
Ecology task cards are an ideal way for students to engage in active learning and reinforce their understanding of key ecological concepts. These task cards typically consist of questions and scenarios related to ecological principles, giving students an opportunity to apply their knowledge and critical thinking skills. However, it can be challenging for teachers to create task cards and to ensure that students receive accurate feedback on their answers. That’s where an ecology task cards answer key comes in.
The ecology task cards answer key serves as a valuable resource for both teachers and students. It provides the correct answers to the questions and scenarios presented on the task cards, allowing students to assess their understanding and identify any misconceptions they may have. This feedback is crucial for promoting the development of accurate ecological knowledge and improving critical thinking skills.
Furthermore, the ecology task cards answer key can assist teachers in effectively assessing and evaluating their students’ progress. By comparing students’ answers to the provided key, teachers can identify areas of strength and weakness in their students’ understanding of ecological concepts. This information can then be used to tailor future instruction, address any misunderstandings, and provide targeted support to individual students.
In summary, an ecology task cards answer key is an invaluable tool for both teachers and students. It promotes active learning, reinforces understanding, and allows for accurate assessment and evaluation. By utilizing this resource, teachers can ensure that their students are receiving the feedback and support they need to develop a strong foundation in ecology.
What are Ecology Task Cards?
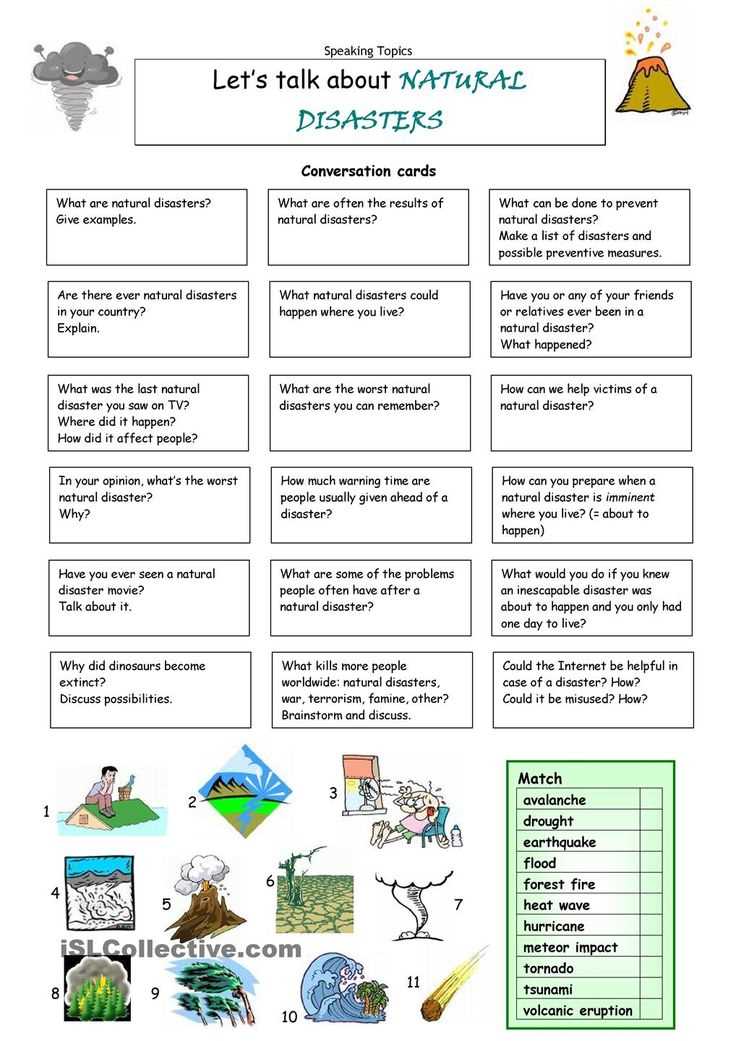
Ecology task cards are a educational tool used to teach and assess students’ knowledge in the field of ecology. These task cards are designed to cover various topics related to the study of interactions between organisms and their environment, including ecosystems, food webs, biomes, and conservation.
The task cards typically consist of questions or scenarios related to ecological concepts, and students are required to provide answers or solutions. They are commonly used in classrooms as a form of interactive learning, allowing students to actively engage with the material and apply their knowledge in a practical way.
