
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction, where the numerator and the denominator are both integers. When working with rational numbers, it is important to be able to compare and order them. This skill is essential in many fields, such as mathematics, physics, and economics, where making comparisons and ordering data is crucial.
One way to practice comparing and ordering rational numbers is by using a worksheet. A worksheet provides a structured format for students to solve problems and practice their skills. A key component of any worksheet is the answer key, which provides the correct answers and serves as a guide for students.
In the context of comparing and ordering rational numbers, a worksheet answer key in PDF format is an excellent resource. PDF format allows for easy printing and sharing, making it convenient for both students and teachers. With a PDF answer key, students can easily check their work and understand where they went wrong, while teachers can assess their students’ progress and provide feedback.
Overall, having a comparing and ordering rational numbers worksheet answer key in PDF format is a valuable tool for both students and teachers. It facilitates self-assessment and provides a means of measuring progress. By practicing and mastering these skills, students can develop a solid foundation in mathematics and enhance their problem-solving abilities.
Comparing and Ordering Rational Numbers Worksheet Answer Key PDF: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to comparing and ordering rational numbers, having a comprehensive answer key in PDF format can be an invaluable resource. This ensures that educators and students alike have access to the correct answers, allowing for a deeper understanding of the concepts being taught.
One of the key benefits of using a worksheet answer key in PDF format is that it provides a clear and organized breakdown of the steps needed to compare and order rational numbers. This can help students grasp the process more easily, allowing for better retention and application of the knowledge in future assignments and assessments.
The answer key often includes helpful explanations and examples, making it an excellent tool for both independent study and classroom instruction. Students can refer to the key to check their work, identify any mistakes, and learn from them. Educators can also use the answer key to reinforce concepts, address common misconceptions, and facilitate class discussions.
The PDF format of the answer key makes it easily accessible and printable, allowing for convenient use in various learning environments. It can be shared electronically, saved on personal devices, or printed out as needed. This flexibility ensures that students and educators can access the answer key whenever and wherever it is most beneficial.
In conclusion, a comprehensive answer key in PDF format for comparing and ordering rational numbers is an invaluable resource for both students and educators. Its clear breakdown of steps, helpful explanations, and accessible format make it a valuable tool for enhancing learning and understanding in this topic area.
Understanding Rational Numbers
In mathematics, rational numbers are a type of number that can be expressed as a fraction, where the numerator and denominator are both integers. They can also be represented as terminating or repeating decimals. Rational numbers include all integers, as well as fractions such as 1/2, 3/4, and -5/6.
One important property of rational numbers is that they can be ordered and compared. This means that we can determine whether one rational number is greater than, less than, or equal to another rational number. By comparing the numerator and denominator of two fractions, we can make these comparisons.
For example: To compare the rational numbers 2/3 and 3/4, we can cross-multiply: 2 x 4 = 8 and 3 x 3 = 9. Since 8 is less than 9, we can conclude that 2/3 is less than 3/4.
Rational numbers can also be plotted on a number line. By assigning a point on the number line to each rational number, we can visualize their order and relationships.
Understanding rational numbers is essential in many areas of mathematics, including algebra, geometry, and calculus. They are used to solve equations, represent proportions and ratios, and describe real-world quantities such as time, distance, and money.
In conclusion: Rational numbers are an important and fundamental concept in mathematics. They represent fractions and decimals that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers. By understanding and comparing rational numbers, we can make sense of their order and relationships, and apply them to various mathematical problems and situations.
Importance of Comparing and Ordering Rational Numbers

Rational numbers play a crucial role in mathematics and everyday life. They are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction or ratio of two integers. Comparing and ordering rational numbers is an essential skill that allows us to make sense of these numbers and their relationships.
One of the main reasons why comparing and ordering rational numbers is important is because it helps us understand the relative values of different quantities. By comparing rational numbers, we can determine which is greater or lesser, and by ordering them, we can arrange them in a logical sequence. This is particularly useful when working with measurements, money, or any situation where quantities need to be ranked or prioritized.
Comparing rational numbers is also valuable in problem-solving and decision-making. For example, when analyzing data or evaluating options, we often need to compare the effectiveness or efficiency of different choices. Rational numbers provide a way to quantify and compare these options, allowing us to make informed decisions based on concrete evidence. Without the ability to compare rational numbers, we would be limited in our ability to analyze and evaluate various alternatives.
