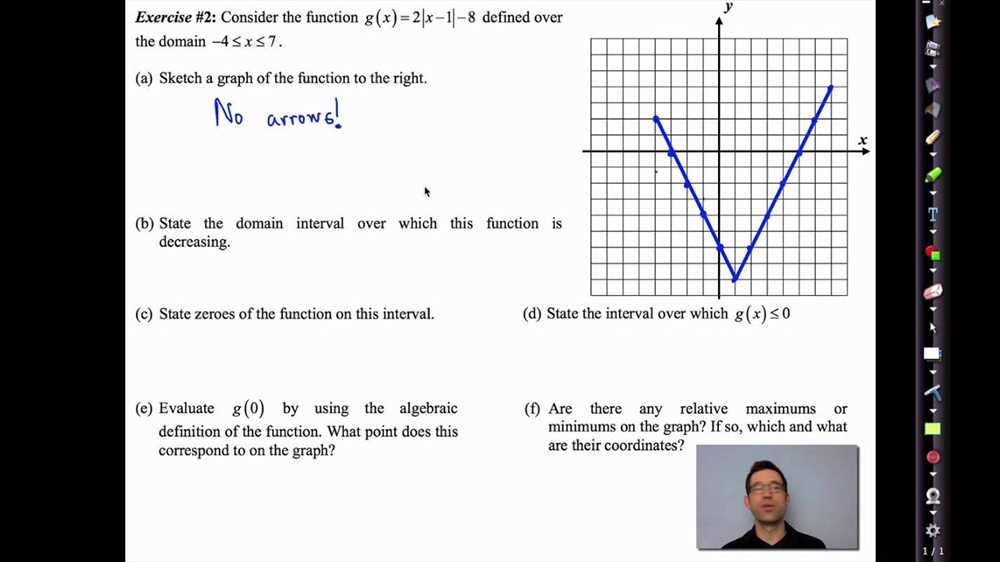
When studying mathematics, it is important to understand different types of functions and their properties. One fundamental concept is comparing two functions. This involves analyzing and contrasting the behavior, graphs, and equations of two different functions.
Comparing two functions allows mathematicians to identify similarities and differences between them, helping them to comprehend the underlying patterns and structures. By exploring the characteristics of functions, mathematicians can better understand their properties and make connections to real-world situations.
There are various ways to compare functions, such as looking at their domain and range, identifying their rates of change, or examining their graph transformations. These comparisons can reveal symmetries, intercepts, asymptotes, and other important features that provide insight into the functions’ behavior and relationships.
Understanding how to compare functions is essential for solving problems, making predictions, and analyzing mathematical models. It enables mathematicians to make informed decisions, draw meaningful conclusions, and apply their knowledge to diverse areas such as physics, economics, engineering, and computer science.
Comparing Two Functions Answer Key
When comparing two functions, there are several key factors to consider in order to determine their similarities and differences. These factors include the domains and ranges of the functions, their rates of change, and the presence of any asymptotes or intercepts.
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values for the function. By examining the domain of each function, we can determine if there are any restrictions on the input values. The range of a function, on the other hand, refers to the set of all possible output values. Comparing the domains and ranges of two functions can help us identify if they have any similarities or differences in the values they can take.
Another important factor when comparing two functions is their rate of change. The rate of change of a function describes how the output values change in relation to the input values. By examining the slopes of the functions or their derivative functions, we can determine if they have similar or different rates of change. This can help us understand how the functions behave and how quickly they increase or decrease.
Finally, it is important to consider any asymptotes or intercepts of the functions. An asymptote is a line that a function approaches but never crosses, while an intercept is a point where a function crosses the x-axis or the y-axis. By examining the presence of asymptotes or intercepts, we can identify any similarities or differences between the two functions.
In conclusion, when comparing two functions, it is important to consider their domains and ranges, rates of change, and the presence of any asymptotes or intercepts. By analyzing these key factors, we can better understand the similarities and differences between the functions and gain insight into their behavior and properties.
Understanding Functions
A function is a fundamental concept in mathematics and computer science. It is a relation that associates one input value with exactly one output value. Functions can be represented in various ways, such as algebraic expressions, graphs, or tables. They are used to describe and analyze the behavior of mathematical and computational models.
In mathematics, a function is often denoted by a symbol, followed by parentheses that enclose the input value. For example, f(x) represents a function f with input x. The output value, which is the result of applying the function to the input, is denoted by f(x). Functions can be defined explicitly, such as f(x) = 2x + 3, or implicitly, such as the equation of a circle, x^2 + y^2 = r^2.
Key properties of functions:
- Domain: The set of all possible input values for a function.
- Range: The set of all possible output values for a function.
- One-to-one correspondence: Each input value is associated with exactly one output value.
- Function composition: The combination of two or more functions to create a new function.
Understanding functions is crucial in many areas of study, including calculus, linear algebra, and computer programming. Functions provide a way to describe, analyze, and solve mathematical and computational problems. They enable us to model and understand the relationships and patterns that exist in the world around us.
