
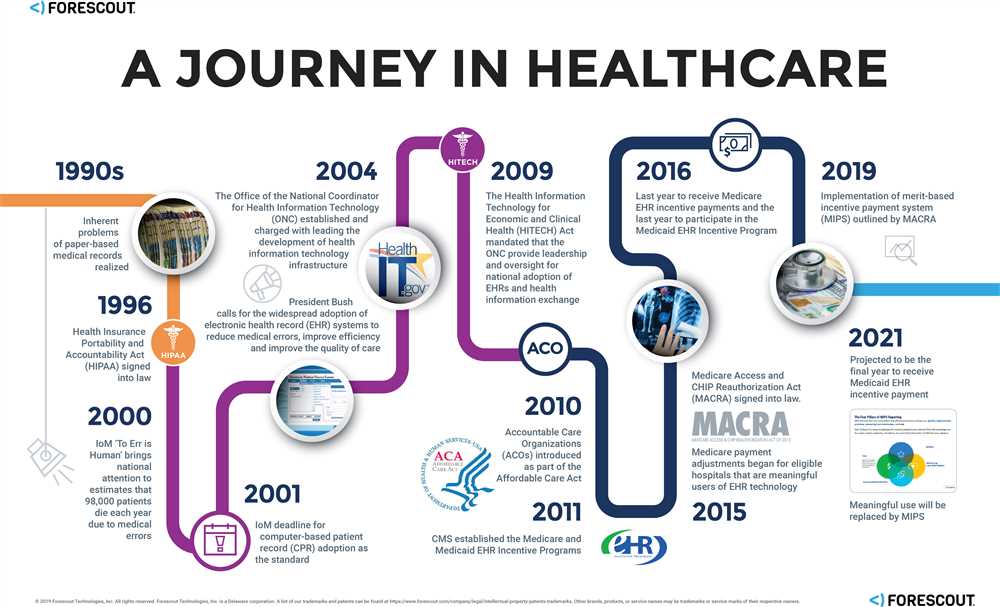
Healthcare has evolved significantly throughout history, with advancements in medical knowledge, technology, and the organization of healthcare systems. Understanding the history and trends of healthcare is essential for comprehending the current state of the field and predicting future developments.
One significant trend in the history of healthcare is the shift from traditional medicine to evidence-based practices. In the past, medical treatments were often based on superstition and untested theories. The development of scientific methods and research has led to a more systematic and evidence-based approach to healthcare, ensuring that treatments and interventions are backed by scientific evidence.
Another important trend in healthcare is the increasing emphasis on preventive care. While historical approaches to healthcare focused primarily on treating illnesses and injuries, modern healthcare systems are recognizing the importance of preventing diseases and promoting overall wellness. This shift towards preventive care aims to reduce healthcare costs, improve population health, and enhance the quality of life for individuals.
Additionally, technological advancements have revolutionized healthcare in recent decades. From the invention of x-rays and antibiotics to the use of electronic health records and telemedicine, technology has greatly impacted the quality and accessibility of healthcare services. These advancements have allowed for more accurate diagnoses, more efficient treatment options, and improved communication and coordination among healthcare providers.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the history and trends of healthcare is crucial for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and patients alike. By recognizing the evolution of healthcare practices and the current trends shaping the field, we can better adapt to the changing healthcare landscape and effectively address the healthcare needs of individuals and communities.
Chapter 1: History and Trends of Healthcare Answer Key
The history and trends of healthcare play a crucial role in understanding the development and evolution of the industry. This answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the key concepts discussed in Chapter 1.
1. Define healthcare:

Healthcare refers to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of illness, injury, and disease in individuals. It encompasses a wide range of medical services, including primary care, specialty care, and emergency services.
2. Explain the evolution of healthcare:
The evolution of healthcare can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where traditional healers and herbal remedies were prevalent. Over time, advancements in medical knowledge and technology led to the establishment of formal medical institutions and the development of modern healthcare systems. The Industrial Revolution and scientific discoveries further revolutionized healthcare, leading to significant improvements in medical practices and patient outcomes.
3. Identify the major trends in healthcare:

- Rising healthcare costs: Healthcare costs have been steadily increasing, placing a significant burden on individuals, families, and governments.
