
In the study of biology, classification is an important tool for organizing and categorizing organisms. The process of classification involves grouping organisms based on their shared characteristics and organizing them into a hierarchical system. This system helps scientists understand the relationships between different organisms and allows for easier identification and study of species.
Classification worksheets are a common tool used in biology education to help students practice and reinforce their understanding of classification. These worksheets typically provide students with a list of organisms and ask them to classify each organism into the appropriate taxonomic levels. This helps students develop their critical thinking and observation skills, as they must carefully analyze the characteristics of each organism in order to make accurate classifications.
The answer key for a classification of organisms worksheet serves as a guide for students to check their work and ensure that they have correctly classified each organism. The answer key provides the correct classifications for each organism, allowing students to compare their own answers and identify any mistakes or areas for improvement.
By using a classification of organisms worksheet and the corresponding answer key, students are able to actively engage with the material and reinforce their understanding of classification. This type of hands-on activity helps students develop their scientific skills and prepare them for future studies in biology and related fields.
Classification of Organisms Worksheet Answer Key: Explained
The classification of organisms is an essential concept in biology that helps us understand the diversity of life on Earth. The “Classification of Organisms Worksheet” provides students with an opportunity to practice their skills in taxonomy and grasp the key concepts of classification. This answer key aims to explain the correct answers to the questions posed in the worksheet, facilitating better learning and comprehension.
1. What is classification?
In the answer key, the concept of classification is defined as the process of organizing living organisms into different groups based on common characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It involves identifying similarities and differences among organisms and assigning them to specific categories.
2. How are organisms classified?
This question in the worksheet focuses on the different classification levels. In the answer key, the hierarchical nature of classification is explained, starting from the broadest category, the kingdom, and moving to successively more specific categories or taxa, such as phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
3. What is binomial nomenclature?
The answer key elucidates the concept of binomial nomenclature, which is the internationally accepted naming system for organisms. It explains that binomial nomenclature assigns a unique scientific name to each species, consisting of a genus name and a species name. The use of Latin or Latinized names ensures universal understanding and avoids confusion.
4. How does classification help in studying organisms?
The answer key emphasizes that classification helps scientists categorize and organize organisms into groups, making it easier to study and understand the vast diversity of life on Earth. By arranging organisms based on their evolutionary relationships and shared characteristics, classification allows for the identification of patterns, the study of evolutionary trends, and the prediction of traits in related species.
5. Why is classification important in biology?
In the answer key, the importance of classification in biology is highlighted. It explains that classification enables scientists to communicate effectively, by using standardized names and categories. It also plays a crucial role in identifying and conserving endangered species, understanding ecological relationships, and providing a framework for further scientific research and discovery.
To further reinforce the understanding of the classification process, additional examples and illustrations can be provided in the answer key. The key should also include references to reputable sources for further exploration and learning. By explaining the answers in a clear and concise manner, the answer key enhances the educational value of the “Classification of Organisms Worksheet.”
What is Classification of Organisms?

The classification of organisms is the process of categorizing living things into different groups based on their characteristics and relationships. It helps scientists organize and understand the vast diversity of species on Earth.
Key phrases: classification, categorizing, living things, characteristics, relationships, diversity, species, Earth.
Classification: Classification is the systematic arrangement of organisms into different groups or categories based on their similarities or differences. It involves identifying and grouping organisms based on their shared characteristics, such as physical features, genetic traits, and behavior.
Categorizing: Categorizing involves sorting organisms into specific groups or categories based on their shared attributes. This process allows scientists to organize and manage the immense variety of living organisms on Earth.
Living things: Living things refer to organisms that are considered alive, displaying the characteristics of life, such as growth, reproduction, metabolism, and response to stimuli. These include plants, animals, fungi, protists, and bacteria.
Characteristics: Characteristics are the distinguishing features or qualities that define an organism. These can include physical attributes, such as size, shape, color, and structure, as well as behavioral traits, such as feeding habits, locomotion, and communication.
Relationships: Relationships refer to the connections and associations among different organisms. These relationships can be based on evolutionary history, ecological interactions, or shared ancestry. By analyzing relationships, scientists can determine the evolutionary or genetic relatedness between species.
Diversity: Diversity refers to the wide range and variety of different organisms found in the natural world. The classification of organisms helps to organize, document, and understand this immense diversity, enabling scientists to study and conserve the Earth’s biological resources effectively.
Species: Species is the basic unit of classification. It refers to a group of organisms that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. Each species has unique characteristics and occupies a particular ecological niche.
Earth: Earth is the planet on which we live, and it is home to a rich and diverse array of organisms. The classification of organisms helps us better understand the complexities and interconnectedness of the Earth’s ecosystems and contributes to our knowledge of the planet’s biodiversity.
The Importance of Classification
Classification is a fundamental aspect of biology that allows scientists to organize and understand the vast diversity of organisms on our planet. By classifying organisms into different groups based on their shared characteristics, we can make sense of the complex web of life and gain insights into evolutionary relationships and ecological interactions.
One of the key benefits of classification is the ability to identify and name new species. This is crucial for scientific research and conservation efforts. When a new organism is discovered, its classification allows scientists to determine its unique characteristics, understand its role in the ecosystem, and study its evolutionary history. Without classification, it would be impossible to communicate and share information about different species effectively.
Classification also helps us understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. By grouping organisms based on shared characteristics, scientists can construct evolutionary trees that trace the ancestry and relationships between different species. This information is essential for studying the processes of evolution and understanding how different species have adapted and diversified over time.
Another important aspect of classification is taxonomy, which is the science of naming and classifying organisms. Taxonomy provides a standardized system for identifying and naming species, ensuring that each organism has a unique and universally recognized name. This allows scientists around the world to communicate efficiently and avoid confusion when discussing different organisms.
Overall, classification is vital for expanding our knowledge of the natural world, promoting effective conservation efforts, and understanding the intricacies of evolution. It enables us to organize and categorize the vast array of organisms, facilitating scientific research, and enabling meaningful discussions about the rich diversity of life on our planet.
Key Terms in Classification
In the field of biology, classification refers to the process of organizing and categorizing organisms into groups based on their similarities and differences. This helps scientists better understand the diversity of life on Earth. There are several key terms and concepts that are essential to understanding classification.
Taxonomy is the science of classification. It involves identifying, naming, and grouping organisms based on their characteristics. Taxonomy provides a systematic framework for organizing and studying the vast array of living organisms.
Species is the basic unit of classification. It refers to a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Species are identified by their unique combination of characteristics.
- Genus: A genus is a group of closely related species. It is the next level of classification after species. Organisms within the same genus share more similarities than those in different genera.
- Family: A family is a group of related genera. It represents a higher level of classification and includes organisms that share common characteristics.
- Order: An order is a group of related families. It further categorizes organisms based on shared characteristics.
- Class: A class is a group of related orders. It represents a higher level of classification and includes organisms that share more general characteristics.
- Phylum: A phylum is a group of related classes. It represents a higher level of classification and includes organisms that share even broader characteristics.
- Kingdom: A kingdom is the highest level of classification. It includes all organisms that share common characteristics and is divided into several phyla.
These key terms provide a framework for understanding the hierarchy and organization of classification. By using these terms, scientists are able to effectively communicate and study the vast array of life on Earth.
Levels of Classification

