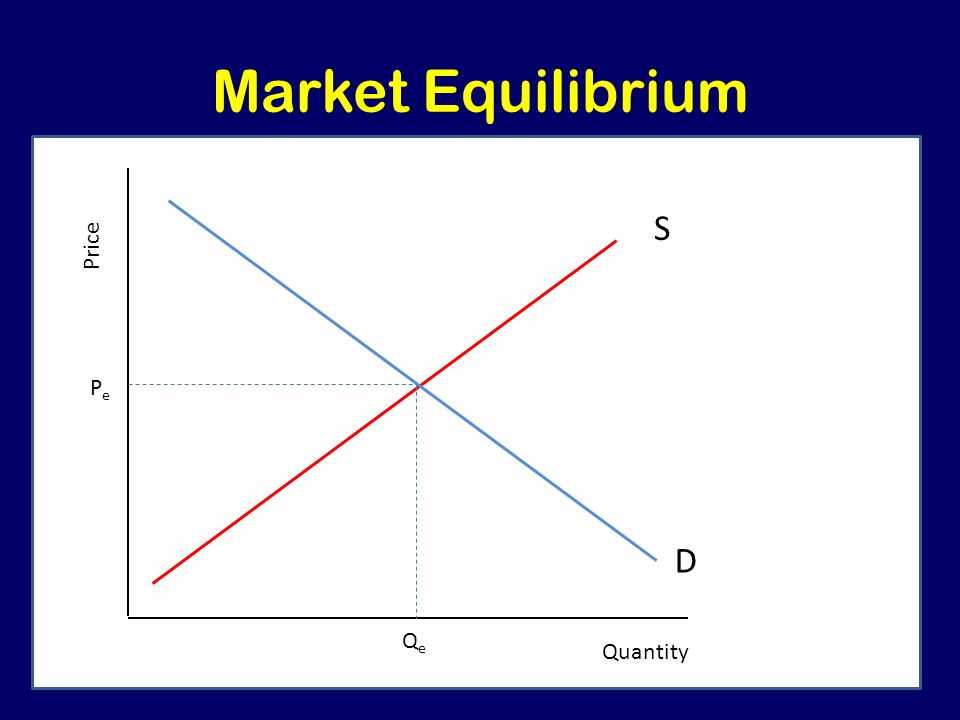
Understanding changes in market equilibrium is crucial for anyone involved in the world of economics. Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in a stable price. However, various factors can influence market equilibrium and cause shifts in the supply and demand curves.
One way to understand these changes is through the use of worksheet answers. These worksheets provide a practical way for students and professionals to analyze how different scenarios affect market equilibrium. They often include questions about the impact of changes in consumer preferences, technology advancements, government regulations, and external shocks on supply and demand.
By working through these worksheet answers, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of how the interplay between supply and demand affects prices and quantities in the market. They can learn to identify different types of shifts in supply and demand curves, such as changes in quantity demanded or supplied, changes in consumer income, and changes in the prices of related goods.
Overall, changes in market equilibrium worksheet answers provide a valuable tool for analyzing and predicting market dynamics. They allow individuals to apply theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios and enhance their decision-making skills in the field of economics. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or a business professional, working through these worksheets can greatly contribute to your understanding of market equilibrium and its ever-changing nature.
Changes in Market Equilibrium Worksheet Answers
In the study of economics, understanding market equilibrium is crucial. Market equilibrium refers to the point where the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in a stable price. However, market equilibrium can be affected by various factors, leading to changes in supply and demand and ultimately altering the equilibrium price and quantity in the market.
When there is a change in market equilibrium, it is important to analyze the factors that caused the shift. One factor that can affect equilibrium is changes in consumer preferences or tastes. For example, if there is an increase in the popularity of a particular product, it can lead to an increase in demand, shifting the demand curve to the right. This shift will result in a higher equilibrium price and quantity.
Another factor that can impact market equilibrium is changes in the prices of related goods. If the price of a substitute good decreases, consumers may shift their preference towards that substitute, causing a decrease in demand for the original product. This shift in demand will result in a lower equilibrium price and quantity. On the other hand, if the price of a complement good increases, it can lead to a decrease in demand, shifting the demand curve to the left and resulting in a lower equilibrium price and quantity.
