
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with shapes, sizes, and properties of figures and spaces. It plays a crucial role in understanding the world around us, as well as in various practical applications. One important aspect of studying geometry is testing our understanding through chapter tests.
Chapter 3 of a geometry course covers a range of topics, including angles, parallel lines, and transversals. These concepts lay the foundation for more advanced concepts in geometry. When it comes to preparing for the chapter test, having access to the correct answers is essential for self-assessment and improvement.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of the answers to Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in geometry. By understanding the reasoning behind each answer, students can not only gauge their understanding but also identify areas that require further study. Let’s dive into the answers and their explanations!
Chapter 3 Chapter Test A Geometry Answers
In chapter 3 of geometry, students are typically introduced to various concepts such as angles, parallel lines, and polygons. The chapter test is designed to assess students’ understanding of these topics and their ability to apply the concepts in problem-solving situations. It is important for students to review and practice these concepts before taking the test to ensure their success.
When preparing for the chapter test, it is essential for students to have a clear understanding of the definitions and properties of angles. This includes knowing the different types of angles (acute, obtuse, right, and straight) and how to measure and classify them. Students should also be comfortable using angle addition and angle subtraction to solve problems involving angle measures.
Another important topic covered in chapter 3 is parallel lines and transversals. Students should be able to identify the different types of angles formed when a transversal intersects parallel lines, such as corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate exterior angles. They should also know the relationships between these angles and how to use them to solve problems.
The chapter test may also include questions on polygons, such as identifying the number of sides and angles in different types of polygons (triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, etc.). Students should be familiar with the properties and characteristics of these polygons, including the sum of interior angles and the types of triangles (scalene, isosceles, equilateral).
Overall, a thorough understanding of the concepts presented in chapter 3 of geometry is essential for success on the chapter test. By reviewing and practicing these concepts, students can feel confident in their ability to answer the test questions accurately and efficiently.
Understanding Chapter Tests in Geometry
Chapter tests in geometry are an essential part of assessing students’ understanding and mastery of geometric concepts and skills. These tests are designed to evaluate students’ knowledge of the specific topics covered in the chapter, as well as their ability to apply these concepts to solve problems and prove theorems.
One important aspect of chapter tests in geometry is the inclusion of a variety of question types. This may include multiple-choice questions, short answer questions, and proof-based questions. By including a range of question types, teachers can effectively assess students’ understanding at different levels of complexity.
When preparing for a chapter test in geometry, it is important for students to review their class notes, textbook, and any additional materials provided by the teacher. They should also practice solving problems and proving theorems related to the topics covered in the chapter. This will help them become familiar with the types of questions they may encounter on the test and build their confidence in applying the concepts they have learned.
In addition to reviewing content, students should also pay attention to the format of the test. They should understand how many questions will be included, the allotted time for the test, and any specific instructions or guidelines provided by the teacher. This will help them manage their time effectively during the test and ensure that they are able to complete all the questions within the given time frame.
Overall, chapter tests in geometry serve as an important tool for both teachers and students. They allow teachers to assess students’ understanding and progress, while giving students an opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge and skills. By understanding the purpose and format of these tests, students can better prepare and perform well in their geometry assessments.
Importance of Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in Geometry

The Chapter 3 Chapter Test A is an essential component of learning and assessing one’s understanding of geometry concepts. This test serves as an evaluation tool to measure students’ knowledge and mastery of the material covered in Chapter 3. By assessing students’ understanding of the key concepts and skills, this test helps identify areas where additional support and teaching may be necessary.
One of the main reasons why the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A is crucial is that it allows both students and teachers to gauge the effectiveness of the instruction and learning process. If students perform well on the test, it indicates that they have grasped the concepts and can apply them correctly. Conversely, if students struggle or perform poorly, it suggests that further instruction and practice are needed to reinforce the material and address any misconceptions. This feedback is invaluable in guiding teachers’ instructional decisions and designing interventions tailored to students’ needs.
- The Chapter 3 Chapter Test A also helps students consolidate their learning and reinforce their understanding of geometry concepts. By revisiting the material and applying it in a test setting, students deepen their knowledge and improve their problem-solving skills. The test provides an opportunity for students to demonstrate their ability to analyze, evaluate, and solve geometric problems, which are essential skills in geometry and other math-related disciplines.
