Civilizations in Asia Unit Test is a comprehensive assessment to evaluate students’ understanding of the various ancient civilizations that existed in Asia. This test aims to test students’ knowledge of key concepts, historical events, cultural practices, and the impact of these civilizations on the development of Asia as a region.
The test covers a range of topics, including the Indus Valley Civilization, the Yellow River Civilization, the Mesopotamian Civilization, the Ancient Egyptian Civilization, and the Ancient Greek Civilization. Students will be required to demonstrate their understanding of the geographical features, religious beliefs, social structures, and economic systems of these civilizations.
This unit test is designed to challenge students and encourage critical thinking. It will assess their ability to analyze primary and secondary sources, interpret historical maps and artifacts, and make connections between historical events. The test will also assess students’ ability to communicate their understanding through well-structured written responses.
By taking the Civilizations in Asia Unit Test, students will have the opportunity to deepen their knowledge of ancient civilizations, develop their historical thinking skills, and gain a broader understanding of the diverse cultures that have shaped Asia’s rich history.
Civilizations in Asia Unit Test
As part of the study on civilizations in Asia, students will be given a unit test to assess their understanding of the topic. The test will cover various aspects of Asian civilizations, including their origins, development, cultural achievements, and impact on the world. Students will be required to demonstrate their knowledge through multiple-choice questions, short answer responses, and possibly essay questions.
The unit test will begin with questions on the early civilizations of Asia, such as the Indus Valley Civilization and the Shang Dynasty. Students will be expected to identify the geographical locations of these civilizations, describe their social structures, and explain the significance of their cultural achievements. They will also need to demonstrate an understanding of the impact of geography on the development of these early civilizations.
The test will then move on to the later civilizations of Asia, such as the Maurya Empire, Gupta Empire, and Tang Dynasty. Students will be asked to analyze the reasons for the rise and fall of these empires, discuss their political and economic systems, and analyze their cultural contributions. They will also need to compare and contrast these civilizations with others studied in the unit, highlighting similarities and differences in their development and achievements.
Overall, the unit test on civilizations in Asia will test students’ knowledge and understanding of the complex and diverse history of the continent. It will require them to think critically, make connections between different civilizations, and analyze the impact of geography, politics, and culture on their development. By successfully completing the unit test, students will demonstrate their mastery of the subject and their ability to apply their knowledge to historical analysis.
Ancient Civilizations in Asia
Ancient Asia was home to some of the world’s most significant civilizations. These civilizations left behind a rich legacy of culture, technology, and political systems. From the Indus Valley Civilization to the Han Dynasty, Asia was a vibrant hub of innovation and diversity.
One of the most remarkable ancient civilizations in Asia was the Indus Valley Civilization. Flourishing around 3300-1300 BCE, it spanned across present-day Pakistan and northwest India. The Indus Valley Civilization was known for its well-planned cities, advanced drainage systems, and vibrant trade networks. Archaeological discoveries have revealed fascinating insights into their art, agriculture, and sophisticated urban planning.
The Indus Valley Civilization:
- Flourished around 3300-1300 BCE.
- Well-planned cities and advanced drainage systems.
- Thriving trade networks.
- Insights into art, agriculture, and urban planning.
Another significant ancient civilization in Asia was the Han Dynasty in China. It emerged in 206 BCE and lasted until 220 CE, leaving a lasting impact on Chinese history and culture. The Han Dynasty is known for its centralized government, development of the civil service examination system, and advancements in technology and science. They also expanded their territory through military conquests and established the famous Silk Road trade route.
The Han Dynasty:
- Emerged in 206 BCE and lasted until 220 CE.
- Centralized government and civil service examination system.
- Advancements in technology and science.
- Expansion through military conquests and establishment of the Silk Road trade route.
Ancient civilizations in Asia played a crucial role in shaping the region’s history and development. Their achievements in various fields continue to inspire and fascinate people today. By studying these civilizations, we gain valuable insights into the past and appreciate the contributions of Asian cultures to the world.
Key Characteristics of Asian Civilizations
Asian civilizations are known for their rich history, diverse cultures, and significant contributions to the development of human civilization. These civilizations have several key characteristics that have shaped their identities and left a lasting impact on the world.
Economic Prosperity: One of the defining features of Asian civilizations is their economic prosperity. Through trade networks, such as the Silk Road, Asian civilizations were able to establish strong economic ties with other regions, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. The agricultural practices developed in ancient China and India allowed for surplus food production, enabling the growth of urban centers and the development of complex economies.
Social Hierarchy: Another key characteristic of Asian civilizations is the presence of social hierarchies. From the caste system in ancient India to the Confucian social order in China, these societies followed strict social structures that determined individuals’ roles and status. These hierarchical systems had a significant influence on the political, economic, and cultural landscape of Asian civilizations, shaping their values and social norms.