Furthermore, comparing and ordering rational numbers helps in understanding and solving equations and inequalities. In algebra, equations and inequalities frequently involve rational numbers. By comparing and ordering these numbers, we can determine the solutions to equations and inequalities, as well as identify patterns and relationships that can simplify the problem-solving process. Being proficient in comparing and ordering rational numbers is, therefore, crucial in mastering algebraic concepts and advancing in higher-level mathematics.
In conclusion, the ability to compare and order rational numbers is essential in various aspects of mathematics and everyday life. It helps us understand relative values, make informed decisions, solve equations and inequalities, and overall, develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. Therefore, it is important to practice and master this skill in order to excel in mathematics and beyond.
Key Concepts in Comparing Rational Numbers
Comparing rational numbers involves determining which number is greater or less than the other. This can be done by using the concepts of greater than (>), less than (<), or equal to (=). When comparing rational numbers, it is important to understand that rational numbers can be written in different forms, such as fractions, decimals, or percents.
One key concept in comparing rational numbers is understanding the relationship between the numerators and denominators. In a fraction, the numerator represents the number of parts being considered, while the denominator represents the total number of equal parts in the whole. When comparing fractions with the same denominator, the fraction with the larger numerator is greater. On the other hand, when comparing fractions with the same numerator, the fraction with the smaller denominator is greater.
Another key concept in comparing rational numbers is converting decimals to fractions or fractions to decimals. Decimals can be converted to fractions by considering the place value of the decimal digits. Each digit to the right of the decimal point represents a power of 10, such as tenths, hundredths, or thousandths. On the other hand, fractions can be converted to decimals by dividing the numerator by the denominator.
When comparing rational numbers in different forms, such as fractions and decimals, it is important to convert them to the same form for an accurate comparison. This can be done by converting fractions to decimals or decimals to fractions using the concepts mentioned above.
In conclusion, understanding key concepts in comparing rational numbers, such as the relationship between numerators and denominators and converting between different forms, is crucial for accurately comparing and ordering rational numbers. These concepts provide a foundation for performing various operations with rational numbers and furthering mathematical understanding.
Techniques for Comparing Rational Numbers
Comparing rational numbers is an important skill in mathematics. Rational numbers include both fractions and decimals. There are several techniques that can be used to compare rational numbers, helping us determine which number is greater, lesser, or if they are equal.
1. Converting to a common denominator: One method is to convert both fractions to a common denominator. This allows us to compare the numerators directly. By multiplying the numerator and denominator of each fraction by the denominator of the other fraction, we can create equivalent fractions with the same denominator. We can then compare the numerators to determine which is greater.
2. Decimal representation: Another technique is to convert both fractions to decimals. We can do this by dividing the numerator by the denominator. Once we have the decimal representation, we can compare the numbers directly. When comparing decimals, it is important to look at the digits after the decimal point. The number with the greater digit in the first decimal place is greater.
3. Number line: A number line can also be a useful tool for comparing rational numbers. We can plot the fractions or decimals on a number line and visually see which number is greater, lesser, or if they are equal. By creating a number line from the smallest number to the largest number, we can easily determine the order of the rational numbers.
4. Ordering from least to greatest: Another approach is to order the rational numbers from least to greatest. We can do this by comparing pairs of numbers at a time and rearranging them according to their values. By repeating this process, we can arrange all the rational numbers in the desired order.
5. Using inequalities symbols: Lastly, we can use inequalities symbols (<, >, ≤, ≥) to compare rational numbers. By comparing the numerators and denominators, we can determine the relationships between the fractions. If the numerators of two fractions are equal, the fraction with the lesser denominator is greater. If the denominators are equal, the fraction with the greater numerator is greater. If neither the numerators nor the denominators are equal, we can create equivalent fractions with a common denominator and compare the numerators.
These techniques provide different approaches to comparing rational numbers, and the choice of technique often depends on the specific numbers being compared. With practice, we can become more skilled at comparing and ordering rational numbers.
Key Concepts in Ordering Rational Numbers

In mathematics, rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers. They can take the form of fractions or decimals. When ordering rational numbers, it is important to understand key concepts such as the number line, inequality symbols, and comparing numerators and denominators.
The number line is a visual representation of numbers, with the positive numbers to the right of zero, and the negative numbers to the left. Rational numbers can be plotted on the number line to determine their relative position. The number line helps in understanding which numbers are greater or lesser than others.
