
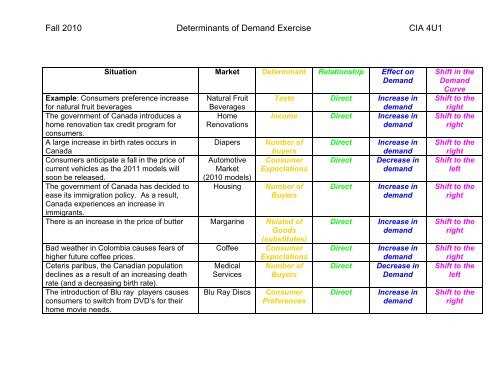
Understanding the determinants of demand is crucial for businesses and economists alike. By analyzing these factors, we can gain insights into what affects the demand for goods and services in the market. In this article, we will explore the worksheet answers for the determinants of demand, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
One of the key determinants of demand is consumer preferences and tastes. The demand for a product is heavily influenced by the preferences and tastes of consumers, as they dictate what goods and services they are willing to purchase. For example, if a new fashion trend emerges and becomes popular, the demand for clothing items related to that trend will increase.
Another determinant of demand is the price of related goods. This includes both substitutes and complements. Substitutes are products that can be used in place of one another, while complements are products that are consumed together. If the price of a substitute good decreases, consumers may switch to that alternative, leading to a decrease in demand for the original product. Conversely, if the price of a complement good increases, the demand for both products may decrease.
Furthermore, income level is a significant determinant of demand. The purchasing power of consumers is influenced by their income, and this can greatly impact the demand for various goods and services. As income increases, consumers may have more disposable income available for discretionary purchases, leading to an increase in demand for luxury items. On the other hand, if income decreases, the demand for non-essential goods may decrease.
In conclusion, the determinants of demand play a crucial role in understanding the factors that influence the demand for goods and services in the market. By considering consumer preferences and tastes, the price of related goods, and income levels, businesses and economists can better analyze and predict demand patterns, ultimately driving strategic decision-making and market success.
Determinants of Demand Worksheet Answers
Understanding the determinants of demand is crucial for analyzing and predicting changes in consumer behavior. A worksheet on this topic can be used to test and reinforce knowledge of the factors that influence demand for a product or service. Here are some possible answers to a determinants of demand worksheet:
- Price: Price is one of the most important determinants of demand. As price decreases, quantity demanded tends to increase, and vice versa. This relationship is known as the law of demand.
- Income: The income of consumers also affects demand. With a higher income, people can afford to buy more, leading to an increase in demand. Conversely, a decrease in income can lead to a decrease in demand.
- Tastes and preferences: Consumer preferences play a significant role in determining demand. If consumers favor a particular product or have a changing taste, demand may increase for that product.
- Market size: The size of the market and the number of potential consumers can impact demand. A larger market size often leads to higher demand since there are more potential buyers.
- Related goods: The demand for a product can be influenced by the prices and availability of related goods. Substitute goods, which can be used in place of each other, may see an increase in demand if the price of the other substitute increases. Complementary goods, on the other hand, often see a decrease in demand if the price of the complementary good increases.
These are just a few examples of the determinants of demand that can be included in a worksheet. Other factors, such as expectations, demographics, and government regulations, can also be explored to provide a comprehensive understanding of demand dynamics.
What are Determinants of Demand?
The determinants of demand are the factors that influence the decision of individuals or households to purchase a particular good or service. These factors include:
- Price: The price of a product is a major determinant of demand. When the price of a product increases, the demand for it generally decreases. Conversely, when the price decreases, the demand increases. The relationship between price and demand is known as the law of demand.
- Income: The income of individuals or households can have a significant impact on their demand for certain goods or services. As income increases, individuals may be more willing and able to purchase higher-priced goods, leading to an increase in demand.
- Consumer preferences: The preferences and tastes of consumers also play a role in determining demand. Different individuals may have different preferences for certain products, which can influence their decision to purchase.
- Population: The size and composition of the population can influence demand. Changes in population size or demographics can affect the demand for certain goods or services. For example, an increase in the elderly population may lead to an increase in demand for healthcare services.