Key Concepts in Comparing Functions
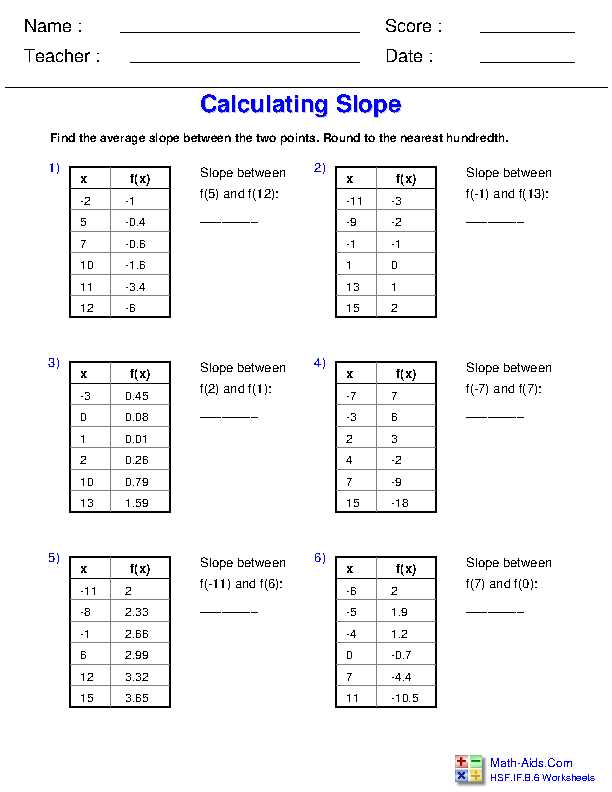
When comparing functions, there are several key concepts to understand. One important concept is the idea of domain and range. The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values, while the range is the set of all possible output values. By comparing the domains and ranges of two functions, we can determine if they are the same or different.
Another important concept is the behavior of the functions. This includes understanding whether the functions are increasing or decreasing, and whether they have maximum or minimum points. By comparing these aspects, we can determine if one function is larger or smaller than the other over a given interval.
Additionally, it is important to consider the shapes of the functions. This can be done by looking at the graphs of the functions. By comparing the shape of the graphs, we can determine if one function is steeper or flatter than the other. This can be useful in finding the rate of change or slope of the functions.
Furthermore, it is important to compare the equations or formulas of the functions. This can help us identify any similarities or differences in the expressions of the functions. By comparing the equations, we can determine if the functions have the same coefficients, exponents, or constants.
Evaluating Functions Algebraically
When evaluating functions algebraically, we substitute a given value into the function and simplify the expression to find the output, or the value of the function at that particular input. This process allows us to analyze and understand how the function behaves for different values of the independent variable.
First, let’s start with the basic concept of a function. A function is a relationship between two sets of numbers, where each input in the first set (called the domain) corresponds with exactly one output in the second set (called the range). In mathematical notation, we usually represent a function as f(x), where x is the independent variable.
To evaluate a function algebraically, we substitute a specific value for x in the function f(x) and perform the necessary calculations. For example, if we have the function f(x) = 2x – 3, and we want to find the value of f(4), we would substitute 4 for x in the function: f(4) = 2(4) – 3 = 8 – 3 = 5.
When evaluating more complex functions, such as quadratic or trigonometric functions, we follow the same process of substituting the given value into the function and simplifying the expression. It is important to be careful with calculations and follow the correct order of operations to get accurate results.
By evaluating functions algebraically, we are able to analyze the behavior of the function for different inputs and make predictions about its properties. This process is essential in various areas of mathematics, such as calculus, where we often need to find the rate of change of a function or determine critical points. Overall, evaluating functions algebraically provides us with a powerful tool to understand and work with mathematical relationships.
Analyzing Graphs of Functions
When analyzing graphs of functions, it is important to consider various aspects of the graph to gain a deeper understanding of the function’s behavior. One important aspect to consider is the domain and range of the function. The domain is the set of all possible input values, while the range is the set of all possible output values. By examining the graph, we can determine if there are any restrictions on the input values or if there are any values that the function cannot output.
Another important aspect to consider is the slope of the graph. The slope gives us information about the rate at which the function is changing. A positive slope indicates that the function is increasing, while a negative slope indicates that the function is decreasing. A horizontal line has a slope of zero, indicating that the function is not changing at all. By analyzing the slope of the graph at different points, we can determine where the function is increasing or decreasing.
Additionally, we can analyze the concavity of the graph to gain insight into the function’s behavior. The concavity refers to the curvature of the graph. A graph can be concave up, concave down, or neither. A concave up graph has a positive second derivative and opens upward, while a concave down graph has a negative second derivative and opens downward. By examining the concavity of the graph, we can determine where the function is concave up or concave down.
In summary, when analyzing graphs of functions, it is important to consider the domain and range, the slope, and the concavity. By examining these aspects of the graph, we can gain a deeper understanding of the function’s behavior and make more informed conclusions about its properties.
