
A microscope is a powerful tool used to observe objects and organisms at a microscopic level. In order to understand how a microscope works, it is important to know the different parts and functions of this intricate instrument. This article provides an answer key for coloring the different parts of a microscope, helping users to familiarize themselves with its components.
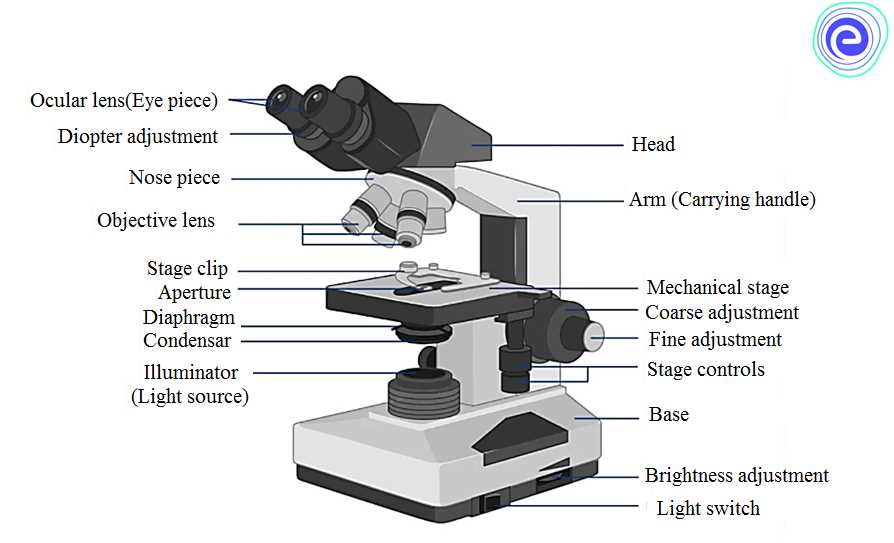
The first part of a microscope to be colored is the eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens. This is the part that the user looks into to view the specimen. Typically, the eyepiece is removable and can be adjusted to fit the user’s eyes. It is important to color this part carefully as it allows the user to see the magnified image clearly.
Next, the objective lens should be colored. The objective lens is the part of the microscope that is closest to the specimen. It is responsible for magnifying the image and comes in different magnification powers, such as 4x, 10x, and 40x. Each magnification power is represented by a different objective lens, so it is important to color this part accurately to distinguish between them.
Other parts of the microscope that need to be colored include the stage, which holds the specimen, and the condenser, which focuses the light onto the specimen. The coarse and fine adjustment knobs, used to focus the microscope, should also be colored. Lastly, don’t forget to color the base, which provides stability to the microscope.
By coloring the different parts of the microscope, users can gain a better understanding of its components and their functions. Understanding the various parts of the microscope is essential for properly using and maintaining this valuable scientific tool.
The Importance of Microscopes
Microscopes play a vital role in many scientific fields, allowing scientists to observe and study objects at a molecular and cellular level. They enhance our understanding of the natural world and have revolutionized various scientific disciplines. Let’s explore the importance of microscopes in more detail.
Advancing medical research: Microscopes have been instrumental in the field of medicine, enabling researchers and healthcare professionals to examine cells, tissues, and organisms with high precision. They have helped identify and understand various diseases, contributing to the development of new treatments and medications.
Unveiling the mysteries of biology: Microscopes have allowed biologists to delve deep into the intricate world of living organisms. By studying cells, microorganisms, and tissues under a microscope, scientists have made groundbreaking discoveries about the structure and functioning of living organisms, leading to advancements in fields such as genetics and microbiology.
- Revealing the wonders of the microscopic world: Microscopes have allowed us to explore and appreciate the beauty and complexity of the invisible world. From the intricate patterns on a butterfly wing to the delicate structure of a snowflake, microscopes have revealed the hidden beauty all around us.
- Improving industrial processes: Microscopes are essential tools in industries such as electronics, materials science, and quality control. They enable researchers and engineers to study and analyze the properties, structure, and composition of materials, ensuring the production of high-quality products.