Additionally, changes in production costs can also influence market equilibrium. If the cost of production decreases, producers may be willing to supply more of a product at each price level. This will shift the supply curve to the right, resulting in a lower equilibrium price but a higher equilibrium quantity. Conversely, if the cost of production increases, it can lead to a decrease in supply, shifting the supply curve to the left and resulting in a higher equilibrium price but a lower equilibrium quantity.
In conclusion, changes in market equilibrium occur due to various factors such as changes in consumer preferences, prices of related goods, and production costs. It is important to understand these factors and how they affect supply and demand in order to analyze and predict changes in market equilibrium. By doing so, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and adapt to the ever-changing dynamics of the market.
Understanding Market Equilibrium
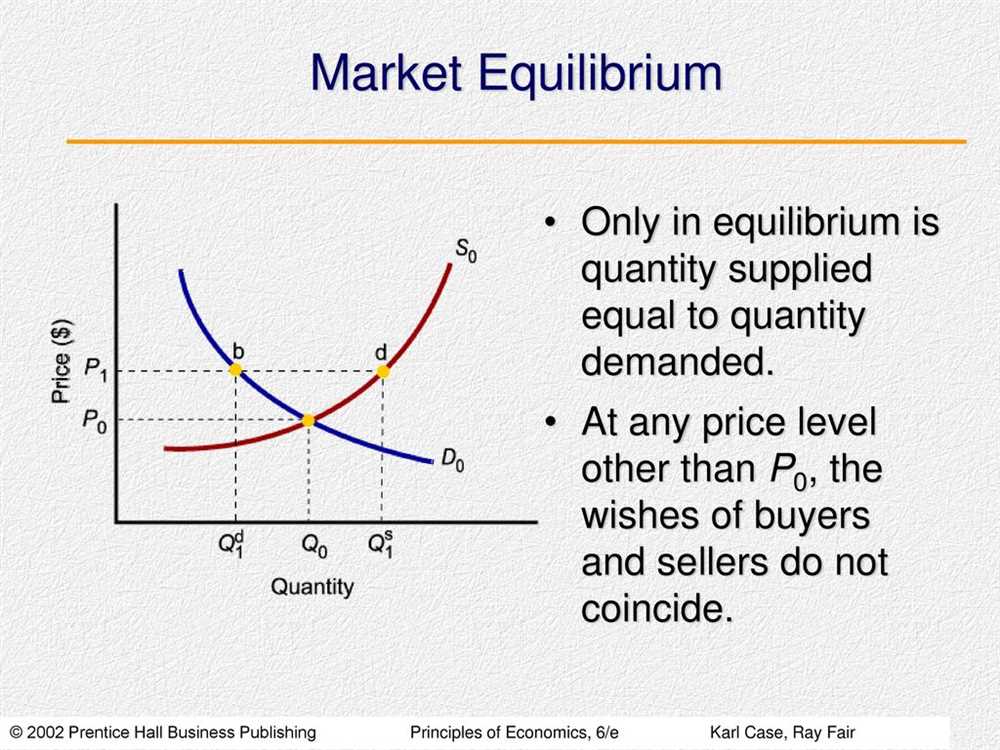
In the field of economics, market equilibrium is a crucial concept that plays a fundamental role in determining the prices of goods and services. It refers to the state of a market where the demand for a particular product or service is equal to its supply. When a market is in equilibrium, the quantity demanded by consumers matches the quantity supplied by producers, leading to a balance between the two forces.
The market equilibrium is determined by the interaction of supply and demand curves. The demand curve represents the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that consumers are willing to purchase at that price. On the other hand, the supply curve illustrates the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that producers are willing to supply at that price. The equilibrium price is the point where the demand and supply curves intersect, and the equilibrium quantity is the quantity at which this intersection occurs.
Changes in market conditions can lead to shifts in the supply or demand curve, consequently affecting the equilibrium price and quantity. For example, an increase in consumer income or a change in taste and preferences can result in an increase in demand, shifting the demand curve to the right. This would lead to a higher equilibrium price and quantity. On the other hand, if there is a decrease in production costs or an increase in the number of suppliers, the supply curve would shift to the right, resulting in a lower equilibrium price and higher equilibrium quantity.
Understanding market equilibrium is essential for businesses, policymakers, and consumers as it provides valuable insights into how prices are determined and how changes in market conditions can impact the economy. By analyzing market equilibrium, businesses can make informed decisions regarding pricing and production levels, while policymakers can implement policies to stabilize the economy. Consumers can also benefit by understanding market equilibrium as it helps them anticipate price changes and make informed purchasing decisions.
