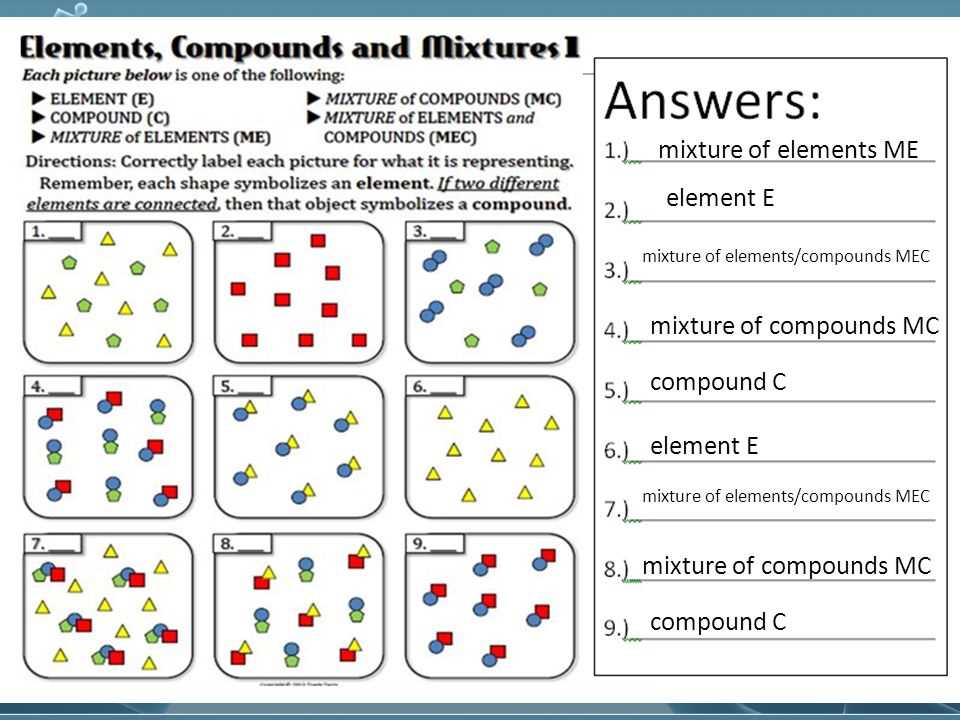
Understanding the different forms of matter is fundamental to grasping the intricacies of chemistry. As students delve into this subject, worksheets serve as valuable tools to reinforce their knowledge. Offering a comprehensive overview, the elements, compounds, and mixtures worksheet provides a mix of theoretical and practical exercises for students to enhance their understanding of these fundamental concepts.
The worksheet presents a range of questions and problems that challenge students to distinguish between elements, compounds, and mixtures, as well as to identify their unique characteristics. By engaging with real-life examples and practical scenarios, students are encouraged to apply their knowledge and develop problem-solving skills, which are essential in scientific inquiries.
With carefully crafted elements, compounds, and mixtures worksheet answers in PDF format, teachers can efficiently assess students’ comprehension and guide their learning journey. As students work through the exercises, they will explore the properties of elements, compounds, and mixtures, understand their differences, and learn how these concepts relate to the composition of matter in the world around us.
Understanding the Basics
Understanding the basics of elements, compounds, and mixtures is essential for anyone studying chemistry. These concepts form the foundation of the subject and provide a framework for understanding the behavior of matter.
At the most basic level, an element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are represented by symbols, such as H for hydrogen and O for oxygen, and are organized on the periodic table. Each element has its own unique set of properties and characteristics.
A compound is a substance that is made up of two or more different elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio. Compounds can be represented by chemical formulas, which show the types of elements present and the number of atoms of each element in a single unit of the compound. For example, the compound water (H2O) is made up of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
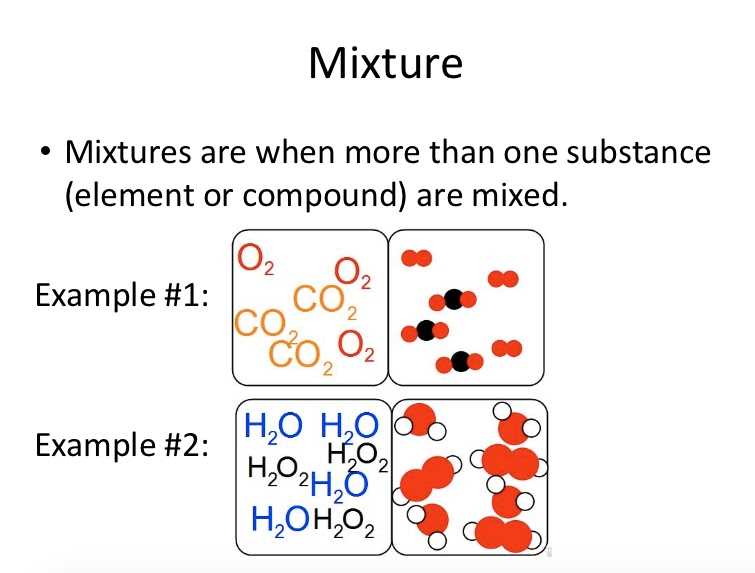
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Unlike compounds, the substances in a mixture retain their individual properties. Mixtures can be either homogeneous, where the components are evenly distributed and cannot be visually distinguished, or heterogeneous, where the components are not evenly distributed and can be visually distinguished. Examples of mixtures include saltwater (homogeneous) and salad dressing (heterogeneous).
