
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a crucial diagnostic tool used to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart. It provides valuable information about the heart’s rhythm, conduction system, and overall cardiac health. To interpret an ECG correctly, healthcare professionals need a comprehensive understanding of cardiac anatomy, physiology, and the interpretation of various waveforms.
HAPI, which stands for Heart Activity Performance Indicator, is an answer key designed to assist healthcare professionals and students in accurately analyzing ECGs. It provides a systematic approach to interpreting complex ECG waveforms and helps identify any abnormalities in the heart’s electrical activity.
With the help of HAPI Answer Key, healthcare professionals can quickly review and analyze ECG patterns, identify irregularities, and make informed clinical decisions. It offers a simplified yet comprehensive guide to understanding the significance of different waveforms, such as P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves, in relation to heart function and potential cardiac abnormalities.
Ecg Activity Haspi Answer Key

The Ecg Activity Haspi Answer Key is a resource that provides answers to the questions and activities included in the Ecg Activity Haspi curriculum. This curriculum is designed to teach students about electrocardiography (Ecg) and its significance in healthcare. By completing the activities and reviewing the answer key, students can deepen their understanding of Ecg interpretation and the role it plays in diagnosing and monitoring cardiac conditions.
The answer key provides detailed explanations for each question and activity, allowing students to check their work and learn from their mistakes. It also includes additional information and resources to further expand students’ knowledge of Ecg interpretation and cardiovascular health. The Ecg Activity Haspi Answer Key can be used by educators as a teaching tool or by students for independent study and self-assessment.
- The Ecg Activity Haspi Answer Key covers a range of topics including Ecg waveforms, cardiac anatomy, Ecg lead placement, and common abnormalities.
- By reviewing the answer key, students can gain confidence in their ability to interpret Ecg tracings and identify potential cardiac abnormalities.
- The Ecg Activity Haspi curriculum and answer key are aligned with educational standards and provide a comprehensive introduction to Ecg interpretation.
Overall, the Ecg Activity Haspi Answer Key is a valuable resource for educators and students alike, providing a clear and concise understanding of Ecg interpretation and its importance in healthcare. By utilizing this answer key, students can enhance their knowledge and skills in Ecg interpretation, preparing them for future studies or careers in healthcare.
What is ECG Activity?

ECG, or electrocardiogram, activity refers to the electrical impulses generated by the heart during each cardiac cycle. These electrical impulses are then recorded and displayed as a graph on an ECG machine. This graph provides valuable information about the heart’s rhythm and function.
The ECG activity is measured using electrodes that are placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the electrical signals produced by the heart and transmit them to the ECG machine. The machine then converts these signals into a graphical representation, allowing healthcare professionals to analyze the heart’s activity.
The ECG activity can reveal various abnormalities or irregularities in the heart’s electrical conduction system. It can help diagnose conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and conduction disorders. By analyzing the ECG activity, doctors can determine the overall health of the heart and identify any potential cardiac problems.
Components of ECG Activity:
- P-wave: Represents the depolarization of the atria, or the contraction of the atrial muscles.
- QRS complex: Represents the depolarization of the ventricles, or the contraction of the ventricular muscles.
- T-wave: Represents the repolarization of the ventricles, or the recovery of the ventricular muscles.
By analyzing the different components of the ECG activity and their timing, healthcare professionals can identify abnormalities or disturbances in the heart’s electrical system. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of various cardiac conditions.
Importance of ECG Activity
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a crucial tool in diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions. It is a non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity of the heart and provides valuable information about the heart’s rhythm, rate, and overall function. ECG activity is essential for identifying several cardiac abnormalities and can help doctors make informed decisions regarding treatment and management.
Early detection and diagnosis: ECG activity plays a vital role in the early detection and diagnosis of various heart conditions. By analyzing the ECG waveform, doctors can identify abnormalities such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, and heart block. This allows for timely intervention and treatment, preventing further complications.