Identifying Characteristics of Functions
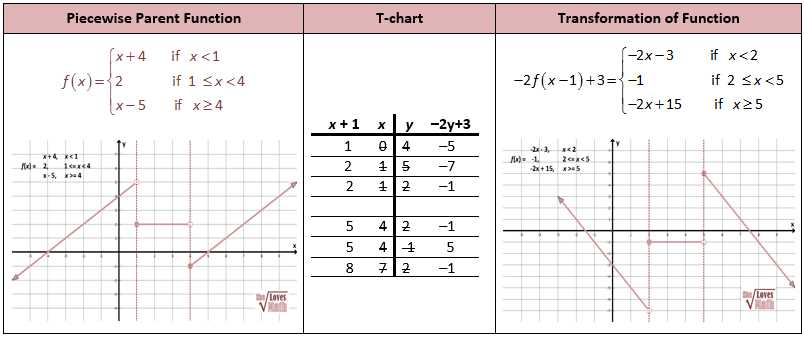
When comparing two functions, it is important to be able to identify and understand their characteristics. By examining these characteristics, we can gain insights into how the functions behave, their relationships, and their overall properties. Some key characteristics to consider when analyzing functions include:
- Domain and Range: The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values, while the range refers to the set of all possible output values. These sets can help us determine the limitations and overall behavior of a function.
- Linearity: Linearity refers to whether a function is linear or non-linear. Linear functions have a constant rate of change and can be represented by a straight line. Non-linear functions have varying rates of change and cannot be represented by a straight line.
- Continuity: Continuity refers to whether a function is continuous or discontinuous. Continuous functions have no breaks or jumps in their graph, while discontinuous functions have one or more points of discontinuity where the function is undefined or has a jump in its values.
- Monotonicity: Monotonicity describes the direction of change in a function. A function can be increasing (always going up), decreasing (always going down), or neither, where it alternates between increasing and decreasing intervals.
- Periodicity: Periodicity refers to whether a function repeats itself after a certain interval. Periodic functions have a repeating pattern, while non-periodic functions do not.
- Asymptotes: Asymptotes are lines or curves that a function approaches but never reaches. They represent the behavior of the function as the input values approach certain limits.
By considering these characteristics, we can gain a deeper understanding of how functions behave, how they are related to one another, and how they can be compared. Whether we are studying mathematical functions, computer algorithms, or real-world processes, analyzing these characteristics can provide valuable insights and aid in making informed decisions.
Comparing Rates of Change
Rates of change are a fundamental concept in mathematics that help us understand how one variable changes in relation to another. When comparing rates of change, it is important to analyze the slope of the functions or equations being compared. The slope represents the rate at which one variable is changing with respect to the other.
When comparing two functions, we can look at the slopes of their graphs to determine which function is changing at a faster or slower rate. If a function has a steeper slope, it means that it is changing at a faster rate compared to another function with a shallower slope. On the other hand, if the slope is negative, it indicates that the function is decreasing or changing in the opposite direction.
For example:
Let’s compare the rates of change of two linear functions: y = 2x and y = 3x + 2. The slopes of these functions are 2 and 3, respectively. This means that for every unit increase in x, the corresponding y-coordinate increases by 2 for the first function and 3 for the second function. Therefore, the second function y = 3x + 2 has a steeper slope and is changing at a faster rate compared to the first function y = 2x.
When comparing rates of change, it is important to consider the context and units of the variables involved. For example, if we are comparing the rates of change of two cars, one in miles per hour and the other in kilometers per hour, we need to convert the units to ensure a meaningful comparison.
In summary, comparing rates of change involves analyzing the slopes of functions or equations to determine which one is changing at a faster or slower rate. The slope represents the rate at which one variable changes with respect to another, and a steeper slope indicates a faster rate of change.
Solving Equations with Functions
In mathematics, equations with functions involve finding the values of variables that satisfy the given equation. Functions are mathematical expressions that relate inputs (variables) to outputs. Solving equations with functions requires manipulating the equation to isolate the variable and then implementing algebraic techniques to solve for its value.
When solving equations with functions, one must follow certain steps. First, identify the function and its inverse if it exists. Inverse functions allow us to simplify the equation by applying the inverse function to both sides. This helps in isolating the variable and making the equation easier to solve.
Next, use algebraic methods to simplify the equation and rearrange terms. This may involve combining like terms, distributing, or applying properties of equality. The goal is to isolate the variable on one side of the equation and move all other terms to the other side.
After simplifying, solve for the variable by performing inverse operations to both sides of the equation. The inverse operations will undo the operations performed earlier, allowing us to find the value of the variable. It is important to perform the same operation on both sides to maintain equality between the two sides of the equation.
Finally, check the solution by substituting the found value of the variable back into the original equation. If the substitution results in a true statement, then the solution is valid. If the substitution does not yield a true statement, then the solution is incorrect, and the process needs to be repeated.
- Identify the function and its inverse
- Apply inverse operations to isolate the variable
- Check the solution by substituting back into the equation
In conclusion, solving equations with functions requires applying algebraic techniques to manipulate and isolate the variable. By following a systematic approach and checking the solution, one can find the values of the variables that satisfy the given equation.