Benefits of using ecology task cards:
- Engagement: Task cards provide a hands-on approach to learning, keeping students actively involved in the lesson.
- Assessment: They can be used as a formative or summative assessment tool to gauge students’ understanding of ecology concepts.
- Flexibility: Task cards can be utilized in various settings, such as individual or group work, stations, or as part of a review game.
- Differentiation: They can be adapted to different learning levels, allowing teachers to challenge advanced students or provide extra support for struggling learners.
- Critical thinking: Task cards often require students to analyze situations, make connections, and apply their knowledge, promoting higher-order thinking skills.
Overall, ecology task cards provide an interactive and versatile way to teach ecology concepts and evaluate students’ understanding. They offer an engaging learning experience that encourages critical thinking, application of knowledge, and collaboration among peers.
Definition and Purpose of Ecology Task Cards
Ecology task cards are educational tools designed to help students learn and practice concepts related to ecology. These cards typically consist of a set of questions or problems that require students to apply their knowledge of ecological principles and processes. Each card presents a specific scenario or situation related to ecological interactions, and students are tasked with analyzing the information and providing an appropriate response.
The purpose of ecology task cards is to engage students in active learning and critical thinking about ecological concepts. By working through these cards, students develop their problem-solving skills and deepen their understanding of ecological principles. These cards can be used in various educational settings, including classrooms, homeschooling environments, and online learning platforms.
Ecology task cards cover a wide range of topics within the field of ecology, including population dynamics, community interactions, nutrient cycling, energy flow, and biodiversity. They often incorporate real-life examples and scenarios, which allow students to connect ecological concepts to the world around them and understand the relevance and importance of these concepts. Moreover, these task cards can be tailored to different grade levels and learning objectives, making them a versatile tool for teachers and educators.
Overall, ecology task cards provide an interactive and engaging way for students to learn and practice ecological concepts. They promote active learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, and help students develop a deeper understanding of the complex relationships and processes that shape our natural world.
How to use ecology task cards
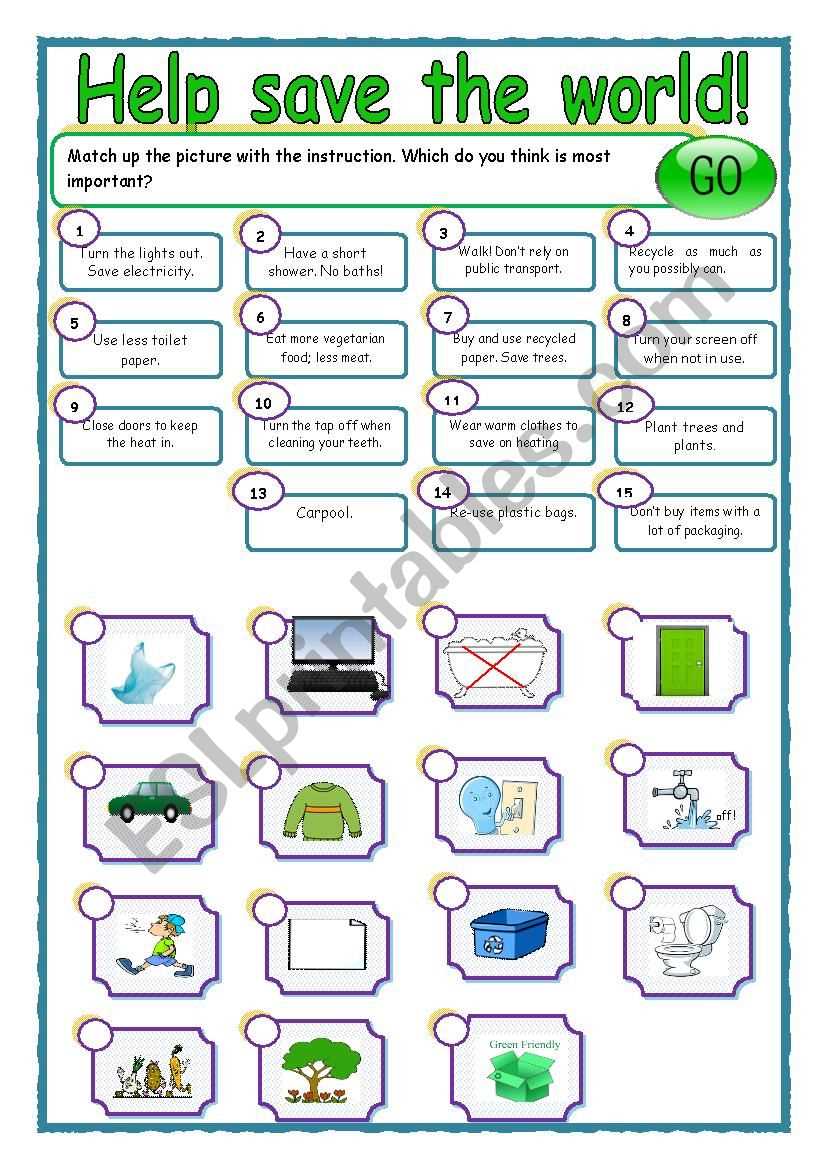
Ecology task cards are an excellent tool for learning and assessing knowledge in the field of ecology. They provide a hands-on and interactive way to engage students and test their understanding of various ecological concepts.