Monitoring heart health: ECG activity is routinely used to monitor a patient’s heart health, especially in cases of known heart diseases or during cardiac procedures. Continuous ECG monitoring during surgery or in the intensive care unit helps healthcare professionals detect and address any changes or abnormalities in real-time, ensuring prompt intervention if necessary. Additionally, ambulatory ECG monitoring, such as Holter monitoring, helps track heart activity over a prolonged period and provides valuable data for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Assessing treatment effectiveness: ECG activity is used to assess the effectiveness of various treatments for heart conditions. By comparing ECG readings before and after interventions such as medication, surgeries, or lifestyle changes, doctors can measure improvements in heart function and adjust treatment plans accordingly. This allows for personalized and targeted approaches to managing heart conditions and optimizing patient outcomes.
Risk stratification: ECG activity is an essential tool in risk stratification for cardiovascular events. Abnormalities in the ECG, such as prolonged QT intervals or ST segment deviations, can indicate an increased risk of cardiac events, including sudden cardiac arrest or arrhythmic episodes. By identifying high-risk individuals, healthcare professionals can implement preventive measures, such as medication or implantable devices, to reduce the risk of potentially life-threatening incidents.
Long-term monitoring: ECG activity is crucial for long-term monitoring of cardiac patients. Regular ECG assessments help track changes in heart function over time, allowing doctors to detect disease progression or complications. This enables proactive management and adjustment of treatment plans to ensure optimal cardiac health.
Overall, ECG activity is of utmost importance in the field of cardiology. It provides valuable insights into heart function, aids in early detection and diagnosis, guides treatment decisions, and facilitates long-term monitoring of patient progress. With advancements in technology and the development of portable ECG devices, this essential tool is becoming more accessible, allowing for improved patient care and outcomes.
How Does ECG Activity Work?
Electrocardiogram (ECG) activity is a diagnostic tool used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. It provides valuable information about the heart’s rhythm and overall health. ECG recordings are performed by placing electrodes on the skin, usually on the chest, which detect the electrical signals generated by the heart. These signals are then amplified and displayed on an ECG machine or monitor, allowing healthcare professionals to analyze and interpret them.
The electrical activity of the heart is generated by specialized cells called pacemaker cells, which create and conduct electrical signals throughout the heart. These signals coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the heart’s chambers, allowing the efficient pumping of blood. When the heart is functioning normally, the ECG tracing will show a consistent pattern of waves, representing the different phases of the cardiac cycle.
The main components of an ECG recording include the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. The P wave represents the depolarization (contraction) of the atria, the QRS complex represents the depolarization of the ventricles, and the T wave represents the repolarization (relaxation) of the ventricles. Abnormalities in the shape, duration, or timing of these waves can indicate various cardiac conditions, such as arrhythmias, ischemia, or myocardial infarction.
To interpret an ECG recording accurately, healthcare professionals analyze the duration, amplitude, and morphology of the waves. They look for specific patterns and abnormalities that may indicate heart disease or other conditions. By understanding the electrical activity of the heart, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about treatment and monitor the effectiveness of interventions. ECG activity is a valuable tool in cardiovascular medicine and plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing heart-related conditions.
Understanding the ECG Signal
The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) signal is a representation of the electrical activity of the heart. It provides valuable information about the rhythm, rate, and structure of the heart. Understanding the ECG signal is crucial in diagnosing and managing various cardiac conditions.
The ECG signal is a graphical representation of the electrical conduction system of the heart. It is recorded by placing electrodes on the skin, which detect the electrical impulses generated by the heart. These impulses are then amplified, filtered, and displayed on the ECG machine or monitor. The ECG signal consists of several waves and intervals, each representing a specific electrical event in the heart.
The ECG signal begins with the P wave, which represents the depolarization of the atria. This is followed by the QRS complex, which represents the depolarization of the ventricles. The T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The duration and shape of these waves can provide important information about the health of the heart.
By analyzing the ECG signal, healthcare professionals can determine if the heart is beating at a normal rate and rhythm. They can also detect abnormalities such as arrhythmias, conduction defects, and ischemia. Additionally, the ECG can provide information about the size and position of the heart chambers, as well as the presence of any structural abnormalities.
In summary, understanding the ECG signal is essential for evaluating the electrical activity and function of the heart. It allows healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage various cardiac conditions, providing valuable information for treatment decisions and patient care.
