Proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining good health and wellness. In Chapter 10 of our nutrition series, we delve into Lesson 2, which focuses on understanding the essential nutrients our bodies need to function optimally. This lesson provides an answer key to help us identify and comprehend the critical components of a balanced diet.
As we explore the lesson, we learn about the importance of macronutrients, which are the nutrients required in large quantities. These include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which provide the energy needed for bodily functions. In addition to macronutrients, we also discover the significance of micronutrients, which are needed in smaller amounts but are equally vital for supporting various bodily processes.
Understanding the roles and sources of these essential nutrients is crucial for making informed food choices. With the help of the answer key, we can identify the main sources of each nutrient, such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and lean meats. By incorporating a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods into our diet, we can ensure that our bodies receive the necessary vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds.
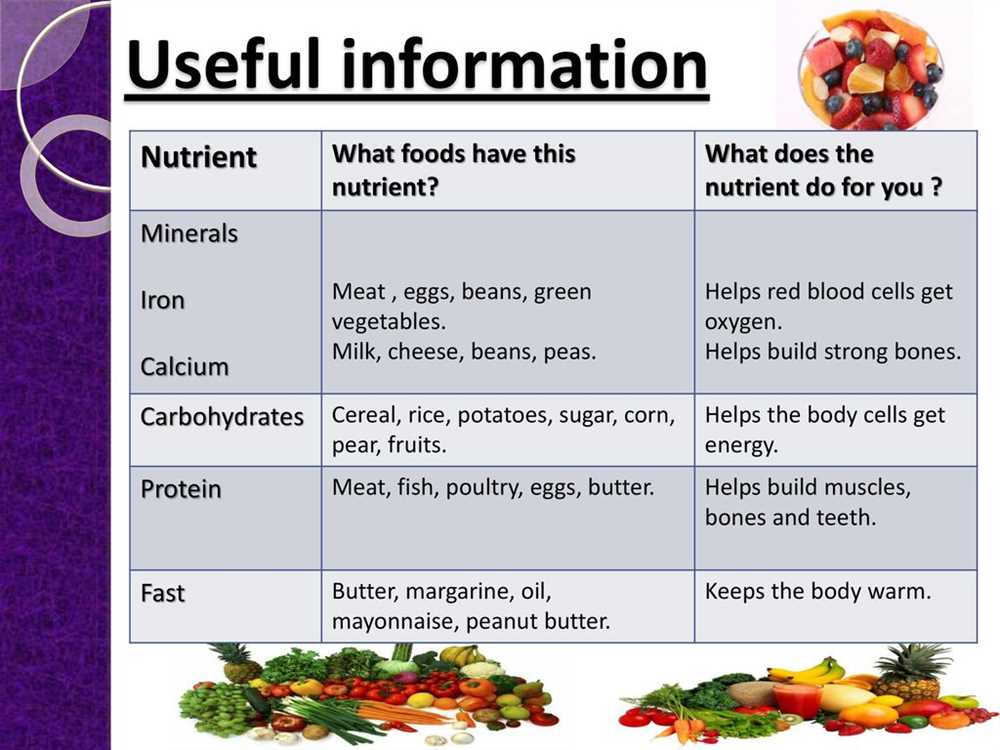
Chapter 10 Nutrition for Health Lesson 2 Nutrients Answer Key
In Chapter 10 of “Nutrition for Health”, Lesson 2 focuses on understanding the different nutrients that our bodies need for optimal health. This answer key will provide a breakdown of the key nutrients discussed in the lesson.
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They can be found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is used by the body as fuel.
2. Proteins
Proteins play a crucial role in the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. They are made up of amino acids and can be found in foods such as meat, fish, poultry, beans, and nuts.
3. Fats
Fats are a concentrated source of energy and are necessary for the absorption of certain vitamins. They can be found in foods such as oils, butter, cheese, and fatty meats. It is important to consume fats in moderation as they can contribute to weight gain and other health issues.
4. Vitamins
Vitamins are essential for maintaining good health and preventing disease. They can be divided into two categories: fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and water-soluble vitamins (C and the B vitamins). Vitamins can be found in a variety of foods, such as fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and whole grains.
