
In Chapter 3 of the Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook, we delve into the fascinating world of the human body. This chapter provides a comprehensive understanding of the various systems and structures that make up our anatomy and how they function in unison to maintain our overall health and well-being.
The main focus of this chapter is to provide answers to the exercises and questions in the workbook, allowing students to test their knowledge and reinforce key concepts. By actively engaging in the coloring and labeling activities, students will develop a deeper understanding of the intricate details and organization of the different body systems.
Within this chapter, you will find answers to questions related to the skeletal system, muscular system, nervous system, and more. Through coloring and labeling diagrams, students will learn about the structure of bones, the types and functions of muscles, and the intricate network of nerves that allow us to sense and respond to our environment.
Additionally, this chapter explores the importance of homeostasis and how our body systems work together to maintain a state of balance. By coloring and labeling diagrams that depict feedback mechanisms, students will gain an understanding of how our body regulates temperature, blood sugar levels, and other key variables.
Overall, Chapter 3 of the Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook plays a crucial role in enhancing students’ comprehension of the human body. By providing detailed answers and engaging coloring activities, this chapter fosters active learning and helps students develop a solid foundation in anatomy and physiology.
Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook Answers
When studying anatomy and physiology, it can be helpful to use visual aids such as coloring books to reinforce your understanding of the material. The Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook is a popular resource that provides students with an interactive way to learn the intricacies of the human body. This chapter focuses on the answers to the various exercises and coloring pages found within the workbook.
To aid in your study, the chapter breaks down the answers by sections, such as the skeletal system, muscular system, and integumentary system. Each section provides a detailed explanation of the answers to the questions and coloring exercises found in the workbook. This allows students to review and reinforce their understanding of the concepts covered in each section.
For example, in the skeletal system section, you will find answers to questions about bone structure, types of joints, and the functions of the skeletal system. Additionally, the section provides coloring pages that allow you to visually identify and label different bones and joints in the human body.
Overall, the chapter serves as a valuable resource for students studying anatomy and physiology. By providing detailed answers to the exercises and coloring pages in the workbook, students can enhance their understanding of the material and improve their overall comprehension of the human body.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Skeletal System
- Muscular System
- Integumentary System
- And more…
Overview of Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook

The Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook is an invaluable tool for students studying the intricate systems of the human body. In Chapter 3, students delve into the structures and functions of cells, which are the building blocks of all living organisms.
This chapter begins with an exploration of the structure and functions of the plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane. Students will learn about its composition and the role it plays in maintaining the integrity of the cell. They will also gain an understanding of the various types of membrane transport, such as passive diffusion and active transport.
The next section focuses on the nucleus, the control center of the cell. Students will discover the different parts of the nucleus, including the nuclear envelope and nucleolus, and learn about the vital role it plays in controlling cellular activities, including DNA replication and protein synthesis.
Moving on, students will explore the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which are involved in protein synthesis, modification, and transport. They will also learn about the structure and functions of mitochondria, which serve as the powerhouses of the cell by producing ATP through cellular respiration.
The chapter concludes with a discussion on the structure and functions of various cellular organelles, including lysosomes, peroxisomes, and centrioles. Students will gain insight into how these organelles contribute to the overall function and health of the cell.
Overall, Chapter 3 of the Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook provides a comprehensive overview of the structures and functions of cells, laying the foundation for a deeper exploration of the human body’s complex systems.
The Importance of Understanding Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and physiology are foundational sciences in the field of healthcare. This knowledge is essential for healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, and medical researchers. Understanding anatomy and physiology provides a framework for understanding how the human body functions and how it can be affected by certain conditions or diseases.
One key aspect of understanding anatomy is being able to identify and describe the different structures in the body. This includes knowing the names and locations of bones, muscles, organs, and other tissues. This knowledge is important for diagnosing and treating patients, as it allows healthcare professionals to accurately assess and evaluate the body’s condition. In addition, understanding the structure of the body helps healthcare professionals perform procedures and surgeries safely and efficiently.
Physiology, on the other hand, deals with how the different systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis and carry out various functions. It involves studying processes such as digestion, circulation, respiration, and reproduction. Understanding physiology enables healthcare professionals to understand how different systems interact and affect each other. This knowledge is crucial for diagnosing and treating diseases, as well as for developing new treatments and interventions.
Furthermore, a solid understanding of anatomy and physiology helps with patient communication. Healthcare professionals who can explain complex medical terms and concepts in plain language are better able to educate and inform their patients. This fosters a stronger doctor-patient relationship and promotes patient empowerment and involvement in their own healthcare decisions.
In conclusion, understanding anatomy and physiology is essential for healthcare professionals. It provides them with the knowledge and skills necessary to diagnose, treat, and educate patients. Without this understanding, healthcare professionals would not be able to effectively carry out their roles and responsibilities in the field of healthcare.