Philosophical and Spiritual Traditions: Asian civilizations have also made notable contributions to the development of philosophical and spiritual traditions. Ancient civilizations such as India and China gave rise to major philosophical teachings, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism. These belief systems provided guidance on moral conduct, ethical values, and the pursuit of enlightenment, shaping the mindset and values of millions of people across Asia.
Technological Advancements: Asian civilizations have a long history of technological advancements. Ancient China, for example, was known for its inventions such as paper, gunpowder, and the compass. These inventions not only revolutionized various aspects of life within Asia but also had a profound impact on global history. Asian civilizations also excelled in fields such as architecture, medicine, and art, leaving behind a rich legacy of innovative ideas and techniques.
The Contributions of Asian Civilizations to World History
Asian civilizations have made significant contributions to world history, shaping various aspects of human society and leaving a lasting impact on cultures around the globe. One notable contribution is the development of written language systems. Ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt in Asia were among the first to use written language to record information, creating the building blocks for future civilizations to build upon. This paved the way for the creation of complex legal codes, religious texts, and literary works that have influenced countless societies throughout history.
Another significant contribution of Asian civilizations is the advancement of scientific knowledge. Ancient Chinese civilizations, for example, made remarkable progress in fields such as astronomy, mathematics, medicine, and technology. These advancements, such as the invention of the compass, gunpowder, and papermaking, revolutionized various industries and spread to other civilizations, ultimately shaping the modern world as we know it today.
In addition to language and scientific advancements, Asian civilizations have had a profound impact on art and culture. The intricate artwork and craftsmanship of ancient Asian civilizations, such as the beautiful sculptures of the Indus Valley or the delicate porcelain of China, have influenced artistic styles and techniques around the world. Asian civilizations also played a crucial role in the development of various forms of performing arts, including classical music, dance, and theater. These artistic traditions continue to be celebrated and admired globally, showcasing the rich cultural heritage of Asia.
The contributions of Asian civilizations to world history extend beyond language, science, and art. They have also made significant contributions in the fields of philosophy, religion, and governance. Philosophical ideas, such as Confucianism and Buddhism, originated in Asia and have had a profound impact on ethical and moral systems worldwide. Asian civilizations also developed sophisticated systems of governance, with ancient empires like the Maurya, Gupta, and Mongol Empires shaping political structures and diplomacy that would influence future civilizations.
In conclusion, the contributions of Asian civilizations to world history are vast and diverse. From the development of written language systems and scientific advancements to the influence on art, culture, philosophy, and governance, Asian civilizations have left an indelible mark on human civilization. The remarkable achievements of these civilizations continue to be remembered, celebrated, and admired, demonstrating the immense impact they have had on shaping the world we live in today.
The Qin Dynasty in China
The Qin Dynasty, also known as the Qin Empire, was an imperial dynasty that ruled China from 221 to 206 BC. It was the first dynasty in Chinese history to have a centralized government and establish the title of emperor as the highest position of authority. The Dynasty was founded by Qin Shi Huang, who unified various states in China under his rule and implemented numerous reforms to strengthen the central government.
One of the key achievements of the Qin Dynasty was the construction of the Great Wall of China. The emperor ordered the connection of existing walls to form a continuous fortification against invasions from the north. This colossal project involved the mobilization of a large workforce and significant resources. The Great Wall of China, which still stands as a symbol of Chinese civilization today, played a crucial role in the defense of the empire.
Key Features of the Qin Dynasty:
- Centralized Government: The Qin Dynasty established a system of central government where all power resided with the emperor. This allowed for efficient decision-making and control over the vast territory.
- Legalism: Qin Shi Huang implemented the philosophy of Legalism, which emphasized strict adherence to laws and harsh punishments for any violations. This ensured order and stability within the empire.
- Standardization: The Qin Dynasty standardized various aspects of Chinese society, including weights, measures, currency, and even the written script. This promoted uniformity and facilitated administration and communication.
- Terracotta Army: One of the most famous achievements of the Dynasty was the creation of the Terracotta Army. It consists of thousands of life-sized clay soldiers, horses, and chariots, intended to accompany Qin Shi Huang in the afterlife.
