Understanding gross income is a crucial step in managing personal finances. Whether you are an employee, a freelancer, or a business owner, having a clear understanding of how to calculate your gross income is essential for budgeting, tax planning, and overall financial well-being. In this article, we will explore the key concepts and calculations involved in determining gross income, and provide a comprehensive answer key to help you navigate any related questions or problems.
First and foremost, it is important to define what gross income actually means. Gross income refers to the total amount of money you earn, before any deductions or taxes are taken out. This includes all sources of income, such as wages, salaries, tips, self-employment earnings, rental income, and any other forms of income you may receive. Knowing your gross income is crucial for determining your tax liability and understanding your overall financial health.
Calculating your gross income involves adding up all the different sources of income you have received during a specific period of time, usually a year. This can be done by gathering your pay stubs, invoices, bank statements, and any other relevant documents that verify your income. Once you have gathered all the necessary information, you can simply add up the amounts to determine your total gross income. It is important to keep in mind that different types of income may be subject to different tax rates or deductions, so it is always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or refer to the appropriate tax regulations for specific guidance.
Chapter 1 Gross Income Answer Key

In Chapter 1, we learn about the concept of gross income and how it is calculated for tax purposes. Gross income includes all income received by an individual, whether in the form of money, property, or services. However, there are certain types of income that are not included in gross income, such as gifts, inheritances, and life insurance proceeds.
One key aspect of determining gross income is understanding what qualifies as taxable income. Generally, all income received is considered taxable, unless specifically excluded by law. Some examples of taxable income include wages, salaries, tips, commissions, rental income, and self-employment income. It is important to note that even if you do not receive a formal statement of income, you are still required to report it on your tax return.
To calculate gross income, you start with your total income and then subtract any deductions or adjustments to arrive at your adjusted gross income (AGI). Deductions can include expenses such as business expenses, education expenses, and certain medical expenses. Once you have your AGI, you can then determine your taxable income by subtracting any applicable exemptions and deductions.
It is important to keep accurate records of your income and expenses throughout the year to ensure you can accurately calculate your gross income. This includes keeping track of any income you receive, such as earnings from a job or rental property, as well as any expenses you incur that may be deductible.
In conclusion, understanding the concept of gross income and how it is calculated is crucial for accurately reporting and paying taxes. By following the guidelines and regulations set forth by the IRS, individuals can ensure they are properly reporting their income and deductions, avoiding any potential penalties or audits.
Importance of Gross Income
Gross income is a key concept in understanding an individual’s financial situation and plays a crucial role in various aspects of personal finance. It refers to the total amount of income earned before any deductions or taxes are taken out. Here, we will explore the importance of gross income in detail.
1. Determining Tax Liability: Gross income is used as the starting point in calculating an individual’s tax liability. It serves as the basis for determining the applicable tax rate and the amount of taxes owed. Understanding one’s gross income is essential for proper tax planning and compliance.
2. Budgeting and Financial Planning: Gross income provides a clear picture of one’s earning potential, allowing individuals to create realistic budgets and make informed financial decisions. By knowing their gross income, individuals can assess their ability to meet various financial goals, such as saving for retirement, paying off debt, or making major purchases.
3. Qualifying for Loans and Credit: Lenders often consider an individual’s gross income when evaluating loan applications. It helps lenders assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan and determines the loan amount that can be granted. A higher gross income may increase the chances of loan approval and secure better lending terms.
4. Salary Negotiations: When negotiating salary or compensation packages, understanding one’s gross income is crucial. It enables individuals to assess the overall value of the offer and negotiate from a position of knowledge. By knowing their gross income, individuals can confidently discuss salary expectations and evaluate the impact of any potential deductions or benefits.
5. Financial Transparency: Gross income plays a vital role in maintaining financial transparency, especially when dealing with joint finances or shared expenses. It allows individuals to have open discussions about income, contribute to household expenses proportionally, and plan for shared financial goals effectively.
In conclusion, gross income holds significant importance in personal finance. It serves as a foundation for tax calculations, helps individuals budget and plan their finances, influences loan eligibility, assists in salary negotiations, and promotes financial transparency. Understanding one’s gross income is essential for making informed financial decisions and managing overall financial well-being.
Definition of Gross Income