Classification is the process of categorizing organisms based on their characteristics and relationships. The levels of classification provide a hierarchical structure that helps scientists organize and study the vast diversity of life on Earth. There are seven main levels of classification: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
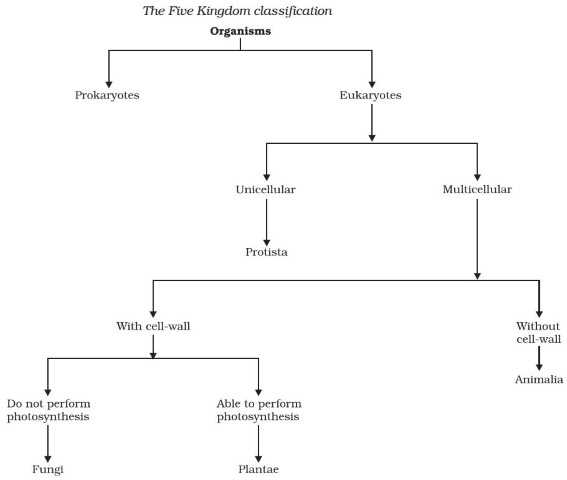
Kingdom: The highest level of classification, the kingdom, groups organisms into five main categories: animals, plants, fungi, protists, and bacteria. Each kingdom represents a broad group of organisms with similar characteristics.
Phylum: The next level of classification, the phylum, further organizes organisms within each kingdom based on shared characteristics. Phyla are divided into smaller groups called classes.
Class: Classes are subdivisions of phyla and contain organisms that share similar characteristics and traits. Within each class, organisms are further categorized into orders.
Order: Orders are groups of organisms within a class that have even more specific characteristics in common. Within each order, organisms are further classified into families.
Family: Families are groups of organisms within an order that share even more specific characteristics. Within each family, organisms are further classified into genera.
Genus: The genus is a level of classification that groups together closely related species. Within each genus, organisms are further categorized into species.
Species: The species is the lowest and most specific level of classification. It consists of individual organisms that are capable of reproducing with one another and producing fertile offspring.
In summary, the levels of classification provide a systematic way to categorize and study the incredible diversity of life on Earth. By organizing organisms into distinct groups based on their characteristics and relationships, scientists can better understand the evolutionary history and relationships between different species.
Binomial Nomenclature

Binomial nomenclature is a scientific naming system used to classify organisms. It was developed by Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century. This system assigns each organism a unique two-part name, consisting of a genus name and a species name. The names are written in Latin and are always italicized or underlined.
The first part of the name is the genus, which is a group of closely related species. The genus name is always capitalized. For example, in the name Homo sapiens, Homo is the genus name. The second part of the name is the species, which refers to a specific organism within the genus. The species name is always written in lowercase. In the example Homo sapiens, sapiens is the species name.
The purpose of binomial nomenclature is to provide a standardized and universal system for naming and classifying organisms. This system allows scientists from different regions and languages to communicate and share information about organisms without confusion. It also helps to organize and categorize the vast diversity of life on Earth.
- Each organism can only have one valid scientific name according to the rules of binomial nomenclature.
- The first part of the name (genus) is always capitalized, while the second part (species) is always written in lowercase.
- The name should be written in italics or underlined when typed.
- Binomial nomenclature allows for easier identification and classification of organisms.