Factors Affecting Market Equilibrium

In economics, market equilibrium refers to the point where the supply of a good or service matches the demand for it. It is the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. However, market equilibrium is not fixed and can be influenced by various factors that affect the supply and demand of a product or service.
1. Changes in consumer preferences: Consumer preferences play a significant role in determining the demand for a product. If there is a shift in consumer preferences towards a particular product, it can lead to an increase in demand, causing an upward shift in the demand curve. As a result, the market equilibrium price and quantity will also change.
2. Changes in production costs: Changes in production costs, such as raw material prices, wages, or taxes, can affect the supply of a product. If production costs increase, suppliers may reduce their production, leading to a decrease in supply and an upward shift in the supply curve. This can result in an increase in the market equilibrium price and a decrease in the quantity demanded.
3. Changes in government policies: Government policies, such as price controls or subsidies, can have a significant impact on the market equilibrium. Price controls, such as maximum price limits, can create shortages or surpluses by restricting the price from reaching the equilibrium level. Subsidies, on the other hand, can encourage an increase in supply and a decrease in price.
4. Technological advancements: Technological advancements can lead to changes in production methods, which can affect both the supply and demand of a product. For example, the development of a more efficient production process can increase the supply of a product, leading to a decrease in its equilibrium price.
5. Changes in population or demographics: Changes in population or demographics can also impact the market equilibrium. A growing population or a shift in demographics can lead to an increase in demand for certain products or services, causing a shift in the demand curve and changes in the equilibrium price and quantity.
6. External factors: External factors such as natural disasters, political unrest, or changes in international trade agreements can disrupt the supply and demand dynamics of a market. These factors can lead to temporary shortages or surpluses and result in fluctuations in market equilibrium.
Overall, market equilibrium is influenced by a variety of factors, including consumer preferences, production costs, government policies, technological advancements, population changes, and external factors. Understanding these factors and their impact on market equilibrium is essential for businesses and policymakers to make informed decisions.
Demand and Supply Shifts
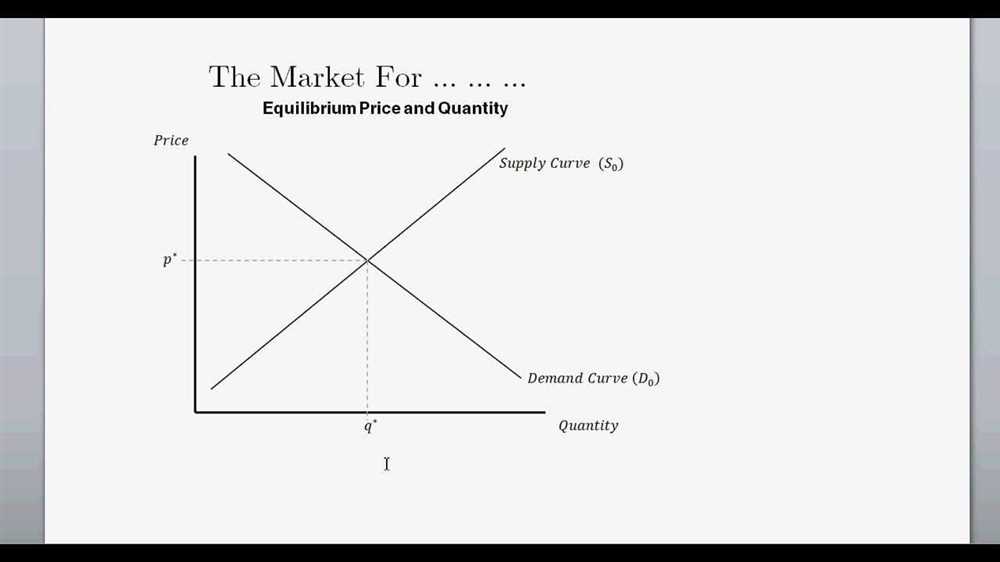
Demand and supply are two fundamental concepts in economics that determine the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. When there is a shift in either the demand or supply curve, the market equilibrium changes, leading to a new price and quantity.