- Advancing environmental science: Microscopes have played a crucial role in understanding and monitoring the environment. By examining microorganisms, pollen, and other tiny particles, scientists can assess the quality of water and air, detect pollutants, and study ecosystems.
In conclusion, microscopes have revolutionized scientific research and our understanding of the world around us. They have contributed to advancements in medicine, biology, industry, and environmental science. Without microscopes, many discoveries and advancements would not have been possible, making them indispensable tools in the scientific community.
Learning about the parts of a microscope
When it comes to understanding how a microscope works, it is essential to familiarize yourself with its various parts. Each component plays a crucial role in facilitating the magnification and visualization of tiny specimens. By knowing the parts and their functions, you can effectively operate a microscope and make accurate observations.
One of the main parts of a microscope is the eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens. It is the component that you look through and gives you a direct view of the specimen. The eyepiece usually provides a magnification of 10x or 15x, allowing you to see the details of the sample.
The objective lenses are another critical part of the microscope. These lenses are located on a rotating turret and come in various magnifications, such as 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. By rotating the turret and selecting the desired objective lens, you can change the overall magnification of the microscope, enabling you to examine the specimen at different levels of detail.
The stage of the microscope is where you place the specimen for viewing. It usually has a glass slide holder and mechanical stage controls, allowing you to move the slide in a precise and controlled manner. The stage clips ensure that the slide stays in place while you focus on the specimen, preventing any accidental movement.
Another essential part of the microscope is the condenser. It is located beneath the stage and helps concentrate and focus the light onto the specimen. By adjusting the condenser’s height and opening, you can control the amount and direction of light, enhancing the clarity and contrast of the image.
Learning about the different parts of a microscope is an essential step in becoming proficient in microscopy. By understanding their functions and how they work together, you can effectively operate a microscope and accurately observe and analyze microscopic specimens.
The microscope and its parts
A microscope is a scientific instrument used to magnify small objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye. It consists of several parts that work together to provide a clear and magnified image of the specimen being observed. Understanding the different parts of a microscope is essential for proper and effective use of this powerful tool.
One of the main parts of a microscope is the eyepiece or ocular lens. This is the part where you look through to see the magnified image of the specimen. The eyepiece usually has a magnification power of 10x, meaning that it enlarges the image by ten times. It is important to keep the eyepiece clean and free from fingerprints or smudges to ensure a clear view.
Objective lenses
The objective lenses are another important part of the microscope. These are located just above the stage and are responsible for further magnifying the image of the specimen. Most microscopes have multiple objective lenses with different magnification powers, typically 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. The lower magnification lenses are used to locate and focus on the specimen, while the higher magnification lenses are used to examine fine details.
- Stage: The stage is the platform where the specimen is placed for observation. It usually has a hole or aperture in the center to allow light to pass through.
- Illuminator: The illuminator is the light source of the microscope, located either above or below the stage. It provides direct or reflected light to illuminate the specimen, enhancing its visibility.
- Coarse and fine focus knobs: These knobs are used to adjust the focus of the microscope. The coarse focus knob is used for rough focusing, while the fine focus knob is used for precise focusing.
- Arm: The arm is the curved part of the microscope that connects the base and the head. It is used to carry and support the microscope.
- Base: The base is the bottom part of the microscope that provides stability and support. It is also used to hold the illuminator in some microscope models.
- Diaphragm: The diaphragm is a part of the microscope that controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen. It can be adjusted to increase or decrease the brightness of the image.
Understanding the different parts of the microscope and their functions is crucial for using the microscope effectively. With proper use and care, the microscope can reveal a whole new world of microscopic organisms and structures, opening up endless possibilities for scientific exploration.
How to Use the Answer Key

When completing a worksheet or assignment that involves coloring the parts of a microscope, an answer key can be a helpful tool to ensure accuracy. Here are some tips on how to use the answer key effectively:
1. Study the Key Features:
Before starting to color, take a close look at the answer key. Identify the different parts of the microscope and familiarize yourself with their names and functions. This will help you understand which areas need to be colored and how they contribute to the overall structure of the instrument.