5. Minerals

Minerals are important for various bodily functions, such as building strong bones and teeth, regulating fluid balance, and aiding in muscle contraction. Some examples of minerals include calcium, iron, potassium, and zinc. They can be found in foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and lean meats.
6. Water

Water is essential for life and is involved in almost every bodily process. It helps to regulate body temperature, transport nutrients, and remove waste. It is important to drink an adequate amount of water every day to stay hydrated.
By understanding the role of each of these nutrients and including a variety of them in our diets, we can maintain optimal health and prevent nutritional deficiencies.
What Are Nutrients?
Nutrients are the essential compounds found in food that our bodies need to function properly and maintain good health. They provide energy, support growth and development, and help regulate various bodily processes. There are six major categories of nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water.
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are broken down into glucose and used by the cells for fuel. Good sources of carbohydrates include grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
Proteins are essential for the growth, maintenance, and repair of body tissues. They are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. Good sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based sources such as beans and tofu.
Fats are an important source of energy and provide insulation for the body. They also help absorb fat-soluble vitamins. Good sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and oils like olive oil and coconut oil.
Vitamins are organic compounds that our bodies need in small amounts to function properly. They play a crucial role in various bodily processes, such as metabolism and immune function. Good sources of vitamins include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products.
Minerals are inorganic compounds that are essential for the body’s structure and regulation. They are necessary for the proper functioning of enzymes, maintaining fluid balance, and bone health. Good sources of minerals include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, meat, and dairy products.
Water is often overlooked, but it is one of the most important nutrients for our bodies. It helps regulate body temperature, aids in digestion, carries nutrients and waste products, and lubricates joints. It is essential to drink an adequate amount of water every day to stay hydrated and support overall health.
In conclusion, nutrients are essential compounds found in food that our bodies need to function properly and maintain good health. They provide energy, support growth and development, and help regulate various bodily processes. By consuming a balanced diet that includes all the necessary nutrients, we can ensure optimal health and well-being.
Why Do We Need Nutrients?

Nutrients are essential for the proper functioning of our bodies. They provide us with the necessary energy, promote growth and repair of tissues, and help maintain a healthy immune system. Without nutrients, our bodies would not be able to perform basic tasks such as breathing, moving, and digesting food.
One key reason why we need nutrients is for energy production. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are all sources of energy that fuel our everyday activities. Carbohydrates are quickly broken down into glucose, which is used by our cells as a primary source of energy. Proteins also provide energy, but their main role is to build and repair tissues. Fats, although often associated with negative health effects, are an important source of energy and aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Another reason why we need nutrients is for growth and development. During childhood and adolescence, proper nutrient intake is crucial for optimal growth and development. Nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and protein are particularly important for bone health and muscle growth. Without these nutrients, children may experience stunted growth and development.
Nutrients also play a role in maintaining a healthy immune system. Certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C and zinc, are known for their immune-boosting properties. They help protect our bodies against infections, promote wound healing, and support the production of immune cells. Without these nutrients, our immune system may be weakened, making us more susceptible to illness and disease.
In conclusion, nutrients are essential for our overall health and well-being. They provide energy, support growth and development, and help maintain a strong immune system. By consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, we can ensure that our bodies receive all the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning.
The Six Essential Nutrients

In order to maintain a healthy body, it is important to consume a balanced diet that includes all six essential nutrients. These nutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. Each of these nutrients plays a vital role in supporting various functions within the body and ensuring overall well-being.
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are found in foods such as bread, rice, pasta, fruits, and vegetables. Carbohydrates provide the body with glucose, which is used for immediate energy or stored as glycogen for later use.
Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues in the body. They are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. Good sources of protein include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, beans, and dairy products.
Fats: Fats are important for the absorption of certain vitamins and for providing the body with energy. They also help protect organs and regulate body temperature. Healthy sources of fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Vitamins: Vitamins are necessary for the proper functioning of the body and help prevent various diseases. There are 13 essential vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin D, and the B vitamins. Vitamins can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products.
Minerals: Minerals are needed for the body to perform various functions, such as maintaining strong bones and teeth, regulating blood pressure, and carrying oxygen in the blood. Examples of minerals include calcium, iron, zinc, and potassium. Good sources of minerals include dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and legumes.