In conclusion, understanding the basics of elements, compounds, and mixtures is crucial for comprehending the world of chemistry. Elements are the building blocks of matter, compounds are the result of chemical combinations, and mixtures are combinations of substances that retain their individual properties. By grasping these fundamental concepts, one can begin to explore and understand the many complexities of chemistry.
Importance of Knowing the Differences
Understanding the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures is crucial in various fields of science and everyday life. By having a clear understanding of these concepts, scientists can accurately analyze and predict the behavior of substances, and individuals can make informed choices about the materials they use.
Elements: Elements are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances and are represented by unique symbols on the periodic table. Knowing the differences between elements is essential in fields such as chemistry and physics. It allows scientists to identify and classify elements based on their properties, atomic structure, and behavior in different conditions.
Compounds: Compounds are substances formed when two or more elements chemically combine. Understanding the differences between compounds is crucial in fields such as pharmaceuticals and materials science. It enables scientists to study the composition, properties, and reactions of compounds, which are essential for developing new drugs, creating innovative materials, and understanding biological processes.
Mixtures: Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. Knowing the differences between mixtures is important in fields such as environmental science and food technology. It allows scientists to analyze and separate mixtures based on their physical properties, such as boiling points and solubility, which is crucial for water purification, waste management, and food processing.
By understanding the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures, scientists can advance their research and make significant contributions to various scientific disciplines. Additionally, individuals can make informed choices about the materials they interact with daily, ensuring their safety and well-being.
Elements Worksheet PDF Answers
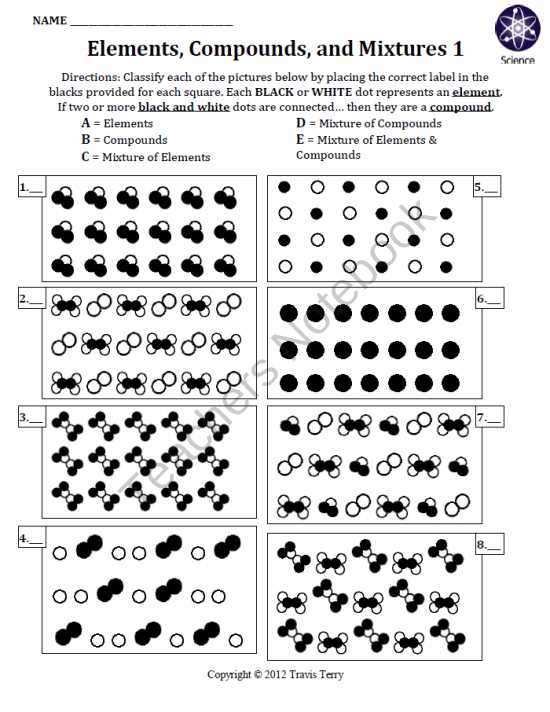
In the study of chemistry, it is important to understand the basic building blocks of matter: elements. Elements are substances that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means. They are represented on the periodic table by symbols and organized according to their atomic number. Each element has unique properties and characteristics that distinguish it from other elements.
One way to learn about elements is through worksheets that provide questions and activities to test your knowledge. A Elements Worksheet PDF is a useful tool that offers a variety of questions related to elements: their symbols, atomic numbers, properties, and uses. By answering these questions, you can reinforce your understanding of elements and their significance in chemistry.
Here are some example answers to elements worksheet questions:
- What is the symbol for carbon? The symbol for carbon is C.
- What is the atomic number of oxygen? The atomic number of oxygen is 8.
- What are the properties of sodium? Sodium is a soft, silver-white metal that is highly reactive and easily forms compounds.
- What is the main use of iron? Iron is mainly used in the production of steel, which is an essential material in construction and manufacturing.
By reviewing and answering questions like these, you can enhance your understanding of elements and their role in the world of chemistry. Elements worksheets are valuable resources that can help you solidify your knowledge and improve your overall comprehension of this fundamental branch of science.