2. Follow the Instructions:

Once you have studied the key features, read the instructions on the worksheet or assignment carefully. Pay close attention to any specific requirements, such as using certain colors or shading techniques. The answer key will serve as a guide to ensure you accurately color each part according to the instructions provided.
3. Use the Key as Reference:
As you start coloring, keep the answer key nearby and use it as a reference. Compare the image on the answer key with your own worksheet to make sure you are coloring the correct parts. The key will help you identify any areas that you might have missed or colored incorrectly.
4. Double-Check for Accuracy:
Once you have completed coloring, take a step back and compare your worksheet with the answer key once again. Look for any discrepancies or mistakes. If you spot any errors, make the necessary corrections to ensure the final result is accurate and reflects the key.
By using the answer key effectively, you can enhance your understanding of the parts of a microscope while also developing attention to detail and accuracy in completing assignments.
Understanding the microscope parts
The microscope is an essential tool in the field of science, allowing us to observe and study microscopic organisms and structures that are invisible to the naked eye. To use the microscope effectively, it is crucial to understand its various parts and their functions.
1. Eyepiece:

The eyepiece, also known as the ocular, is the part of the microscope that you look through. It contains a lens that magnifies the image from the objective lens. Typically, the eyepiece provides a magnification of 10x.
2. Objective lenses:
The objective lenses are located on the revolving nosepiece of the microscope. These lenses come in different magnifications, usually 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. By rotating the nosepiece and selecting the desired objective lens, we can adjust the magnification level of the microscope.
3. Stage:
The stage is a flat platform where the microscope slide is placed for observation. It usually has clips or mechanical slide holders to secure the slide in place. The stage may also have a mechanical or coaxial focus knob for precise movement of the slide.
4. Condenser:
The condenser is located beneath the stage and is responsible for focusing and directing light onto the specimen. It contains a lens that concentrates the light, enhancing the resolution and clarity of the image. Adjusting the condenser can greatly improve the quality of the microscope’s image.
5. Diaphragm:
The diaphragm is a device located within the condenser that controls the amount of light passing through the condenser and onto the specimen. By adjusting the diaphragm, we can regulate the brightness and contrast of the microscope’s image.
6. Coarse and fine focus knobs:
The coarse and fine focus knobs are used to bring the specimen into sharp focus. The coarse focus knob is larger and is used for initial focusing, while the fine focus knob is smaller and permits more precise adjustments to achieve a clear image.
Understanding the different parts of the microscope and how they function is essential for using the microscope effectively. By familiarizing ourselves with these parts, we can optimize the magnification, focus, and lighting to obtain clear and detailed images for scientific observation and analysis.
Eyepiece or ocular lens
The eyepiece or ocular lens is one of the essential parts of a microscope. It is the lens through which the viewer looks to observe the specimen. The eyepiece is usually located at the top of the microscope and is connected to the body tube. It is designed to magnify the image produced by the objective lens.
The eyepiece is typically made of multiple lenses arranged in a specific configuration to provide a clear and magnified view of the specimen. It often has a removable eyecup that provides comfort to the viewer’s eye during observation. The eyepiece lens usually has a low power magnification, typically around 10x, although some microscopes may have adjustable or interchangeable eyepieces with different magnification options.
In addition to providing magnification, the eyepiece also helps to focus and adjust the image. It usually has a small focusing knob or ring that allows the viewer to make fine adjustments to the focus of the microscope. This is particularly important when observing specimens at high magnification to ensure a clear and detailed view.
Key Points:
- The eyepiece is the lens through which the viewer looks to observe the specimen.
- It is located at the top of the microscope and connected to the body tube.
- It provides magnification and helps to focus and adjust the image.
- Typically has a low power magnification, around 10x, with some microscopes having adjustable or interchangeable eyepieces.
In summary, the eyepiece or ocular lens is a crucial component of a microscope that allows the viewer to observe the specimen in a magnified and focused manner. Its design and magnification capabilities contribute to the overall clarity and detail of the observed image, making it an indispensable part of the microscope.