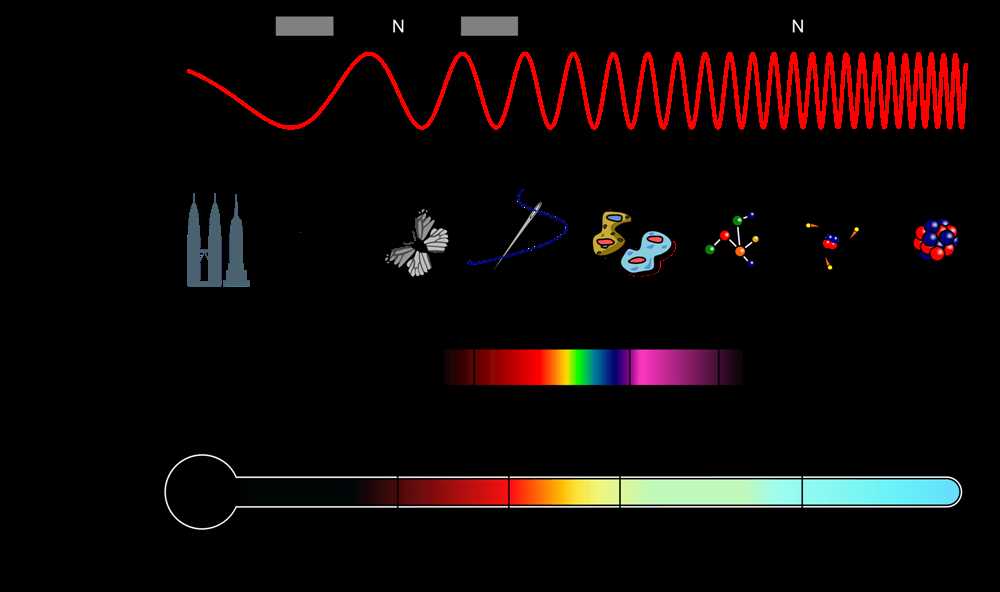
The electromagnetic spectrum is a fascinating field of study that allows us to explore the invisible universe. In this article, we will delve into the answers to some common questions about the electromagnetic spectrum as presented in BrainPOP.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum, you might ask? It is a range of electromagnetic waves, each with a different wavelength and frequency. This spectrum includes everything from radio waves to gamma rays, and visible light is just a small portion of it.
BrainPOP helps us understand how the electromagnetic spectrum is organized. It introduces us to the different types of waves, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each wave has its own unique characteristics and uses. For example, we use radio waves for communication, microwaves for cooking, and X-rays for medical imaging.
When it comes to the question of how fast light travels, BrainPOP provides the answer that it travels at a constant speed of around 186,282 miles per second (299,792 kilometers per second) in a vacuum. This speed is often referred to as the speed of light and is one of the fundamental constants in physics.
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
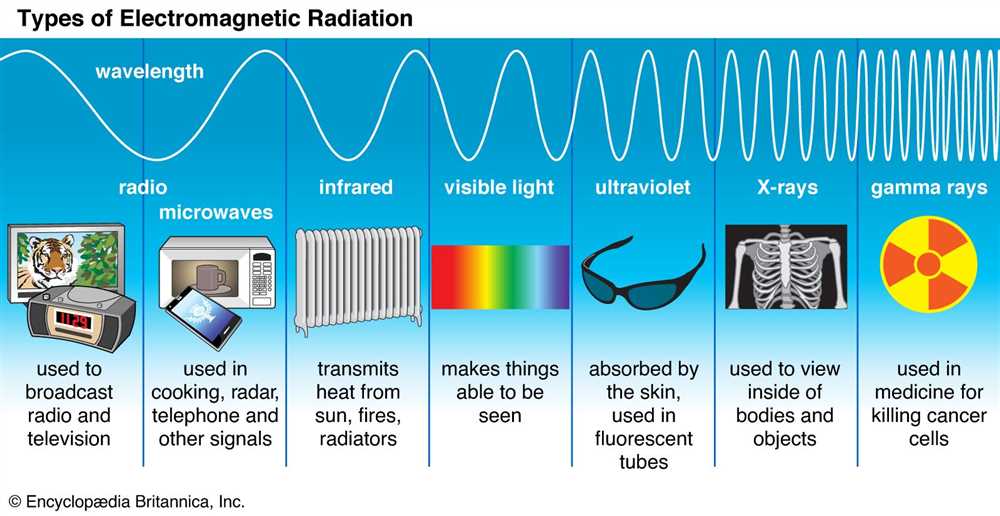
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of electromagnetic waves that includes different forms of energy, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves are all part of the same phenomenon, but they differ in their wavelength and frequency.