Gross income is the total amount of income earned by an individual or business before any deductions or expenses are taken into account. It is a measure of the total money received from all sources, including wages, salaries, tips, bonuses, rental income, and interest. Gross income is an important concept in finance and tax law, as it is used to determine an individual’s tax liability and eligibility for certain benefits and deductions.
There are several key characteristics of gross income that differentiate it from other types of income. First, gross income includes all forms of taxable income, whether they are received in cash or in-kind. This includes not only salary or wages, but also income from investments, real estate, and self-employment. Second, gross income does not take into account any deductions or expenses. It is the total amount earned before any expenses or deductions are subtracted. Third, gross income is an annual figure, representing the total income earned over a specific period of time, typically a calendar year.
In order to calculate gross income, an individual or business must add up all the income received from various sources. This can be done using a variety of methods, such as reviewing pay stubs, bank statements, and tax forms. It is important to note that not all forms of income are considered gross income for tax purposes. Some types of income, such as certain government benefits or gifts, may be excluded from gross income calculations. It is necessary to consult the relevant tax laws and regulations to determine what types of income should be included in gross income.
Gross income plays a crucial role in financial planning and tax compliance. It serves as the starting point for determining an individual’s tax liability and eligibility for certain deductions and benefits. By understanding the definition and calculation of gross income, individuals and businesses can accurately report their income and fulfill their tax obligations.
Types of Income Included in Gross Income
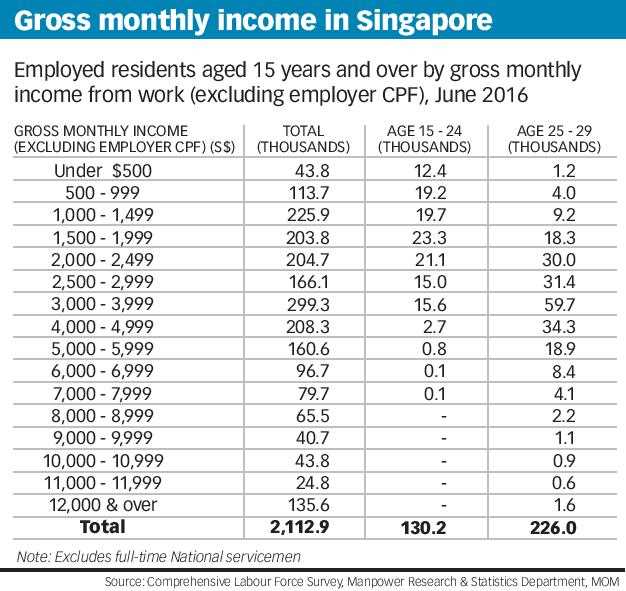
Gross income includes various types of income that individuals earn throughout the year. This income is subject to taxation and must be reported on their tax returns. Here are some key types of income that are included in gross income:
- Wages and Salaries: This includes the income individuals earn from their jobs, including regular wages, salaries, bonuses, tips, and commissions.
- Self-Employment Income: Individuals who are self-employed must report their net income from their business activities. This can include income from freelancing, consulting, or running a small business.
- Interest and Dividends: Income earned from interest on savings accounts, certificates of deposit, or investments, as well as dividends received from stocks and mutual funds, is considered part of gross income.
- Rental Income: If individuals own rental properties and receive rental income from tenants, this income is included in gross income.
- Capital Gains: Profit made from the sale of assets, such as stocks, real estate, or collectibles, is considered a capital gain and is included in gross income.
- Retirement Income: Income received from pensions, annuities, or distributions from retirement accounts, such as IRAs or 401(k)s, is considered part of gross income.
- Social Security Benefits: While not all social security benefits are taxable, a portion of these benefits may be included in gross income, depending on the individual’s income level.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of the types of income that are included in gross income. Individuals should consult with a tax professional or refer to the IRS guidelines for a comprehensive list of what should be included when calculating their gross income.
Exclusions from Gross Income

Gross income is the total amount of income received by an individual or business, but not all income is subject to taxation. There are certain exclusions from gross income that are specifically defined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). These exclusions allow taxpayers to exclude certain types of income from their taxable income, reducing their overall tax liability.
One major exclusion from gross income is the exclusion for gifts and inheritances. Amounts received as a gift or inheritance are generally not considered income and are not taxable. This means that if you receive a cash gift from a family member or inherit property, you do not have to include that amount in your gross income for tax purposes.
Another common exclusion is the exclusion for certain employee benefits. Employer-provided benefits such as health insurance, retirement contributions, and tuition assistance are often excluded from gross income. This means that the value of these benefits is not subject to income tax, providing a significant tax advantage for employees.
Other exclusions from gross income include certain types of scholarships and fellowships, certain life insurance proceeds, and certain types of qualified education expenses. It is important for taxpayers to be aware of these exclusions and properly report their income to ensure they are not paying taxes on income that is not subject to taxation.
In conclusion, exclusions from gross income provide taxpayers with the opportunity to reduce their overall tax liability by excluding certain types of income from their taxable income. By properly understanding and applying these exclusions, taxpayers can maximize their tax savings and effectively manage their finances.
Gross Income Calculation
Calculating gross income is an essential step in understanding one’s financial situation. Gross income is the total amount of income earned before any deductions or taxes are taken out. It includes all sources of income, such as wages, salaries, tips, rental income, and investments.
To calculate gross income, you need to add up all sources of income for a specific period. This can be done by gathering all relevant documents, such as pay stubs, bank statements, and rental agreements. For individuals who receive a regular paycheck, the process is relatively straightforward. You can add up all the earnings from your pay stubs, including base salary, overtime, and any bonuses or commissions.
If you have additional sources of income, such as rental properties or investments, you will need to include those as well. Rental income can be calculated by adding up the total amount of rent received during the specified period. For investments, you will need to include any interest, dividends, or capital gains earned.
Once you have gathered all the necessary information, you can add up all the sources of income to determine your gross income. This total amount will give you a clear picture of your overall earnings before any deductions or taxes are taken out. It is an important figure to know when budgeting, applying for loans, or filing your tax returns.
Reporting Gross Income
When filing your taxes, one of the most important aspects is reporting your gross income. This is the total amount of income you earn before any deductions or exemptions. It includes all sources of income, such as wages, salaries, tips, rental income, and investment income.
Wages and salaries: This is the main source of income for many individuals. It includes the money you earn from your job, whether it’s through hourly wages or an annual salary. It is important to report all wages and salaries accurately to ensure that your tax return is correct.
Tips: If you work in a job where you receive tips, such as in the service industry, these tips must also be reported as part of your gross income. This includes both cash tips and credit card tips. It is important to keep accurate records of your tips to properly report them on your tax return.
Rental income: If you own rental properties and collect rental payments from tenants, this income must also be included in your gross income. Whether you have a single rental property or multiple properties, you must report the rental income on your tax return.
Investment income: This includes income from stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other investments. Whether you receive dividends, interest, or capital gains, this income must be reported as part of your gross income. It is important to keep track of all investment income and accurately report it on your tax return.
Ultimately, reporting your gross income accurately is essential for correctly calculating your tax liability. Failing to report all sources of income can result in penalties and audits. It is important to consult with a tax professional or use tax software to ensure that you accurately report your gross income and take advantage of any deductions or exemptions you may be eligible for.