Water: Water is essential for the proper functioning of the body and is involved in nearly every bodily process. It helps regulate body temperature, transports nutrients and oxygen, and removes waste products. It is important to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support overall health.
In conclusion, consuming a diet that includes all six essential nutrients is crucial for maintaining a healthy body. Each nutrient has its own specific role and contributes to overall well-being. By ensuring a balanced intake of these nutrients, individuals can support their body’s functions and promote optimal health.
Carbohydrates: Fuel for the Body
Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients needed by the body for energy. They are the primary source of fuel for our brain, muscles, and organs. Carbohydrates provide quick energy, as they are easily broken down into glucose, which can be used by our cells for energy production. They are essential for physical activity and maintaining proper bodily functions.
Carbohydrates can be found in a variety of foods such as grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. They come in two main forms: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are found in foods like candy, soda, and processed sweets. They provide quick bursts of energy but are quickly metabolized by the body. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, like whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables, take longer to break down and provide a more sustained release of energy.
It is important to include carbohydrates in our diet to meet our body’s energy needs. However, it is crucial to choose carbohydrates wisely and opt for complex carbohydrates that provide essential nutrients and fiber, rather than simple sugars that offer little nutritional value. The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates varies depending on an individual’s age, gender, and activity level.
- Include whole grains, such as brown rice and whole wheat bread, in your meals to increase your complex carbohydrate intake.
- Choose fruits and vegetables that are rich in carbohydrates, such as bananas and sweet potatoes.
- Avoid or limit your consumption of sugary foods and beverages, as they can lead to weight gain and other health issues.
The body relies on carbohydrates as its primary source of energy, so it is important to fuel it properly with the right types of carbohydrates. Balancing carbohydrate intake with other essential nutrients is key to maintaining good health and energy levels.
Proteins: Building Blocks of the Body
Proteins are a vital nutrient that plays numerous important roles in the human body. They serve as the building blocks of life, as they are responsible for the growth, maintenance, and repair of tissues. Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids, which are joined together to form long chains.
There are 20 different amino acids that can be combined in various ways to create different proteins with different functions. Some amino acids can be synthesized by the body, while others, known as essential amino acids, must be obtained through the diet. These essential amino acids are crucial for overall health and wellbeing.
Proteins are involved in almost every process in the body. They are essential for the formation of enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and transport molecules. Enzymes, for example, speed up chemical reactions in the body, while hormones regulate various bodily functions.
Proteins are also responsible for maintaining the structure and integrity of cells, tissues, and organs. They provide support to muscles, tendons, and ligaments, allowing for movement and physical activity. In addition, proteins play a vital role in the immune system, helping to defend the body against infections and diseases.
Without an adequate intake of protein, the body may experience muscle wasting, slowed growth, weakened immune function, and impaired healing. It is important to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein sources to ensure the body receives all the essential amino acids it needs to function optimally.
Fats: Energy Storage and Insulation
Fats play a crucial role in our body as they serve as a source of energy and insulation. They are a concentrated and efficient form of energy storage. When carbohydrates and proteins are not sufficient to meet the body’s energy demands, fats are broken down to release energy. This energy can be used for various bodily functions such as maintaining body temperature, carrying out physical activities, and supporting vital organs.
Fats provide insulation to our body by forming a protective layer around vital organs and acting as an insulating material. This insulation helps to regulate body temperature and protect the internal organs from external shocks and injuries. Without adequate fat in our body, we would be more susceptible to temperature fluctuations and physical trauma.
The role of fats in energy storage: Fats contain more than twice the amount of energy per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins. This high energy density makes fats an efficient energy storage option. The excess energy from the food we consume is converted into triglycerides and stored in adipose tissues throughout the body. These triglycerides can be broken down and used as a source of energy when needed.
The role of fats in insulation: Fats are an essential component of adipose tissue, which acts as a natural insulation layer in our body. Adipose tissue not only provides insulation but also acts as a cushioning material, protecting organs from external forces. The layer of fat under the skin helps to regulate body temperature by reducing heat loss and preventing cold air from reaching the internal organs.
In conclusion, fats play a vital role in our body as an efficient energy storage option and an insulating material. They provide the necessary energy for various bodily functions and help regulate body temperature. It is important to maintain a balanced intake of fats to ensure proper functioning of our body.