- Advancements in technology: Technological innovations have revolutionized healthcare, enabling the development of advanced diagnostic and treatment methods.
- Aging population: The aging population has resulted in increased demand for healthcare services, particularly for chronic disease management.
- Healthcare reform: Governments around the world have implemented healthcare reforms to improve access, quality, and affordability of healthcare services.
- Focus on preventive care: There is a growing emphasis on preventive care to promote overall health and reduce healthcare costs.
4. Discuss the impact of historical events on healthcare:

Historical events, such as wars, epidemics, and medical breakthroughs, have had a profound impact on healthcare. For example, World War II led to the development of antibiotics and advancements in trauma care. The HIV/AIDS epidemic prompted significant research in virology and the development of antiretroviral therapy. These events have shaped healthcare practices and policies.
5. Explain the role of healthcare professionals:
Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and allied health professionals, play a vital role in delivering quality healthcare. They are responsible for diagnosing and treating patients, providing personalized care, and promoting health and wellness. Healthcare professionals also contribute to research, education, and policy development to advance the field of healthcare.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Primary care | Basic healthcare services provided by primary care providers, such as family doctors and general practitioners. |
| Specialty care | Specialized healthcare services provided by healthcare professionals with expertise in specific medical fields. |
| Industrial Revolution | A period of rapid industrialization in the 18th and 19th centuries, leading to significant advancements in technology, including healthcare. |
| Chronic disease management | The ongoing care and treatment of chronic conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. |
| Antiretroviral therapy | A combination of medications used to treat HIV infection and prevent the progression of AIDS. |
The Evolution of Healthcare
Healthcare has undergone significant evolution throughout history, adapting to the changing needs and advancements in medical knowledge and technology. From ancient times to the present day, healthcare systems have evolved to provide better care and improve patient outcomes.
One of the earliest known systems of healthcare can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Greece. These civilizations developed an understanding of anatomy, performed surgeries, and used herbal remedies to treat various ailments. However, healthcare practices were often influenced by superstitions and religious beliefs.
During the Middle Ages, healthcare was largely provided by religious orders and monasteries. Medieval medicine relied heavily on the theory of the Four Humors and treatments such as bloodletting and herbal medicine. As advancements in medical knowledge and techniques emerged during the Renaissance, the field of medicine began to separate from religious influence and became more scientific.
The 19th century witnessed significant advancements in healthcare, with the development of anesthesia, sterilization techniques, and the discovery of antibiotics. These breakthroughs revolutionized surgical procedures and the treatment of infectious diseases, improving patient outcomes and reducing mortality rates.
Today, healthcare has become highly specialized and technologically advanced. Medical professionals have access to a wide range of diagnostic tools, imaging technologies, and innovative treatments. The focus has shifted towards preventive care, early detection of diseases, and personalized medicine. Trends such as telemedicine and digital health are also transforming the way healthcare is delivered, making it more accessible and convenient for patients.
In conclusion, the evolution of healthcare has been driven by the quest for better understanding of the human body, advancements in medical knowledge, and technological innovations. As healthcare continues to evolve, it is crucial to adapt to changing needs and embrace new technologies to further improve patient care and outcomes.
Ancient Healthcare Practices
Ancient civilizations had their own methods and practices when it came to healthcare. These practices varied depending on the region, culture, and resources available. Despite the lack of modern medical knowledge and technology, ancient societies developed unique approaches to treating and preventing illness.
1. Egyptian Medicine: The ancient Egyptians had a deep understanding of anatomy and medical knowledge. They believed that the body was made up of channels and vessels through which blood and other vital fluids flowed. They used herbs, natural remedies, and surgical procedures to treat a variety of conditions. Egyptian physicians were highly regarded, and their medical texts, such as the Ebers Papyrus, provided detailed instructions on various treatments.
2. Greek Medicine: The ancient Greeks made significant contributions to healthcare. Hippocrates, often referred to as the father of medicine, established a code of ethics for physicians and emphasized the importance of observation and documentation in medical practice. Greek physicians believed in the balance of the four humors (blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile) and used therapies such as diet, exercise, and herbal remedies to restore this balance.