- Furthermore, the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A plays a crucial role in preparing students for future assessments and exams. It allows students to become familiar with the format and types of questions they may encounter in future tests. By practicing and experiencing the test environment, students develop test-taking strategies and build confidence in their abilities. This preparation is beneficial not only for immediate assessments but also for standardized tests, college entrance exams, and other academic evaluations that assess geometry knowledge and skills.
- In summary, the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A is an important tool in the learning and assessment process of geometry. It helps evaluate students’ understanding, provides feedback for instructional decisions, reinforces learning, and prepares students for future assessments. By utilizing this chapter test effectively, both students and teachers can enhance their learning experience and achieve success in geometry education.
Examining the Test Questions in Chapter 3 Chapter Test A

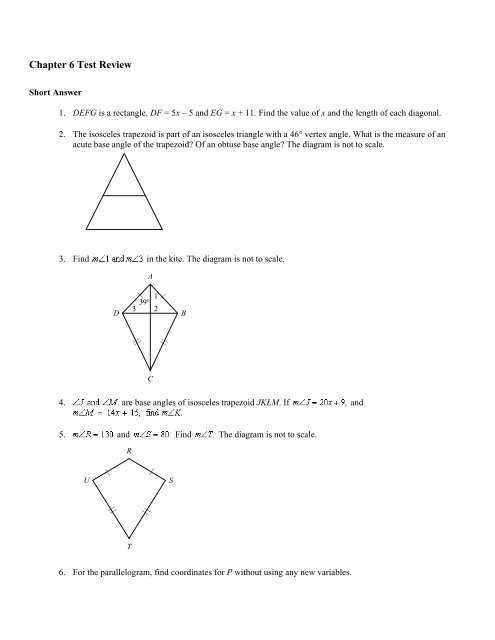
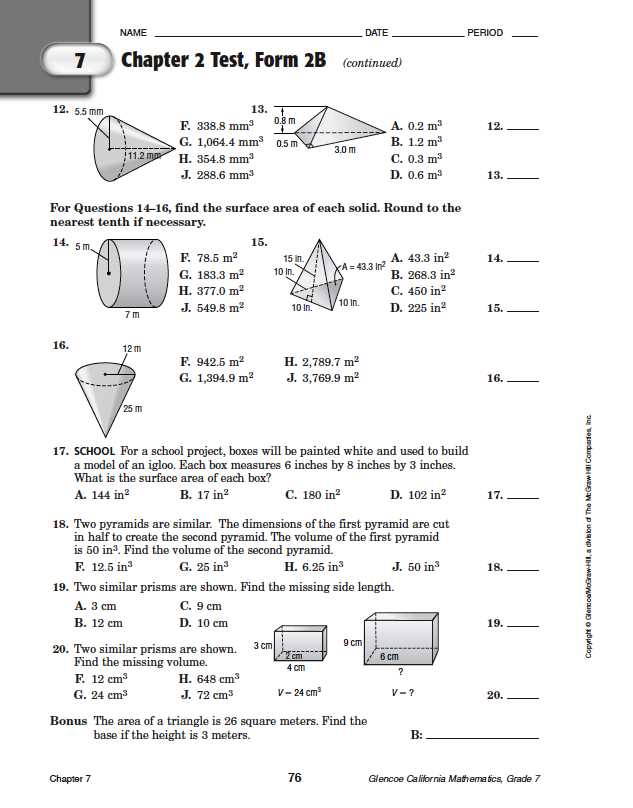
Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in geometry typically covers various concepts and principles learned in Chapter 3 of the textbook. This chapter focuses on properties of polygons, including angles, sides, and diagonals. The chapter test is designed to assess the students’ understanding of these concepts and their ability to apply them in problem-solving situations.
The test consists of multiple-choice and free-response questions that require students to demonstrate their knowledge of polygon properties. Some of the key concepts assessed in this test include the interior and exterior angles of polygons, the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon, identifying types of polygons based on their properties, finding missing angles in polygons, and solving problems involving polygons.
The multiple-choice questions in this test often present students with various scenarios or diagrams of polygons and ask them to identify specific properties of the polygons or to solve problems related to those properties. These questions require students to apply their understanding of the properties of polygons and to use that knowledge to make informed choices among the given options.
The free-response questions in this test typically require students to demonstrate their problem-solving skills and their ability to apply the concepts learned in Chapter 3. These questions may involve finding unknown values or angles in polygons, proving certain properties or relationships between angles or sides of polygons, or solving real-world problems that can be modeled using polygons.
Overall, the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in geometry serves as an important assessment tool to gauge students’ understanding of the concepts and principles related to polygons. It allows teachers to identify areas where students may need additional support or instruction and provides students with an opportunity to showcase their knowledge and problem-solving skills.