Common ECG Activity Terminology
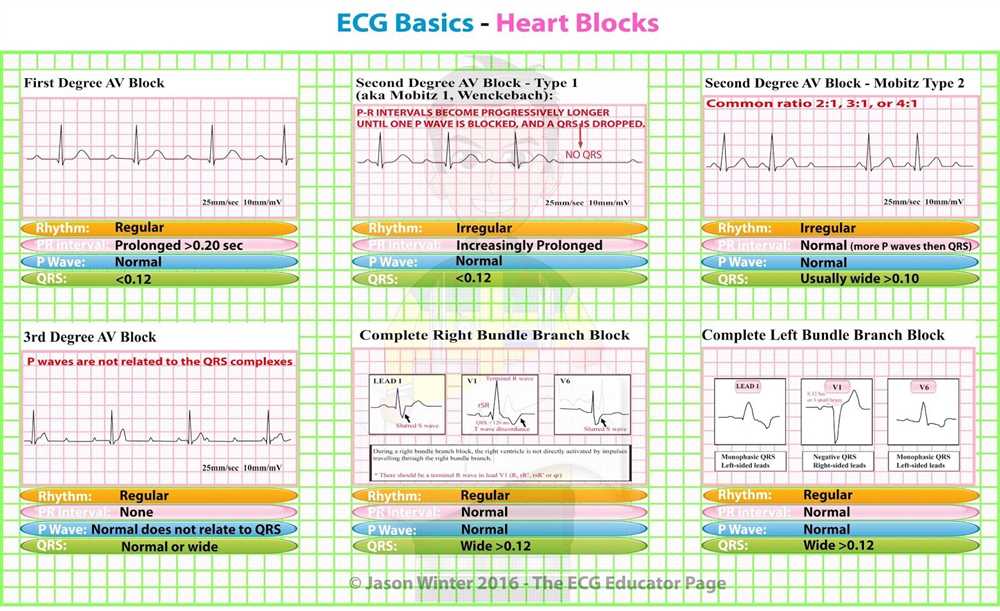
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a commonly used medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Understanding the terminology associated with ECG activity is essential for healthcare professionals to accurately interpret and diagnose cardiac conditions. Here are some of the common terms used in ECG analysis:
- P wave: The P wave represents atrial depolarization, which is the electrical activation of the atria.
- QRS complex: The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, which is the electrical activation of the ventricles.
- T wave: The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, which is the recovery of the ventricles after contraction.
- PR interval: The PR interval measures the time it takes for the electrical signal to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
- QT interval: The QT interval measures the total time it takes for ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
- ST segment: The ST segment represents the period between ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
By analyzing these ECG activity terminologies, healthcare professionals can identify abnormalities and make informed decisions regarding patient care. Some common abnormalities that may be detected include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and myocardial infarction. It is important to note that interpreting ECGs requires expertise and clinical experience, and it is always recommended to consult with a cardiologist for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
ECG Activity Haspi Answer Key Benefits
ECG activity Haspi answer key provides several benefits for students studying electrocardiography. First and foremost, it allows students to check their answers and assess their understanding of the subject. This is crucial for self-assessment and helps students identify areas where they may need further review or clarification.
Additionally, the answer key serves as a valuable study resource. By reviewing the correct answers, students can reinforce their knowledge and improve their retention of key concepts. It helps them gain a better understanding of the underlying principles of ECG interpretation and analysis.
1. Convenient and Time-saving: The answer key provides a quick and efficient way for students to check their answers without having to wait for feedback from an instructor. This saves time and allows students to progress through the material at their own pace.
2. Enhances Learning: The answer key serves as a learning tool by providing explanations and rationale for each answer. This helps students understand the reasoning behind the correct choices and deepens their understanding of ECG interpretation.
3. Self-assessment and Improvement: By using the answer key, students can assess their own performance and identify areas where they need improvement. This allows for targeted review and helps students focus their efforts on the areas that need the most attention.
Overall, the ECG activity Haspi answer key is a valuable resource that enhances learning, promotes self-assessment, and helps students improve their understanding of electrocardiography. It is an essential tool for students studying ECG interpretation and analysis.