3. Traditional Chinese Medicine: Traditional Chinese medicine has a rich history dating back thousands of years. It is based on the concept of Qi, or life force, flowing through the body along meridians. Practitioners of traditional Chinese medicine use acupuncture, herbal medicine, and other therapies to balance the flow of Qi and treat various health conditions. This holistic approach considers the mind, body, and spirit as interconnected.
4. Ayurvedic Medicine: Originating in ancient India, Ayurvedic medicine is one of the oldest healthcare systems in the world. It focuses on achieving balance in the body, mind, and spirit through practices such as diet, herbs, yoga, and meditation. Ayurvedic practitioners believe that each person has a unique constitution, made up of three doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), and aim to restore balance by identifying and addressing imbalances in these doshas.
These ancient healthcare practices laid the foundation for modern medicine. While some of the methods may seem unconventional by today’s standards, they reflect the resourcefulness and ingenuity of our ancestors in their quest for health and healing.
The Impact of the Middle Ages on Healthcare
During the Middle Ages, healthcare practices were heavily influenced by religious beliefs and superstitions. The Catholic Church played a dominant role in society, and its teachings greatly influenced medical practices and attitudes towards health and illness. The church emphasized the importance of spiritual healing and viewed physical ailments as a punishment for sin. This belief led to the practice of confession and penance, where individuals would seek forgiveness for their sins in order to be healed.
Medicine during this time was largely based on traditional knowledge and remedies passed down through generations. Monks and other religious figures often acted as healers and used herbal remedies, bloodletting, and prayers to treat illnesses. The use of charms and amulets was also common, as they were believed to have protective and healing powers. However, these practices were often ineffective and sometimes even harmful, as the understanding of the human body and the causes of diseases was limited.
Medical Institutions and Education
During the Middle Ages, medical education and the establishment of medical institutions were limited. Universities began to emerge during this time, but medical education was not a prominent focus. The study of medicine was often conducted within monasteries and religious communities, where knowledge was primarily based on ancient Greek and Roman texts. Despite the limited formal education, medical practitioners during this period gradually gained more recognition and respect.
Healthcare was mainly provided in the form of religious hospitals, where monks and nuns cared for the sick. These hospitals were typically attached to monasteries or convents and provided basic medical care and shelter for the poor. However, the level of care varied depending on the resources available and the dedication of the religious figures managing the hospitals. Despite the challenges and limitations, these institutions played a crucial role in providing some level of healthcare during the Middle Ages.
Conclusion
The Middle Ages had a significant impact on healthcare practices, shaping the way illnesses were perceived and treated. The dominance of the Catholic Church influenced medical beliefs and practices, often prioritizing spiritual healing over physical remedies. Despite the limitations in medical education and institutions, healthcare was still provided in the form of religious hospitals, contributing to the overall wellbeing of communities during this time.
The Role of the Renaissance in Healthcare
The Renaissance, a period of cultural and intellectual awakening that occurred in Europe from the 14th to the 17th century, played a significant role in the development of healthcare. During this time, there was a renewed interest in the human body and a shift towards a more scientific approach to medicine.
One of the key figures during the Renaissance who influenced healthcare was Andreas Vesalius, a Belgian anatomist. Vesalius challenged the traditional teachings of Galen, a prominent ancient Greek physician, by conducting his own dissections and publishing his findings in his groundbreaking book, “De humani corporis fabrica.” This book revolutionized the study of anatomy and laid the foundation for modern anatomical studies.
The Renaissance also saw the rise of humanism, an intellectual movement that placed emphasis on the potential and dignity of human beings. This led to the establishment of new medical schools and the training of physicians in human anatomy and physiology. The shift towards humanism contributed to an improved understanding of the human body and paved the way for advancements in medical knowledge and practice.
Furthermore, the Renaissance fostered an environment of scientific inquiry and experimentation. Scientists and physicians began to question traditional beliefs and explore new ideas. One of the notable advancements during this time was the development of new surgical techniques, including innovative methods for treating wounds and amputations. This era also saw the use of new instruments, such as forceps and scalpels, which greatly improved surgical procedures.
In conclusion, the Renaissance had a profound impact on healthcare. It brought about a renewed focus on the human body, led to advancements in anatomical studies, emphasized the importance of humanism in medicine, and encouraged scientific inquiry and experimentation. These developments laid the groundwork for modern healthcare and continue to shape the field today.