The Cold War was a period of political tension, military rivalry, and economic competition between the Soviet Union and the United States that lasted from the end of World War II until the early 1990s. The conflict arose from ideological differences, territorial disputes, and the struggle for global dominance between the two superpowers. The Cold War had profound effects on the world, and this DBQ (Document-Based Question) explores its causes, events, and consequences.
This PDF provides answers to the questions posed in the Cold War DBQ. The questions cover a wide range of topics, including the origins of the Cold War, the strategies employed by both sides, and the impact of the conflict on society and culture. By examining primary source documents, students can gain a deeper understanding of this pivotal period in history and develop their critical thinking and analytical skills.
The answers provided in this PDF are supported by evidence from the documents and offer insights into the motivations and actions of key players in the Cold War. They also provide an opportunity for students to engage in meaningful discussions and debates about the causes and consequences of this global conflict. By exploring the complexities of the Cold War, students can gain a better understanding of the forces that shaped the modern world and the lessons that can be learned from this period of history.
Understanding the Cold War: A Historical Overview

The Cold War was a period of intense geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, lasting from the end of World War II in 1945 to the early 1990s. It was characterized by a lack of direct military conflict between the two superpowers, but rather a constant state of political and ideological rivalry.
The origins of the Cold War can be traced back to the end of World War II, when the United States and the Soviet Union emerged as two dominant global powers. Despite being wartime allies against Germany, their competing ideologies and political ambitions quickly led to a breakdown in cooperation and the division of Europe into two spheres of influence.
The United States, championing democracy and capitalism, sought to contain the spread of communism, while the Soviet Union aimed to expand its influence and establish socialist states around the world. This ideological clash set the stage for a long and tense standoff between the two superpowers.
Throughout the Cold War, both the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in a series of proxy wars and proxy conflicts, supporting opposing sides in various conflicts around the world. These included the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and the Soviet-Afghan War, among others.
An arms race also defined the Cold War, as both the United States and the Soviet Union built up their nuclear arsenals in an attempt to deter each other from launching a nuclear strike. This constant fear of nuclear annihilation created a heightened sense of tension and unease during the era.
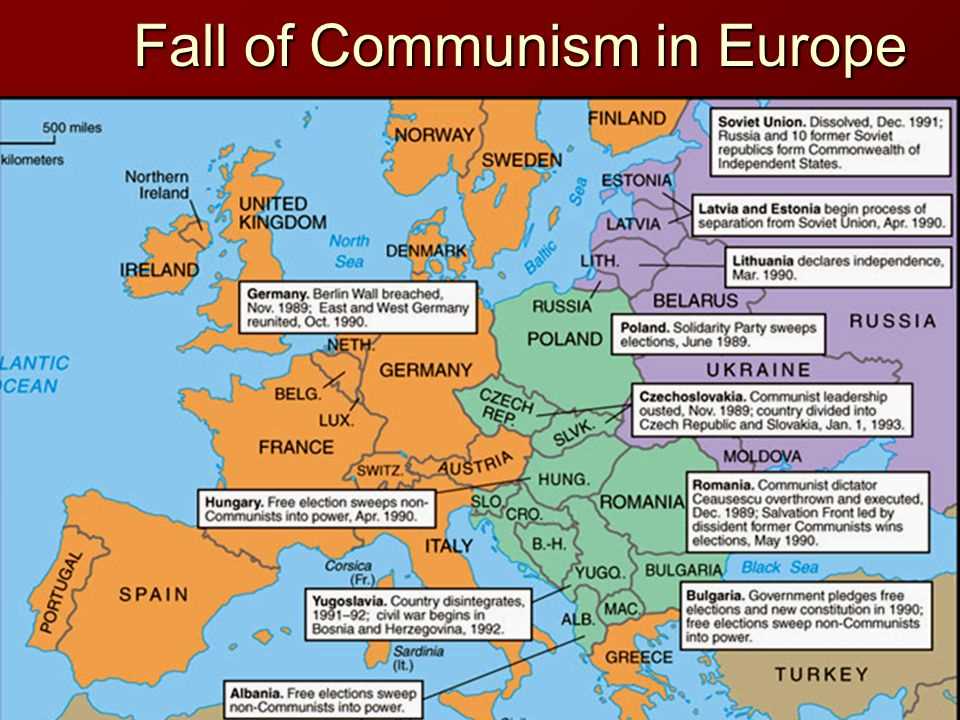
- The Cold War came to an end in the late 1980s and early 1990s with the fall of the Soviet Union and the dissolution of the Warsaw Pact. This marked the end of the bipolar world order that had characterized international relations for decades.
