Welcome to the answer key for Chapter 12 of our English grammar course. In this chapter, we will be taking a comprehensive look at the different parts of speech in the English language. Understanding and correctly identifying the various parts of speech is essential for effective communication and developing strong writing skills.
In this answer key, you will find a detailed breakdown of each part of speech covered in Chapter 12, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each section provides a clear explanation of the function and usage of the specific part of speech, along with examples to illustrate their use in context.
Whether you are a student looking to improve your grammar skills, a teacher searching for additional resources, or simply someone interested in deepening your understanding of the English language, this answer key is designed to help you master the parts of speech. By familiarizing yourself with the different parts of speech and their roles within sentences, you will be better equipped to express yourself accurately and effectively in both spoken and written English.
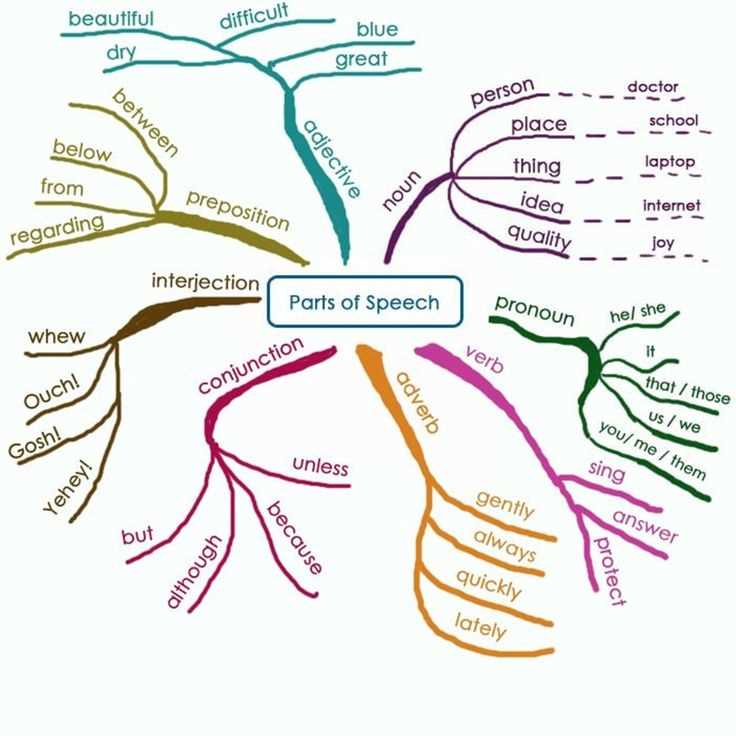
Chapter 12 Parts of Speech Overview Answer Key
In Chapter 12, we reviewed the different parts of speech, which are the building blocks of language. Understanding the different parts of speech is essential for constructing sentences and conveying meaning effectively.
Here is the answer key for the exercises in the chapter:
Noun
- A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Example: The dog ran quickly.
Pronoun
- A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun.
- Example: She is an excellent singer.
Verb
- A verb is a word that expresses an action or a state of being.
- Example: He ran to catch the bus.
Adjective
- An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun.
- Example: The blue sky is beautiful.
Adverb
- An adverb is a word that describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
- Example: She sang loudly at the concert.
Preposition
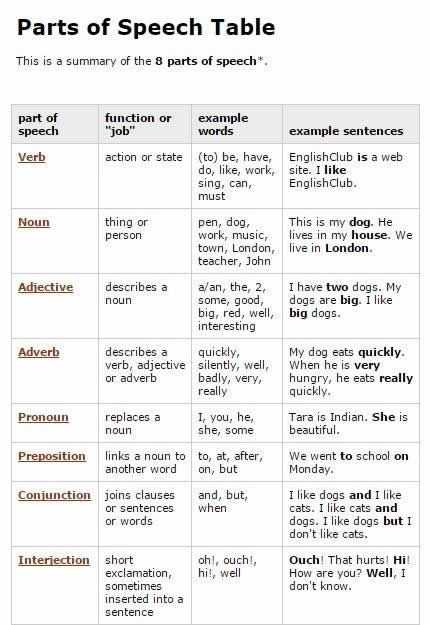
- A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence.
- Example: The book is on the table.
Conjunction
- A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses.
- Example: I like both coffee and tea.
Interjection
- An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotion or surprise.
- Example: Wow, that was amazing!
Remember, identifying the parts of speech in a sentence helps to clarify the meaning and structure of the sentence. Practice identifying the different parts of speech in various sentences to enhance your understanding and improve your communication skills.
Nouns
Nouns are one of the most important parts of speech in the English language. They are used to name people, animals, objects, places, and concepts. Nouns can be concrete, such as “dog” or “car,” which represent tangible things that can be seen and touched. They can also be abstract, such as “love” or “happiness,” which represent ideas or emotions.