At one end of the spectrum, we have radio waves, which have the longest wavelength and lowest frequency. They are commonly used for communication, such as broadcasting radio and television signals. Microwaves, with a slightly shorter wavelength, are used for cooking, cell phone communication, and radar systems.
Infrared rays are next in the spectrum and are often experienced as heat. They are used in remote controls, night vision devices, and thermal imaging cameras. As we move further along the spectrum, we encounter visible light, the range of wavelengths that our eyes can detect. This includes the different colors of the rainbow.
Ultraviolet rays have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than visible light. They are responsible for causing sunburns and can be used in sterilization processes and fluorescent lighting. X-rays and gamma rays are at the opposite end of the spectrum, with the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. X-rays are commonly used in medical imaging, while gamma rays are produced during nuclear reactions.
The electromagnetic spectrum plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, from communication and technology to medicine and scientific research. Understanding and harnessing the different forms of energy in the electromagnetic spectrum have revolutionized many fields and continue to shape our world today.
Understanding the Basics of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of electromagnetic waves that include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves are all forms of energy that travel through space at the speed of light. Each type of wave has a different wavelength, frequency, and energy level.
Let’s start with radio waves. These waves have the longest wavelength and lowest frequency of all the electromagnetic waves. They are used for communication, such as broadcasting radio and television signals. They are also used for activities like radar, where they bounce off objects and provide information about their location and distance.
Microwaves, on the other hand, have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They are commonly used in microwave ovens to heat food, as well as for communication purposes, like satellite transmissions. Infrared waves have even shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than microwaves. They are used for remote controls, night vision cameras, and heat-sensitive imaging.
Visible light is the narrow part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can see with our eyes. It includes all the different colors of light, from red to violet, and has wavelengths that range from about 400 to 700 nanometers. Ultraviolet waves have even shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than visible light. They are responsible for causing sunburns and can be used in sterilizing medical equipment.
X-rays and gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies of all the electromagnetic waves. X-rays are commonly used in medical imaging, like X-ray machines and CT scans, to see inside the body. Gamma rays are extremely powerful and dangerous. They are used in cancer treatment and nuclear medicine, as well as in studying the universe and detecting cosmic events.
In conclusion, the electromagnetic spectrum is a vast range of energy waves that have a variety of uses and applications in our everyday lives. Understanding the basics of the electromagnetic spectrum can help us appreciate the role of different types of waves and how they impact our world.
Exploring the Different Types of Waves in the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a vast range of waves that includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type of wave has its own unique properties and uses, making them essential in various scientific and technological applications.
Radio waves are the longest waves in the spectrum and are commonly used for communication purposes, such as radio and television broadcasting. They have low energy and frequency, allowing them to travel long distances without getting absorbed by the atmosphere. Microwaves, on the other hand, have shorter wavelengths and higher frequency than radio waves. They are widely used in microwave ovens, telecommunications, and radar systems.
Infrared waves are the next type in the spectrum and are often used in heat sensing and night vision technologies. They have longer wavelengths than visible light, allowing them to detect heat emitted by objects. Visible light, as the name suggests, is the part of the spectrum that human eyes can detect. It consists of different colors with varying wavelengths, from red (longest wavelength) to violet (shortest wavelength).
Ultraviolet rays have shorter wavelengths than visible light and are known for their ability to cause sunburn and skin damage. However, they also play a crucial role in disinfection, fluorescence, and tanning. X-rays have even shorter wavelengths and are commonly used in medical imaging to visualize bones and internal organs. They can penetrate soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bones. Lastly, gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest energy among all waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are produced during nuclear reactions and are highly dangerous to living organisms.
In conclusion, the electromagnetic spectrum is a diverse collection of waves that are used in various fields of science and technology. From the long waves of radio waves to the extremely short wavelengths of gamma rays, each type of wave serves its unique purpose and has its own advantages and risks. Understanding and harnessing the power of these waves allow scientists and researchers to explore the world around us and make significant advancements in various areas of study.