- Understanding the Cold War is essential for comprehending the geopolitical landscape of the 20th century and the lasting effects it had on global politics.
The Origins of the Cold War

The Cold War was a period of political tension and military rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union from the end of World War II until the early 1990s. It was characterized by ideological differences, arms race, and proxy wars fought between the two superpowers. The origins of the Cold War can be traced back to several key events and factors.
One of the main factors contributing to the Cold War was the ideological differences between the United States and the Soviet Union. The United States, as a capitalist nation, promoted democracy, free markets, and individual freedoms. On the other hand, the Soviet Union, as a communist state, advocated for a socialist economy, state control, and equal distribution of wealth. These conflicting ideologies created a fundamental divide between the two nations and set the stage for the Cold War.
The end of World War II also played a significant role in the origins of the Cold War. While the United States and the Soviet Union were allies in the fight against Nazi Germany, their post-war goals differed significantly. The United States aimed to promote democracy and economic stability in Europe, while the Soviet Union sought to expand its influence and create a buffer zone of communist states. These conflicting aspirations led to tensions and mistrust between the two superpowers.
Another contributing factor to the origins of the Cold War was the competition for global dominance. Both the United States and the Soviet Union sought to exert their influence and gain allies around the world. This led to a series of proxy wars, where the two superpowers supported opposing sides in conflicts such as the Korean War and the Vietnam War. These proxy wars served as battlegrounds for the ideological and political rivalries between the United States and the Soviet Union.
In conclusion, the origins of the Cold War can be attributed to a combination of factors, including ideological differences, post-war goals, and the competition for global dominance. The ideological divide between capitalism and communism, along with conflicting aspirations and proxy wars, created a period of intense political tension and rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Main Players and Ideological Differences

The United States, as the leader of the capitalist world, believed in the principles of individual freedom, private property, and free market economy. They saw capitalism as the best economic system, providing incentives for innovation, entrepreneurship, and individual success. The US also championed democracy, valuing the political rights and liberties of its citizens. They believed that democracy was the most legitimate form of government, ensuring checks and balances, people’s participation, and protection of human rights.
On the other hand, the Soviet Union adopted communism, a system that aimed for a classless society where all means of production are owned and controlled by the state. They rejected capitalism, considering it exploitative and promoting inequality. The Soviet Union saw communism as the way to achieve social equality, collective ownership, and planned economy. They also believed in a centrally planned government, asserting that this system provided stability and paved the way for the prosperity of the working class.
- The United States promoted capitalism and democracy.
- The Soviet Union embraced communism and centrally planned government.
Document-Based Question (DBQ) Approach
The Document-Based Question (DBQ) approach is a method used in history education to analyze and interpret historical documents. It is a popular tool for teaching and assessing student understanding of historical events and themes. The DBQ approach allows students to engage with primary source materials, such as letters, speeches, photographs, and government documents, to develop their critical thinking, analysis, and writing skills.
The DBQ approach encourages students to examine multiple perspectives and sources of information to construct an argument or thesis based on the evidence provided in the documents. Students are required to analyze the content, context, and purpose of each document, and consider how they relate to the larger historical context. This process helps students to develop a deeper understanding of the complexities of historical events and the motivations and perspectives of different individuals and groups.
When approaching a DBQ, students are usually provided with a set of guiding questions or a specific historical prompt to focus their analysis. They are then required to use evidence from the documents to support their responses. In addition to analyzing the documents, students may also be asked to integrate their own knowledge of the historical period to provide further context and analysis.
The DBQ approach is often used as part of standardized history exams, as it assesses not only content knowledge but also critical thinking and analytical skills. By using primary source documents, students are able to interact with the actual historical sources and develop their ability to evaluate the reliability and bias of different types of evidence. The DBQ approach prepares students for future historical research and analysis and helps them to become informed and active citizens who can critically evaluate information and make evidence-based arguments.
How to Analyze Historical Documents
When analyzing historical documents, there are several key steps to follow in order to gain a deeper understanding of their significance. By approaching these documents with a critical eye, you can uncover valuable insights into the time period, the author’s perspective, and the historical events being discussed. Here are some steps to help guide your analysis:
- Identify the author and their background: Begin by researching the author of the document and their background. This will help you understand their motivations, biases, and credibility. Consider their occupation, political leanings, and any personal connections they may have had to the events being discussed.