- Availability of substitutes: The availability of substitute products can also influence demand. When there are more substitute products available, consumers may be more likely to switch to an alternative if the price of a particular product increases.
- Consumer expectations: Expectations about future prices or changes in income can also impact demand. If consumers expect prices to increase or their income to decrease in the future, they may choose to purchase a product sooner, leading to an increase in demand.
Overall, the determinants of demand help to explain why individuals make certain purchasing decisions and how these decisions are influenced by various factors. By understanding these determinants, businesses and policymakers can better analyze and predict consumer behavior.
Factors that Affect Demand
There are several factors that can affect the demand for a particular product or service. These factors include price, income, tastes and preferences, number of buyers, expectations, and availability of substitutes. The relationship between these factors and demand is complex and can vary depending on the nature of the product and the market conditions.
One of the most important factors that affects demand is the price of the product. In general, as the price of a product increases, the quantity demanded decreases. This is known as the law of demand. However, the relationship between price and demand is not always straightforward. In some cases, a decrease in price may actually lead to a decrease in demand, as consumers may perceive the lower price as an indication of lower quality. On the other hand, a decrease in price may also lead to an increase in demand, as consumers are more willing to purchase the product at a lower price.
Income is another important factor that affects demand. As income increases, consumers have more money to spend on goods and services, leading to an increase in demand. Conversely, as income decreases, consumers have less money to spend, leading to a decrease in demand. This relationship between income and demand is particularly relevant for luxury goods. When income levels are high, consumers may be more willing to purchase luxury items, leading to an increase in demand. However, when income levels are low, consumers may prioritize essential items over luxury goods, leading to a decrease in demand.
- Tastes and preferences: Another factor that affects demand is the tastes and preferences of consumers. The preferences of consumers can change over time, leading to changes in demand. For example, an increase in awareness about health and fitness may lead to an increase in demand for healthy food products.
- Number of buyers: The number of buyers in a market can also affect demand. A larger number of buyers can lead to an increase in demand, as there are more potential consumers for the product. Conversely, a decrease in the number of buyers can lead to a decrease in demand.
- Expectations: The expectations of consumers about future price changes or changes in their own income can also affect demand. For example, if consumers expect the price of a product to increase in the future, they may increase their demand for the product in the present to take advantage of the lower price.
- Availability of substitutes: The availability of substitutes can also affect demand. If there are close substitutes available for a product, consumers may be more willing to switch to the substitute if the price of the original product increases. This can lead to a decrease in demand for the original product.
In conclusion, there are various factors that can affect demand, including price, income, tastes and preferences, number of buyers, expectations, and availability of substitutes. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses to effectively forecast and manage demand for their products and services.
Income
Income is one of the key determinants of demand in economics. It refers to the amount of money an individual or household earns from various sources, such as employment, investments, or government assistance programs. Income plays a crucial role in influencing consumer behavior and the overall demand for goods and services.
When individuals have higher incomes, they have more purchasing power and can afford to buy a greater quantity and variety of goods and services. This leads to an increase in demand for those products in the market. On the other hand, when individuals have lower incomes, their purchasing power is limited, and they may only be able to afford basic necessities, resulting in a decrease in demand for non-essential goods.
There are two types of goods whose demand is directly affected by income: normal goods and inferior goods. Normal goods are those for which demand increases as income increases, while inferior goods are those for which demand decreases as income increases. For example, luxury goods like high-end electronics or designer clothes are considered normal goods, as demand for these products tends to rise as income levels rise. In contrast, lower-quality or generic products may be considered inferior goods, as demand for these items typically decreases as individuals’ incomes increase.
It is important for businesses and policymakers to understand the relationship between income and demand, as it can help them make informed decisions regarding pricing, marketing strategies, and social welfare programs. Changes in income levels can have a significant impact on consumer behavior and the overall health of the economy, making it a crucial factor to consider when analyzing market trends and designing effective economic policies.
Price of Related Goods
One of the factors that can influence the demand for a product is the price of related goods. There are two types of related goods: substitutes and complements.
Substitutes: Substitutes are goods that can be used in place of each other. When the price of a substitute decreases, the demand for the original product tends to decrease. For example, if the price of Coke decreases, some consumers may switch from Pepsi to Coke, causing a decrease in the demand for Pepsi.