Key Concepts in Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook Chapter 3
In Chapter 3 of the Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook, you will delve into the intricate world of cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms, and understanding their structure, functions, and types is crucial to comprehending the human body’s complexity.
Cell Structure: Cells have specific structures that enable them to carry out their functions effectively. These structures include the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. The plasma membrane acts as a selective barrier, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell. The cytoplasm contains organelles, such as mitochondria, ribosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum, which are responsible for various cellular processes. The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material and controls cellular activities.
Cell Functions: Cells perform a wide range of functions essential for the body’s survival. One of the primary functions is to obtain nutrients and eliminate waste through the process of cellular respiration and excretion. Cells also carry out specific metabolic activities, such as protein synthesis, DNA replication, and energy production. Additionally, cells are responsible for cell division, which aids in growth and tissue repair.
Types of Cells: There are two main types of cells in the human body: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a true nucleus and various organelles enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotic cells can be further categorized into animal cells, which make up the human body, and plant cells, which have additional structures like cell walls and chloroplasts.
Cell Diversity: Cells come in various shapes, sizes, and specialized forms. This diversity allows different cells to perform specific functions in the body. For example, nerve cells have long extensions called axons that enable them to transmit electrical signals, while muscle cells are elongated to generate force and create movement. Understanding the unique characteristics of different cell types is crucial in comprehending the overall functioning of organs and systems.
Overall, Chapter 3 of the Anatomy and Physiology Coloring Workbook covers the fundamental concepts of cell anatomy and physiology. By exploring the structure, functions, types, and diversity of cells, you will gain a solid foundation for further exploration of the human body’s intricate workings.
Understanding the Organization of the Human Body
Before delving into the complex study of anatomy and physiology, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of the organization of the human body. The human body is a remarkable system composed of various interconnected parts that work together to maintain homeostasis.
The human body is organized into several levels of structural organization, starting from the smallest building blocks to the largest systems. At the smallest level, you have atoms, which combine to form molecules. Cells are the next level of organization and are the basic functional units of life. They come together to form tissues, which are groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
There are four primary types of tissues in the human body:
- Epithelial tissue: This tissue covers the body surfaces, lines cavities and organs, and forms glands.
- Connective tissue: This tissue provides support and protection, connects and holds organs together, and stores energy.
- Muscle tissue: This tissue is responsible for movement and generating force.
- Nervous tissue: This tissue allows for communication between different parts of the body through electrical signals.
Organ systems are the next level of organization and are composed of different organs working together to perform a specific function. Some examples of organ systems include the respiratory system, digestive system, and cardiovascular system.
The human body has eleven major organ systems:
- Integumentary system: Includes the skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands, providing protection and regulating body temperature.
- Skeletal system: Composed of bones, cartilage, and joints, providing support and protection for internal organs.
- Muscular system: Consists of muscles that work together to generate movement and maintain posture.
- Nervous system: Includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, controlling and coordinating body functions.
- Circulatory system: Composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, responsible for transporting nutrients, oxygen, and waste products throughout the body.
- Respiratory system: Involved in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the external environment.
- Digestive system: Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste products.
- Urinary system: Involved in the production, storage, and elimination of urine and maintaining fluid balance in the body.
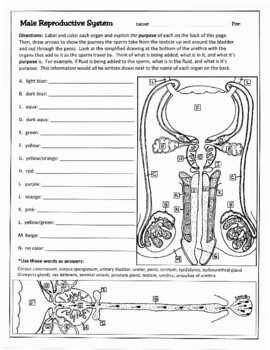
- Reproductive system: Responsible for the production of offspring.
- Endocrine system: Comprised of glands that secrete hormones, which regulate various body functions.
- Immune system: Defends the body against pathogens and foreign substances.
Each level of organization in the human body is interconnected and dependent on one another. Understanding this organization is crucial for studying and appreciating the complexity and functionality of the human body.
Exploring the Cellular Level of Organization
At the cellular level of organization, we delve into the intricacies of the building blocks of life. Cells are the fundamental units of all living organisms, and they come in a variety of shapes and sizes to perform specific functions. Through the process of cell biology, we can study the structure, function, and behavior of cells, shedding light on the complex machinery that keeps our bodies functioning.
The cellular level of organization is characterized by its diversity. Cells can be grouped into two broad categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, contain a nucleus and a range of organelles that compartmentalize various cellular tasks.
Within a eukaryotic cell, organelles work in harmony to carry out essential functions. The nucleus houses the cell’s DNA, acting as the control center for cellular activities. The endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and vesicles are involved in protein synthesis and transportation. Mitochondria produce energy through cellular respiration, while lysosomes break down waste materials. The cytoskeleton provides structural support and facilitates intracellular transport.
Understanding the cellular level of organization is crucial for comprehending the larger systems and processes that occur in the human body. Cells work in coordination to form tissues, which then combine to create organs, and ultimately compose organ systems. By unraveling the intricate mechanisms of cellular function, scientists can gain insights into disease processes, develop therapies, and improve overall human health.