How Does the Electromagnetic Spectrum Influence Daily Life?
The electromagnetic spectrum plays a crucial role in our everyday lives, even if we are not always aware of it. From the moment we wake up in the morning until we go to bed at night, various forms of electromagnetic waves are interacting with us or being utilized in different ways.
Radio waves are a fundamental part of our daily communication. They are used to transmit information through radio stations, television broadcasts, and cell phone signals. Without radio waves, we would not be able to listen to our favorite music or stay connected with friends and family through our mobile devices.
Infrared waves are present in many aspects of our daily routine without us even realizing it. Infrared technology is used in TV remote controls, security systems, and even in cooking appliances like microwave ovens. The heat generated by infrared waves allows us to quickly and efficiently prepare our meals.
Visible light is perhaps the most obvious form of the electromagnetic spectrum that influences our daily life. We rely on visible light to see the world around us and carry out various tasks. It illuminates our homes, workplaces, and streets, allowing us to navigate safely and perform our daily activities.
Ultraviolet rays from the sun pose a significant influence on our daily lives. While moderate exposure to sunlight is necessary for our body to produce vitamin D, excessive exposure can lead to sunburns and skin damage. Therefore, we often use sunscreen, sunglasses, and hats to protect ourselves from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation.
X-rays and gamma rays have a vital role in medical diagnostics and treatments. X-rays are used to examine bones and detect diseases, while gamma rays are used in radiation therapy to treat cancer. These forms of electromagnetic waves have revolutionized the field of medicine and have greatly improved our ability to diagnose and treat various conditions.
Microwaves are commonly used in our kitchens to quickly heat or cook food. They are also used in communication technologies like satellite transmissions and radar systems. Microwaves are essential for our convenience and safety, as they allow us to efficiently prepare meals and navigate and communicate over long distances.
In conclusion, the electromagnetic spectrum is an integral part of our daily life, impacting various aspects of our routine. From communication and entertainment to cooking and medical care, electromagnetic waves play a crucial role in making our lives easier, more efficient, and safer.
Learning about the Relationship between Frequency and Energy in the Electromagnetic Spectrum
When studying the electromagnetic spectrum, it is important to understand the relationship between frequency and energy. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a range of wavelengths and frequencies, with each energy level corresponding to a specific electromagnetic wave. The higher the frequency of an electromagnetic wave, the greater the energy it carries.
In the electromagnetic spectrum, lower frequency waves, such as radio waves and microwaves, have lower energy levels. These waves are often used for communication and heating purposes. As the frequency increases, the energy of the waves also increases. Infrared waves, for example, have higher frequencies and can be used for heat sensing and remote control applications.
As we move further into the electromagnetic spectrum, we encounter visible light waves. Visible light is made up of different colors, each with its own frequency and energy level. Red light, for example, has a lower frequency and energy compared to violet light. The energy of visible light is responsible for our ability to see and distinguish between different colors.
At even higher frequencies and energy levels, we find ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves have the ability to penetrate solid objects and can be used in medical imaging and sterilization processes. However, due to their high energy levels, they also pose potential hazards to living organisms, which is why precautions and protective measures are required when working with them.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between frequency and energy is crucial when studying the electromagnetic spectrum. The spectrum encompasses a wide range of waves, each with its own specific frequency and energy level. By understanding these relationships, we can better utilize and harness the diverse applications and properties of the electromagnetic waves in various fields.