When comparing rational numbers, it is important to pay attention to the inequality symbols. The greater-than symbol (>), less-than symbol (<), greater-than-or-equal-to symbol (≥), and less-than-or-equal-to symbol (≤) are used to compare the values of rational numbers. These symbols indicate the order of the numbers based on their magnitude.
Comparing numerators and denominators is another key concept in ordering rational numbers. The numerator is the top number in a fraction, while the denominator is the bottom number. In order to compare two fractions, their numerators and denominators must be considered. If the numerators are the same, the fraction with the smaller denominator is greater. If the denominators are the same, the fraction with the larger numerator is greater.
Overall, understanding these key concepts in ordering rational numbers is essential in accurately comparing and arranging them. By utilizing the number line, inequality symbols, and comparing numerators and denominators, one can confidently determine the order of rational numbers.
Techniques for Ordering Rational Numbers
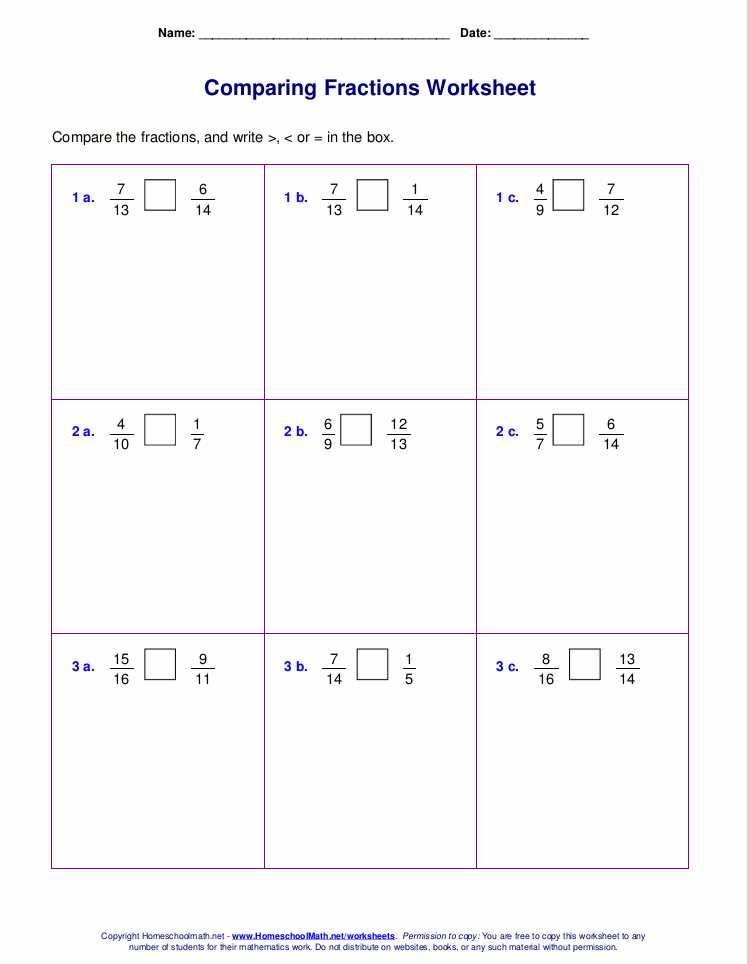
Ordering rational numbers is an important skill in mathematics. It involves arranging numbers in a specific order, either from least to greatest or from greatest to least. There are several techniques that can be used to achieve this.
1. Comparing Denominators: One way to compare rational numbers is by looking at their denominators. When comparing fractions with the same numerator, the fraction with the smaller denominator is the smaller number. For example, if we have to compare 1/2 and 1/3, we can see that 1/3 has a smaller denominator, so it is the smaller fraction.
2. Converting to Decimals: Another method is to convert all the rational numbers into decimal form and then compare them. This can be done by dividing the numerator by the denominator. For example, if we have to compare 3/4 and 5/8, we can convert them to decimals: 3/4 = 0.75 and 5/8 = 0.625. We can see that 0.75 is greater than 0.625, so 3/4 is the greater fraction.
3. Using the Number Line: The number line is a visual representation of the real number system, and it can also be used to compare and order rational numbers. We can plot the given rational numbers on the number line and then observe their positions. The number to the left of another number is always smaller, while the number to the right is greater. This technique allows for a quick and easy comparison of rational numbers.
By using these techniques, we can effectively compare and order rational numbers. Whether we are dealing with fractions or decimals, these methods provide a systematic approach to arranging numbers in the desired order. Practice with these techniques can improve our mathematical skills and make us more proficient in working with rational numbers.