Here are some steps you can follow to effectively use ecology task cards:
- Prepare the task cards: Familiarize yourself with the content and format of the task cards. Make sure you have a clear understanding of the concepts covered and the questions asked. Have the task cards organized and ready for use.
- Introduce the task cards to students: Explain to the students the purpose and importance of using task cards in learning ecology. Set clear expectations and goals for the activity. Show them how to read and interpret the questions on the task cards.
- Distribute the task cards: Divide the students into small groups and distribute a set of task cards to each group. Make sure each group has a set of cards with a mix of different topics and difficulty levels. Assign a group leader or facilitator to keep track of time and ensure that everyone has an equal opportunity to participate.
- Task card activity: Instruct the students to read the questions on the task cards and discuss their answers within their group. Encourage them to use their prior knowledge, collaborate, and support their answers with evidence or examples. Remind them to pay attention to any special instructions or conditions mentioned on the task cards.
- Review and discuss: After a specified time, bring the whole class together and go over the task cards one by one. Have each group share their answers and reasoning. Facilitate a class discussion to address any misconceptions or doubts. Provide additional explanations and examples as needed.
- Assessment and feedback: Use the task cards as a formative assessment tool to evaluate students’ understanding of ecology. Provide constructive feedback and clarification on any incorrect answers or misconceptions. Encourage students to ask questions and seek further clarification.
By following these steps, you can effectively use ecology task cards to engage students, promote active learning, and assess their knowledge in the field of ecology.
Tips for Utilizing Ecology Task Cards Effectively
Ecology task cards are a great tool for teaching and assessing students’ understanding of ecological concepts. Here are some tips for utilizing these task cards effectively:
1. Group Work
One way to engage students and promote collaboration is to have them work in groups with the task cards. Divide your class into small groups and provide each group with a set of task cards. Encourage students to discuss the questions, share their answers, and explain their reasoning to each other. This not only enhances their understanding of the content but also improves their communication and teamwork skills.
2. Differentiated Instruction
Task cards can be used to differentiate instruction by providing different sets of cards based on students’ individual needs or levels of understanding. For example, you can give more challenging task cards to advanced students and simpler ones to those who need extra support. This allows you to meet the diverse needs of your students and ensure that everyone is appropriately challenged.
3. Stations or Centers
Set up stations or centers around your classroom with different task cards at each station. Students can rotate through the stations, working on different sets of task cards. This keeps the activity engaging and allows students to move around and work at their own pace. Consider adding a timer at each station to help students manage their time effectively.
4. Assessment Tool
Task cards can be used as an assessment tool to evaluate students’ understanding of ecological concepts. Collect the completed task cards and review the answers to gauge students’ comprehension. This provides valuable feedback on areas of strength and areas that need further clarification. Consider using a rubric or checklist to assess students’ responses more systematically.
By implementing these tips, you can enhance students’ engagement, promote collaboration, differentiate instruction, and assess their understanding of ecological concepts effectively using task cards. Enjoy exploring the world of ecology with your students!
Benefits of using ecology task cards
The use of ecology task cards in educational settings has numerous benefits for both teachers and students. These task cards provide a hands-on and interactive approach to learning about ecology, allowing students to actively engage with the subject matter and develop a deeper understanding of key concepts. This type of active learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential for students to excel in the field of ecology.