Nouns can be singular or plural. Singular nouns refer to one person, animal, object, or concept, while plural nouns refer to more than one. To form the plural of most nouns, you add “s” to the end, such as “dogs” or “cars.” However, some nouns have irregular plurals, like “children” or “women.”
Nouns can also be categorized by their gender. Some nouns are referred to as “masculine,” like “man” or “boy,” while others are referred to as “feminine,” like “woman” or “girl.” Additionally, there are neutral nouns, which do not have a specific gender, such as “chair” or “table.”
In English, nouns can function as subjects, objects, or complements in sentences. As a subject, a noun performs the action of the verb, while as an object, it receives the action. As a complement, a noun completes the meaning of the sentence. For example, in the sentence “The cat chased the mouse,” “cat” is the subject, “mouse” is the object, and “chased” is the verb.
Overall, nouns play a crucial role in our language by allowing us to identify and describe the world around us. Without nouns, our communication would be limited and our understanding of the world would be greatly diminished.
Pronouns
Pronouns are words that are used in place of nouns. They help to avoid repetition and make sentences more concise. There are several types of pronouns, including personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, reflexive pronouns, and relative pronouns.
Personal pronouns are used to refer to specific people or things. They include pronouns like I, you, he, she, it, we, and they. Personal pronouns can be subject pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they) or object pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us, them). Subject pronouns are used when the pronoun is the subject of a sentence, while object pronouns are used when the pronoun is the object of a verb or preposition.
Possessive pronouns show ownership or possession. They include pronouns like mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, and theirs. Possessive pronouns can be used alone or before a noun to show ownership. For example, “The book is mine” or “That is your pen.”
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same. They include pronouns like myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves. Reflexive pronouns are usually used with a reflexive verb, which is a verb that reflects the action back onto the subject. For example, “I see myself in the mirror” or “He hurt himself while playing.”
Relative pronouns are used to connect clauses or phrases to a noun or pronoun. They include pronouns like who, whom, whose, which, and that. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses, which provide additional information about the noun or pronoun. For example, “The girl who won the race is my sister” or “The book that I read was very interesting.”
Overall, pronouns play an important role in English grammar by replacing nouns and making sentences more concise. They help to avoid repetition and provide clarity in communication.
Verbs
A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being. It is one of the most important parts of speech in the English language and plays a crucial role in forming sentences and conveying meaning. Verbs can be used in different tenses to indicate past, present, or future actions or situations.
The main function of a verb is to show what someone or something does. For example, in the sentence “She runs every morning,” the verb “runs” indicates the action performed by the subject “she.” Verbs can also indicate a state of being, such as in the sentence “He is happy.” In this case, the verb “is” shows the state of being “happy.”
Verbs can be further categorized into different types based on their form and function. Some common types of verbs include action verbs, linking verbs, auxiliary verbs, and modal verbs. Action verbs describe physical or mental actions, such as “run,” “think,” or “read.” Linking verbs connect the subject to a word or phrase that describes or identifies it, such as “be,” “seem,” or “become.” Auxiliary verbs are used to form tense, mood, or voice, such as “have,” “do,” or “will.” Modal verbs express possibility, necessity, or ability, such as “can,” “should,” or “might.”
Verbs also have various forms and functions, such as infinitives, participles, and gerunds. Infinitives are the base form of a verb, such as “to run” or “to eat.” Participles are verb forms that can function as adjectives, such as “running” or “eaten.” Gerunds are verb forms that function as nouns, such as “running” or “eating.” These different forms allow for flexibility and variety in sentence structure and expression.
In summary, verbs are essential elements of language that express actions, occurrences, or states of being. They play a central role in forming sentences and conveying meaning. Understanding the different types and forms of verbs is crucial for effective communication in the English language.
Adjectives
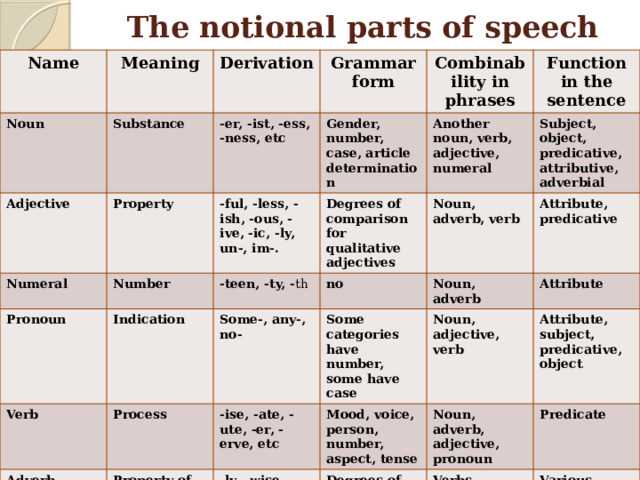
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. It adds more detail or information about the noun or pronoun it is referring to. Adjectives can provide information about the size, shape, color, origin, material, and other characteristics of a noun. They help to make our language more descriptive and expressive.