Demand Shifts: The demand curve represents the willingness and ability of consumers to buy a certain quantity of a good or service at different prices. Several factors can cause a shift in the demand curve. For example, an increase in consumer income will lead to an increase in demand, shifting the curve to the right. On the other hand, a decrease in income will result in a decrease in demand, shifting the curve to the left. Other factors that can shift the demand curve include changes in consumer tastes and preferences, population size, and the prices of related goods.
Supply Shifts: The supply curve represents the willingness and ability of producers to sell a certain quantity of a good or service at different prices. Similar to demand, various factors can cause a shift in the supply curve. For instance, an increase in production costs, such as raw material prices or labor costs, will cause a decrease in supply, shifting the curve to the left. Conversely, a decrease in production costs will lead to an increase in supply, shifting the curve to the right. Other factors that can shift the supply curve include changes in technology, government regulations, and the number of producers in the market.
When there is a shift in either the demand or supply curve, the market equilibrium changes. If there is an increase in demand and no change in supply, the equilibrium price and quantity will increase. Conversely, if there is a decrease in demand and no change in supply, the equilibrium price and quantity will decrease. Similarly, if there is an increase in supply and no change in demand, the equilibrium price will decrease, while the quantity will increase. If there is a decrease in supply and no change in demand, the equilibrium price will increase, while the quantity will decrease.
In summary, demand and supply shifts can lead to changes in the market equilibrium, impacting the price and quantity of goods or services. Understanding these shifts is essential for businesses and policymakers to make informed decisions and predict market outcomes.
Effects of Price Changes
Price changes can have significant effects on the market equilibrium. When the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied by producers tends to increase, while the quantity demanded by consumers tends to decrease. This creates a surplus in the market, as the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. In response to this surplus, producers may adjust their prices downward in order to attract more buyers and reduce the surplus. As a result, the market will eventually reach a new equilibrium where the quantity demanded and supplied are equal again, but at a lower price.
Conversely, when the price of a good or service decreases, the quantity supplied tends to decrease, while the quantity demanded tends to increase. This creates a shortage in the market, as the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. In response to this shortage, producers may increase their prices in order to take advantage of the high demand and maximize their profits. As a result, the market will eventually reach a new equilibrium where the quantity demanded and supplied are equal again, but at a higher price.
Changes in market equilibrium due to price changes can have ripple effects throughout the entire market. For example, if the price of a key input for the production of a certain good increases, the cost of production will also increase. This may lead to a decrease in supply, as producers will be less willing or able to produce the same quantity at a higher cost. Similarly, if the price of a complementary good decreases, the demand for the good itself may increase, leading to an increase in demand and potentially an increase in price.
Overall, price changes play a crucial role in determining market equilibrium. They can affect both the supply and demand for a product, leading to changes in the quantity demanded and supplied, as well as the overall price level. Understanding these effects is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers to make informed decisions in a dynamic market environment.
Analysing Market Equilibrium Worksheet

When studying economics, it’s important to understand the concept of market equilibrium. This refers to the point at which the quantity demanded of a good or service equals the quantity supplied by producers. To analyze market equilibrium, we can use a worksheet that helps us understand the factors that can affect supply and demand.
The market equilibrium worksheet typically includes different scenarios that require students to analyze changes in supply and demand, and examine the resulting effects on the equilibrium price and quantity. It may present situations such as changes in consumer preferences, government regulations, or shifts in production costs.
Once students have filled out the worksheet, they can assess the impact of these changes on market equilibrium. They can determine if there is a surplus or shortage of the good or service, and predict how the equilibrium price and quantity will be affected. This exercise helps students understand the dynamics of supply and demand and how they interact to determine market outcomes.
The key to analyzing the market equilibrium worksheet effectively is to consider the underlying factors that drive supply and demand. It’s essential to understand how changes in these factors can shift the equilibrium and lead to changes in price and quantity. By mastering this concept, students can gain a deeper understanding of how markets function and make predictions about future market outcomes.
- Example worksheet questions to analyze:
- – What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity if there is an increase in production technology?
- – How will a decrease in consumer income affect the market equilibrium?
- – If the government imposes a tax on the production of a good, how will it impact the equilibrium price and quantity?
In conclusion, the market equilibrium worksheet is a valuable tool for studying economics. It helps students analyze changes in supply and demand and their impact on market outcomes. By thoroughly examining these scenarios, students can develop a deep understanding of market dynamics and make informed predictions about future market equilibrium.