Complements: Complements are goods that are typically consumed together. When the price of a complement decreases, the demand for the original product tends to increase. For example, if the price of hot dogs decreases, the demand for hot dog buns may increase, as consumers are more likely to purchase both items together.
In summary, the price of related goods, whether substitutes or complements, can have an impact on the demand for a product. When the price of a substitute decreases, the demand for the original product tends to decrease. On the other hand, when the price of a complement decreases, the demand for the original product tends to increase. Understanding these relationships can help businesses make strategic pricing decisions to maximize their revenues and market share.
Taste and Preferences
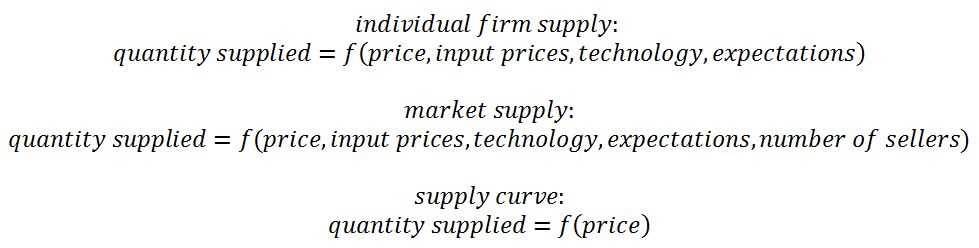
Taste and preferences play a significant role in determining the demand for a particular good or service. They refer to the subjective likes and dislikes of consumers towards different products. A person’s preference is influenced by a variety of factors such as culture, upbringing, personal experiences, and social media. For example, if a person has grown up in a family where organic food was highly valued, they are more likely to have a preference for organic products as adults.
Changes in taste and preferences can impact the demand curve for a product. If, for instance, a new trend emerges where consumers prefer healthier food options, the demand for fast food and sugary beverages may decrease. This shift in preferences can lead to a decrease in demand for certain products and an increase in demand for others. Companies need to monitor changes in taste and preferences to stay relevant and adapt their marketing strategies accordingly.
It’s important to note that taste and preferences are not static. They can change over time due to various factors such as advertising, peer influence, and personal values. Companies often invest heavily in marketing and advertising to shape consumers’ preferences and create demand for their products. By appealing to consumers’ emotions and desires, companies aim to create a favorable perception of their products, ultimately influencing consumer behavior and increasing demand.
Factors Influencing Taste and Preferences:
- Culture and upbringing
- Personal experiences
- Social media and advertising
- Peer influence
- Health and wellness trends
- Environmental concerns
Population and Demographics
The population and demographics of a region play a crucial role in determining the demand for various goods and services. Understanding the characteristics and size of the population can help businesses and policymakers make informed decisions about production, marketing, and resource allocation.
Population size: The total number of people in a specific area is an essential factor in determining demand. A larger population generally translates to a higher potential customer base for businesses. However, it is important to consider the quality of the population as well, such as the age distribution and income levels.
Age distribution: The age distribution of a population can significantly impact demand. For example, regions with a large population of young adults might have a higher demand for trendy fashion, technology, and entertainment products. On the other hand, areas with an aging population may have a higher demand for healthcare and retirement services.
Income levels: The average income and wealth distribution in a region directly influence the demand for goods and services. Higher-income individuals may have more disposable income, leading to increased demand for luxury and high-end products. Lower-income individuals, on the other hand, may prioritize essential goods and services, such as housing, food, and healthcare.
Education and occupation: The educational attainment and occupation of the population also impact demand. Regions with a highly educated population and a high percentage of professionals may have a higher demand for specialized goods and services. Conversely, areas with lower education levels and a higher percentage of blue-collar workers may have different demand patterns.
Population growth and migration: The rate of population growth and migration can significantly affect demand. Regions with a growing population due to natural increase or inbound migration may experience an increase in demand for housing, infrastructure, and consumer goods. Conversely, areas with declining populations may face reduced demand and economic challenges.
In conclusion, population size, age distribution, income levels, education, occupation, and population growth are all important determinants of demand. By analyzing these demographic factors, businesses and policymakers can better understand and predict consumer preferences, adjust their strategies, and meet the needs of the population more effectively.