Adjectives can be used in different positions in a sentence. They can come before a noun (attributive position), after a linking verb (predicative position), or as complements of certain verbs (objective complements). For example:
- Attributive position: The blue sky, a beautiful flower.
- Predicative position: The sky is blue, the flower looks beautiful.
- Objective complement: We painted the walls white, they made the room clean.
Adjectives can also be compared using the comparative and superlative forms. The comparative form is used to compare two things, while the superlative form is used to compare three or more things. For example:
- The cat is big.
- The dog is bigger than the cat.
- The elephant is the biggest of them all.
In addition, adjectives can be used to form compound adjectives by combining two or more words together. These compound adjectives are often hyphenated. For example:
- A well-known author, a five-year-old child, a high-speed train.
Overall, adjectives play an important role in English language by enhancing the description of nouns and pronouns. They help to bring clarity and vividness to our communication, making our language more interesting and engaging.
Adverbs
Adverbs are a part of speech that modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. They provide information on how, when, where, or to what extent an action or state is performed. Adverbs often end in -ly, although there are many adverbs that don’t follow this pattern.
An adverb can provide additional information about a verb. For example, in the sentence “She ran quickly,” the adverb “quickly” describes how she ran. It tells us that she ran in a fast manner. Adverbs can also modify adjectives. In the sentence “He is very tall,” the adverb “very” modifies the adjective “tall” and tells us the extent to which he is tall.
Some adverbs don’t end in -ly and can’t be easily identified. For example, the word “now” is an adverb that indicates the time when an action is happening. Other examples include “here” and “there,” which indicate a location, and “too,” which indicates excess or overabundance. Adverbs can also be formed from adjectives by adding the suffix -ly, such as “quick” becoming “quickly,” or by changing the spelling, such as “careful” becoming “carefully.”
In summary, adverbs provide additional information about verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. They can describe how, when, where, or to what extent an action or state is performed. Adverbs can end in -ly, but not all adverbs do. Some adverbs, like “now” or “here,” don’t follow the typical -ly pattern but still serve to modify other parts of speech.
Prepositions
Prepositions are words that show relationships between different words in a sentence. They indicate location, time, direction, manner, or other relationships.
Some common prepositions include in, on, at, about, after, before, during, and with. These words are used to describe where something is or when something happened.
Location
Prepositions can be used to describe where something or someone is located. For example:
- I live in a small town.
- The book is on the table.
- She is standing at the bus stop.
Time
Prepositions can also be used to describe when something happened or will happen. For example:
- We always have dinner at 7 o’clock.
- The party is on Saturday.
- They will arrive before noon.
Direction
Prepositions can show the direction of movement. For example:
- He walked into the room.
- She ran out of the building.
- They drove along the highway.
In summary, prepositions are important words that help us understand the relationships between different words in a sentence. They can describe location, time, direction, and much more.
Conjunctions

Conjunctions are important parts of speech that connect words, phrases, or clauses together. They are like the glue that holds sentences and ideas together. Without conjunctions, our language would lack cohesion and clarity.
There are three main types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions, correlative conjunctions, and subordinating conjunctions. Coordinating conjunctions join words or groups of words that have equal importance in a sentence. Some common coordinating conjunctions include “and,” “but,” “or,” “nor,” “for,” “yet,” and “so.” For example, in the sentence “I like to swim and bike,” the coordinating conjunction “and” connects the two actions.
Correlative conjunctions, as the name suggests, work in pairs to join similar types of words and phrases. Examples of correlative conjunctions include “either…or,” “neither…nor,” “both…and,” and “not only…but also.” They add emphasis and balance to a sentence. For instance, in the sentence “She is not only funny but also intelligent,” the correlative conjunction “not only…but also” connects the two qualities.
- Coordinating conjunctions – join words or groups of words with equal importance
- Correlative conjunctions – work in pairs to join similar types of words and phrases
- Subordinating conjunctions – introduce dependent clauses that cannot stand alone as sentences
Subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses, which are clauses that cannot stand alone as complete sentences. They show a relationship between the dependent clause and the main clause of a sentence. Examples of subordinating conjunctions include “although,” “because,” “if,” “unless,” “since,” and “while.” In the sentence “Although it was raining, we went outside,” the subordinating conjunction “although” introduces the dependent clause “it was raining.”
Overall, conjunctions play a crucial role in the English language by connecting words, phrases, and clauses. They help to create coherence and structure in our sentences and allow us to express complex thoughts and ideas.