One of the key advantages of using ecology task cards is their versatility. They can be used in a variety of educational settings, including classrooms, science labs, and outdoor environments. This flexibility allows teachers to incorporate task cards into their lessons in a way that best suits their teaching style and the needs of their students. Additionally, task cards can be easily adapted for different grade levels and learning abilities, making them a valuable resource for educators across various levels of schooling.
Benefits for students:
- Active engagement: Ecology task cards encourage students to actively participate in their learning and take ownership of their knowledge.
- Increased retention: The interactive nature of task cards helps students retain information more effectively compared to traditional passive learning methods.
- Improvement in critical thinking: Task cards promote higher-order thinking skills, allowing students to analyze, evaluate, and apply their knowledge to solve problems.
- Enhanced collaborative skills: Task cards can be used in group or partner activities, promoting teamwork and communication skills among students.
- Real-world application: Many ecology task cards involve practical scenarios and case studies, helping students see the relevance of ecological concepts in the real world.
Overall, the use of ecology task cards provides an innovative and effective approach to teaching and learning about ecology. By incorporating these interactive tools into their lessons, teachers can create an engaging and dynamic learning environment that fosters a deeper understanding of ecological concepts and principles.
Enhanced learning and understanding

One effective way to enhance learning and understanding in the context of ecology is through the use of task cards. These task cards provide students with interactive and hands-on activities that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By actively engaging in these tasks, students are able to apply their knowledge and reinforce key concepts in ecology.
Task cards also promote a deeper level of understanding by providing students with opportunities for inquiry-based learning. They are encouraged to explore different ecological scenarios, analyze data, and make connections between different ecological concepts. This process allows students to develop a more holistic understanding of the subject matter, rather than simply memorizing facts and definitions.
Furthermore, task cards can be adapted to different learning styles and abilities, making them accessible to all students. They can be used individually, in small groups, or as part of a whole-class activity. This flexibility allows teachers to differentiate instruction and cater to the diverse needs of their students.
In addition, task cards can also be used as formative assessments to gauge students’ understanding of ecological concepts. By observing students’ responses and discussions during the task card activities, teachers can assess their understanding and address any misconceptions or gaps in knowledge.
In conclusion, the use of task cards in ecology education enhances learning and understanding by providing interactive and hands-on activities, promoting inquiry-based learning, accommodating different learning styles, and serving as formative assessments. By incorporating task cards into their teaching practices, educators can create a more engaging and effective learning environment for their students.
Reinforcement of key ecological concepts
Understanding key ecological concepts is essential for individuals to be able to make informed decisions about how to protect and conserve the environment. By reinforcing these concepts, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of the natural world and the impact of human activities on ecosystems.
1. Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of life on Earth. It encompasses all living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as their interactions with each other and with the environment. Maintaining biodiversity is crucial for the stability and functioning of ecosystems, as it provides essential services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control.
2. Ecosystem: An ecosystem is a community of living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, that interact with each other and with their physical environment. It includes both the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components of a particular area. Ecosystems can range in size from a small pond to a vast forest, and they vary in their structure and function depending on the specific conditions and species present.
3. Ecological footprint: The ecological footprint is a measure of the impact of human activities on the environment. It quantifies the amount of land and resources required to sustain an individual, a population, or a country. The concept of the ecological footprint emphasizes the need to live within the Earth’s ecological limits and to reduce resource consumption and waste generation.
4. Conservation: Conservation refers to the protection, management, and sustainable use of natural resources. It involves efforts to preserve biodiversity, protect ecosystems, and promote the responsible use of natural resources. Conservation practices can include habitat restoration, wildlife management, sustainable agriculture, and the development of renewable energy sources.
5. Climate change: Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other aspects of the Earth’s climate system. It is primarily caused by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Climate change has significant implications for ecosystems and biodiversity, as it can alter the distribution and abundance of species, disrupt ecological processes, and lead to the loss of habitats.
By reinforcing these key ecological concepts, individuals can contribute to the protection and conservation of the environment. Education and awareness are essential in promoting sustainable practices and in finding ways to mitigate the impacts of human activities on ecosystems. Only through a collective effort to understand and apply these concepts can we ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.