The Maurya Empire in India
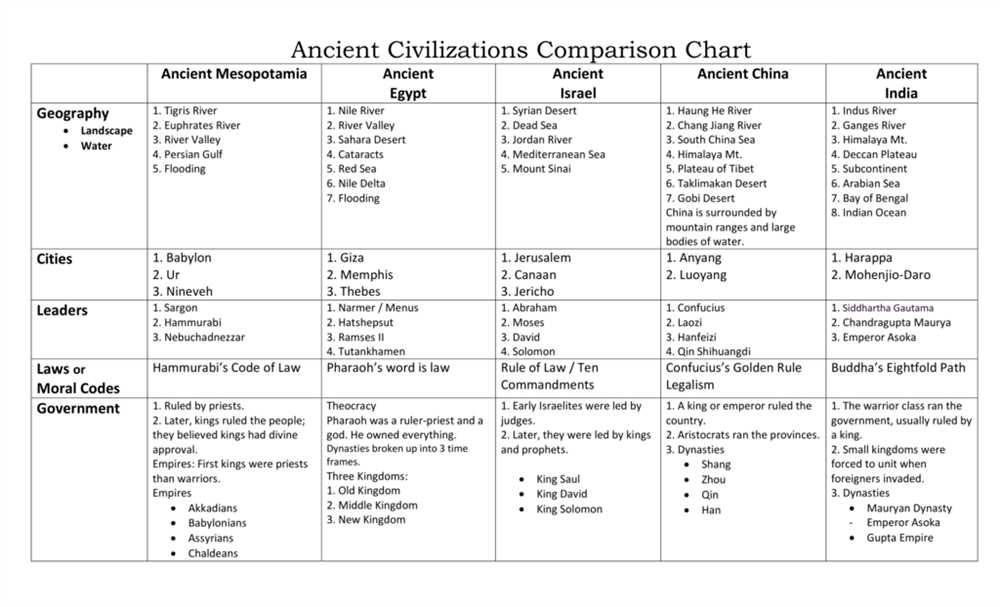
The Maurya Empire was a powerful and influential empire that ruled over a large part of the Indian subcontinent from 322 BCE to 185 BCE. It was founded by Chandragupta Maurya and was known for its vast territorial expansion and well-organized administration. The empire reached its peak under the rule of Ashoka the Great, who embraced Buddhism and promoted peace and religious tolerance.
One of the notable features of the Maurya Empire was its efficient bureaucratic system, known as the Mauryan administration. The empire was divided into provinces, each governed by a royal appointee known as a viceroy. The viceroy was responsible for maintaining law and order, collecting taxes, and ensuring the efficient functioning of the government. The empire also had a well-developed network of spies and informers, which helped the rulers maintain control over their territories.
The Maurya Empire was also known for its military might. It had a vast army consisting of infantry, cavalry, chariots, and elephants. The army was well-trained and disciplined, and it played a crucial role in expanding and defending the empire’s borders. Ashoka’s conversion to Buddhism led to a shift in the empire’s military strategy, with more emphasis on peaceful diplomacy and spreading the teachings of Buddhism.
During its reign, the Maurya Empire made significant contributions in the fields of art, architecture, and literature. The famous Mauryan pillar edicts, which were inscribed with Ashoka’s teachings, are considered masterpieces of ancient Indian art. The empire also witnessed advancements in science and technology, with the construction of sophisticated irrigation systems and the development of medicine.
In conclusion, the Maurya Empire was a powerful and influential empire that left a lasting impact on the history and culture of India. Its well-organized administration, military strength, and contributions in various fields make it a significant civilization in the Asian region.
The Golden Age of Hinduism in Southeast Asia

The Golden Age of Hinduism in Southeast Asia refers to a period in history when Hinduism flourished and had a significant influence on the cultures and civilizations of the region. This period, which lasted from around the 4th to the 14th century, saw the spread of Hinduism from the Indian subcontinent to Southeast Asia through trade, cultural exchange, and political conquests.
During this time, powerful Hindu empires, such as the Srivijaya Empire, the Chola Empire, and the Khmer Empire, emerged in Southeast Asia. These empires were known for their advanced architecture, monumental temples, art, literature, and sophisticated systems of governance. Hinduism, with its rich mythology, rituals, and philosophical teachings, played a central role in the development of these empires and the cultural life of the people.
Hindu temples, such as Angkor Wat in present-day Cambodia, Prambanan in Indonesia, and Bagan in Myanmar, were built as physical manifestations of the divine and served as spiritual and cultural centers. These temples feature intricate carvings depicting scenes from Hindu epics like the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, showcasing the artistic and architectural brilliance of the time.
It was also during this period that Hinduism influenced other aspects of Southeast Asian life, including languages, literature, dance, music, and social customs. Sanskrit, the sacred language of Hinduism, became the language of the elites and was used in inscriptions, official documents, and religious texts. Hindu epics and stories were translated into local languages, blending with indigenous beliefs and traditions.
While the Golden Age of Hinduism eventually gave way to the spread of Islam and other religious traditions in Southeast Asia, its impact can still be seen in the region’s art, architecture, and cultural practices. It served as a foundation for future civilizations and contributed to the rich cultural diversity that characterizes Southeast Asia today.