The Role of Electromagnetic Waves in Communication and Technology
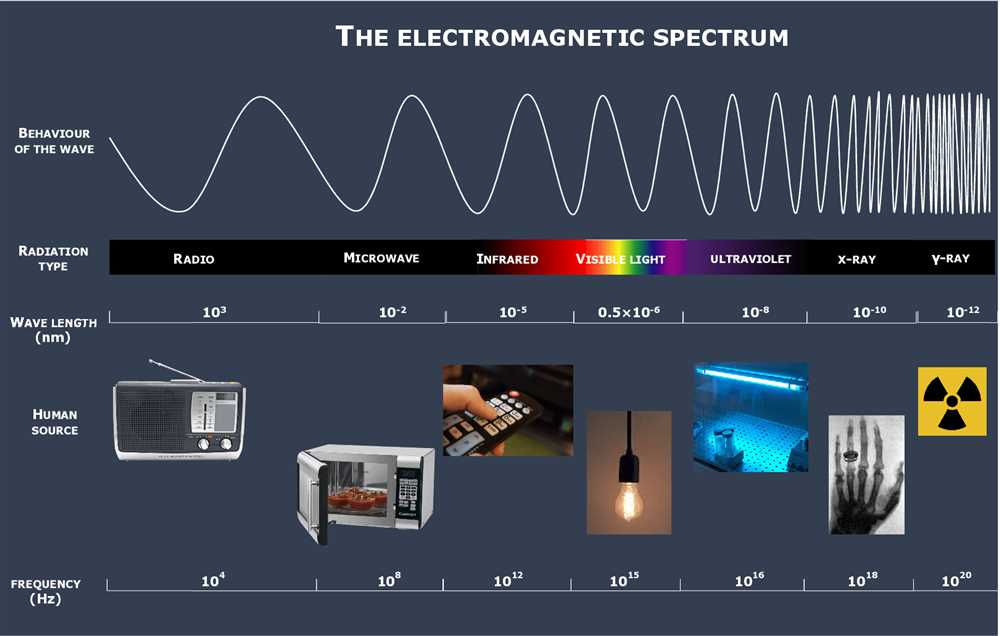
The electromagnetic spectrum plays a crucial role in modern communication and technology. Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that can travel through space and carry information. These waves are used in various ways to transmit data, communicate wirelessly, and power devices.
One of the key uses of electromagnetic waves is in wireless communication. Radio waves, which are a type of electromagnetic wave with the longest wavelength, are used to transmit signals for radio and television broadcasting. They are also used for cellular communication, allowing people to make phone calls and send text messages without the need for physical cables. This has greatly increased the mobility and convenience of communication.
In addition to wireless communication, electromagnetic waves are also used in technology such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. These technologies use shorter wavelength waves, such as microwaves and infrared waves, to transmit data wirelessly between devices. Wi-Fi allows us to connect to the internet without the need for physical cables, while Bluetooth enables the wireless transfer of data between devices such as smartphones, tablets, and headphones.
Moreover, electromagnetic waves are used in medical imaging technologies such as X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). X-rays use high-energy waves to create images of the internal structures of the body, helping doctors diagnose and treat various conditions. MRI uses a combination of radio waves and magnetic fields to produce detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues.
In conclusion, electromagnetic waves play a crucial role in communication and technology. They enable wireless communication, power wireless devices, and are used in medical imaging. The ability to transmit information wirelessly and create detailed images has revolutionized the way we communicate, access information, and diagnose medical conditions.
Examining the Electromagnetic Spectrum in Astronomy and Astrophysics

The study of the electromagnetic spectrum is crucial in the field of astronomy and astrophysics. By examining the various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation emitted by celestial bodies, scientists are able to gather important information about the universe.
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of wavelengths, from radio waves with the longest wavelengths to gamma rays with the shortest wavelengths. Each wavelength corresponds to a different form of electromagnetic radiation, and each has its own unique properties and interactions with matter.
Radio waves, for example, have long wavelengths and low frequencies. They are commonly used in radio astronomy to study celestial objects and phenomena. Microwaves, on the other hand, have slightly shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies. They are often used in studies of the cosmic microwave background radiation, which is considered a remnant of the Big Bang.
Infrared radiation lies in between the microwaves and visible light. It is emitted by warm objects in space, allowing astronomers to detect and study cosmic dust and objects that may be otherwise invisible. Visible light, the part of the spectrum that is visible to the human eye, is important for gathering information about stars, planets, and other celestial bodies.
Ultraviolet radiation has shorter wavelengths than visible light and is emitted by extremely hot objects, such as the Sun. It is often used to study the composition and temperature of stars and other high-energy phenomena in the universe. X-rays have even shorter wavelengths and are commonly used in X-ray astronomy to study black holes, supernovae, and other energetic processes.
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are extremely energetic and are often associated with nuclear reactions and other violent cosmic events. Gamma-ray astronomy provides insights into the most extreme and energetic phenomena in the universe.
By examining the electromagnetic spectrum across different wavelengths, astronomers and astrophysicists can uncover a wealth of information about the universe. It allows them to study objects and phenomena that are invisible or difficult to observe using other means, providing a deeper understanding of the cosmos.