- Examine the context: Context is crucial when analyzing historical documents. Consider the time period in which the document was created, the historical events taking place, and the intended audience. Understanding the broader context will inform your interpretation of the document.
- Analyze the content: Dive into the content of the document itself. Look for key themes, arguments, and evidence presented by the author. Consider the tone, language used, and any biases or perspectives that may be present. Pay attention to any gaps or omissions in the document, as these can provide valuable insights as well.
- Compare with other sources: To gain a more comprehensive understanding, compare the document with other primary and secondary sources from the same time period. Look for similarities, differences, and contradictions in order to evaluate the document’s reliability and accuracy.
- Consider the audience: Think about the intended audience of the document and how that may have influenced its content. Consider the author’s goals and how they may have tailored their message to resonate with their target audience.
- Evaluate the document’s significance: Finally, assess the document’s significance in relation to the broader historical narrative. Reflect on its impact, whether it shaped public opinion, influenced policy, or altered the course of events. Consider the document’s long-term implications and relevance to the historical period.
By following these steps, you can analyze historical documents more effectively and uncover valuable insights into the past. Remember to approach each document with a critical mindset, questioning the author’s perspective and considering multiple sources to form a well-rounded understanding.
Analyzing Cold War Documents

The Cold War was a period of intense geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, characterized by military build-up, proxy wars, and ideological conflicts. To understand the complex dynamics of this era, it is crucial to analyze documents from various sources, including government reports, speeches, and diplomatic cables.
One such document is the Truman Doctrine, presented by President Harry S. Truman in 1947. In this speech, Truman outlined the need for the United States to provide economic and military assistance to countries threatened by communism. The document reflects the containment policy and the belief that the spread of communism presented a direct threat to American security interests. By analyzing this document, we can gain insights into the mindset and motives of the United States during the early years of the Cold War.
Another important document is the Warsaw Pact, signed by the Soviet Union and its Eastern European allies in 1955. This document was a military alliance aimed at countering NATO and solidifying Soviet control over Eastern Europe. By examining the language and provisions of the Warsaw Pact, we can understand the Soviet Union’s intentions to expand its influence and maintain a buffer zone between itself and the Western powers.
Furthermore, analyzing diplomatic cables, such as the Kennan Telegram, can provide valuable insights into the Cold War. The Kennan Telegram, authored by George F. Kennan in 1946, outlined the policy of containment and the perceived threat of Soviet expansionism. By delving into the details and context of this document, we can gain a deeper understanding of the United States’ approach to dealing with the Soviet Union.
Overall, analyzing Cold War documents allows us to reconstruct the historical context, motivations, and strategies of the major players involved. By examining these primary sources, we can develop a nuanced understanding of the Cold War and its lasting impact on global politics.
Document 1: The Truman Doctrine
The Truman Doctrine, announced by President Harry S. Truman in 1947, was a significant policy change in the United States’ approach to international affairs during the Cold War. The doctrine was outlined in a speech delivered to a joint session of Congress, where Truman emphasized the need to contain the spread of communism, particularly in Greece and Turkey. This document reflects the United States’ commitment to supporting nations that were under threat of communist expansion.
In his speech, Truman argued that the United States had a responsibility to support countries that resisted communist influence, as communism posed a threat to democracy and freedom. He requested Congress to authorize $400 million in aid to Greece and Turkey, stating that it was necessary to prevent communism from taking hold in these countries. This marked a shift in U.S. foreign policy, as it signaled a departure from the policy of isolationism that had characterized the pre-World War II era.
Truman’s doctrine was significant because it established the principle of containment, which became the cornerstone of U.S. foreign policy during the Cold War. Through the Truman Doctrine, the United States committed itself to providing economic and military assistance to countries fighting against communism. This policy laid the groundwork for future interventions, such as the Marshall Plan and the formation of NATO, which aimed to contain the spread of communism and promote democratic values.
The Truman Doctrine had long-lasting effects on the international stage. By pledging support to countries threatened by communism, the United States positioned itself as a global power and leader of the free world. It marked a shift in U.S. foreign policy, from a more isolationist stance to an active role in promoting and defending democracy and capitalism. The doctrine also set the stage for the ideological rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, known as the Cold War, which influenced global politics for decades to come.