Tips for Answering Geometry Questions in Chapter 3 Chapter Test A
When preparing for the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in Geometry, it is important to approach the questions strategically. Here are some tips to help you answer the questions effectively:
- Read the question carefully: Take the time to understand what the question is asking before attempting to solve it. Pay attention to any given information and identify what is being asked.
- Review the concepts: Make sure you have a solid understanding of the key concepts covered in Chapter 3. This will help you approach the questions with confidence.
- Draw diagrams: Geometry problems often involve visual representations. Use diagrams to visualize the given information and better understand the problem.
- Apply geometric formulas: Familiarize yourself with the formulas and theorems relevant to the topics covered in Chapter 3. This will enable you to apply them correctly when solving problems.
- Check for logical reasoning: Geometry problems often require logical reasoning to arrive at the correct answer. Make sure your solution is logical and makes sense in the context of the problem.
- Check your work: After solving a problem, double-check your answer and ensure that you have answered all parts of the question. Review your calculations and make sure they are accurate.
By following these tips, you can improve your performance on the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in Geometry. Good luck!
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Chapter 3 Chapter Test A
When taking the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in geometry, it is important to be aware of common mistakes that students often make. By avoiding these mistakes, you can improve your chances of getting a better score on the test. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
1. Not Reviewing Key Concepts:
One common mistake is not properly reviewing the key concepts learned in Chapter 3. It is important to have a solid understanding of topics such as angles, parallel lines, and triangle properties before taking the test. Make sure to review your notes, textbook, and any additional resources available to you.
2. Misunderstanding Definitions:
Another common mistake is misunderstanding or misinterpreting the definitions of geometric terms. It is important to know the precise definitions of terms such as congruent, perpendicular, and bisect. Make sure to carefully read the questions and answer choices, and choose the option that correctly aligns with the given definitions.
3. Failing to Draw Accurate Diagrams:
Accurate diagrams are essential for solving geometry problems. One common mistake is rushing through the process of drawing diagrams or not including all necessary information. Take your time to ensure that your diagrams are clear, labeled correctly, and accurately represent the given information.
4. Skipping Steps:
Many geometry problems require multiple steps to solve. Skipping steps or not showing your work can lead to errors and incorrect answers. Make sure to clearly show each step of your solution, and double-check your work to ensure accuracy.
Avoiding these common mistakes can greatly improve your performance on the Chapter 3 Chapter Test A in geometry. By reviewing key concepts, understanding definitions, drawing accurate diagrams, and showing your work, you can increase your chances of success on the test.
Sample Answers and Explanations for Chapter 3 Chapter Test A
1. In a triangle ABC, angle A measures 40 degrees and angle B measures 70 degrees. What is the measure of angle C?
Answer: To find the measure of angle C, we can use the fact that the sum of the angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees. So, we subtract the measures of angles A and B from 180. Thus, angle C = 180 – 40 – 70 = 70 degrees.
2. Given that triangle PQR is an isosceles triangle with PQ = PR, if angle P measures 60 degrees, what is the measure of angle R?
Answer: In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are congruent. Therefore, angle P = angle R. Since angle P measures 60 degrees, angle R also measures 60 degrees.
3. Triangle XYZ is a right triangle with XY = 6 cm and YZ = 8 cm. What is the length of side XZ?
Answer: Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can find the length of side XZ. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. So, we can set up the equation: 6^2 + x^2 = 8^2. Solving for x, we find x = √(8^2 – 6^2) = √64 = 8 cm. Therefore, the length of side XZ is 8 cm.
4. Given that triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle with side length 10 cm, what is the measure of each angle?
Answer: In an equilateral triangle, all angles are congruent and measure 60 degrees. Therefore, each angle in triangle ABC measures 60 degrees.
5. In triangle DEF, the measure of angle D is twice the measure of angle F, and the measure of angle E is 30 degrees less than the measure of angle F. What are the measures of angles D, E, and F?
Answer: Let x be the measure of angle F. Since angle D is twice the measure of angle F, angle D = 2x. Angle E is 30 degrees less than angle F, so angle E = x – 30. The sum of the measures of the angles in a triangle is 180 degrees, so we can set up the equation: 2x + x + (x – 30) = 180. Solving for x, we find x = 70. Therefore, angle D = 2 * 70 = 140 degrees, angle E = 70 – 30 = 40 degrees, and angle F = 70 degrees.