Exploring the Periodic Table
The Periodic Table is a powerful tool used by scientists to organize and categorize elements based on their properties. It is a systematic arrangement of all known elements in the universe, with each element assigned a unique atomic number, symbol, and atomic weight. By studying the patterns and trends of elements on the Periodic Table, scientists can make predictions about their behavior and discover new elements and compounds.
One of the key features of the Periodic Table is its organization into periods and groups. Periods are horizontal rows that represent the number of energy levels or shells an element has. The number of shells determines an element’s size and reactivity. Groups are vertical columns that represent elements with similar chemical properties. Elements in the same group tend to have the same number of valence electrons, which affects their reactivity and bonding ability.
Each element on the Periodic Table is represented by a unique symbol, usually a one or two-letter abbreviation derived from its name. The symbol is accompanied by the element’s atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus. The atomic weight, which represents the average mass of an element’s atoms, is also listed for each element.
The Periodic Table is divided into several distinct blocks: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. These blocks correspond to the different types of orbitals in which electrons reside. The s-block and p-block elements are commonly found in everyday materials, while the d-block and f-block elements are often used in applications requiring unique properties and characteristics, such as catalysis or magnetism.
In conclusion, the Periodic Table is a powerful tool that allows scientists to better understand the properties and behaviors of elements. Its organized structure provides a wealth of information and enables scientists to make predictions and discoveries that have a profound impact on various scientific fields.
Identifying Elements and Their Properties
In the science of chemistry, it is important to be able to identify different elements and their unique properties. Elements are the building blocks of matter and cannot be broken down into simpler substances. Each element has its own distinctive set of characteristics that help scientists differentiate between them.
One way to identify an element is by its atomic number. The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom of that element. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, which means it has one proton. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8, indicating it has eight protons. By knowing the atomic number, scientists can determine the identity of an element.
Another important property of elements is their atomic mass. The atomic mass represents the average mass of all the isotopes of an element. Isotopes are variations of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass is usually listed in the periodic table and is based on a weighted average of these isotopes.
Elements also have unique physical and chemical properties that help distinguish them. Physical properties include characteristics such as density, boiling point, melting point, and color. For example, gold is a dense metal that has a distinct yellow color. Chemical properties relate to how an element reacts with other substances. Oxygen, for instance, is highly reactive and readily combines with other elements to form compounds.
In conclusion, identifying elements and their properties is crucial in the field of chemistry. By understanding an element’s atomic number, atomic mass, physical properties, and chemical properties, scientists can accurately classify and study different elements. This knowledge forms the foundation of our understanding of matter and how substances interact with one another.
Compounds Worksheet PDF Answers
Here, you will find the answers to the compounds worksheet in PDF format. The compounds worksheet is designed to help you practice identifying different compounds and their chemical formulas. By completing this worksheet, you can gain a better understanding of how compounds are formed and named.
Answer Key:
- 1. Sodium chloride (NaCl): This compound is formed by combining sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) atoms in a 1:1 ratio. The chemical formula for sodium chloride is NaCl.
- 2. Carbon dioxide (CO2): This compound is formed by combining one carbon (C) atom with two oxygen (O) atoms. The chemical formula for carbon dioxide is CO2.
- 3. Water (H2O): This compound is formed by combining two hydrogen (H) atoms with one oxygen (O) atom. The chemical formula for water is H2O.
- 4. Calcium carbonate (CaCO3): This compound is formed by combining one calcium (Ca) atom with one carbon (C) atom and three oxygen (O) atoms. The chemical formula for calcium carbonate is CaCO3.
- 5. Methane (CH4): This compound is formed by combining one carbon (C) atom with four hydrogen (H) atoms. The chemical formula for methane is CH4.
These are just a few examples of compounds and their chemical formulas. By studying and practicing with worksheets like this one, you can become more familiar with the different compounds and their compositions. This knowledge will be useful in various fields, such as chemistry, biology, and even everyday life.
What Are Compounds?
Compounds are substances that are formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements. These elements can be either metals or non-metals. The properties of compounds are often different from the properties of the elements that make them up. Compounds have a fixed ratio of elements and can only be separated into their individual components through a chemical reaction.
When elements come together to form a compound, they combine in a specific way. This is known as the chemical formula of the compound. The chemical formula represents the types and quantities of atoms in a compound. It consists of chemical symbols and subscripts, which indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
For example, water (H2O) is a compound formed by the chemical combination of two hydrogen (H) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms in water is always 2:1, giving it its unique properties and characteristics.
Compounds can have a wide range of physical and chemical properties. Some compounds are toxic, while others are beneficial to living organisms. Compounds can also have different states of matter, such as solid, liquid, or gas, depending on the temperature and pressure conditions. The study of compounds and their properties is an important part of chemistry.
Formulas and Naming Conventions
When discussing elements, compounds, and mixtures, it is important to understand the formulas and naming conventions used to represent them.
Elements: Each element is represented by a unique symbol, usually consisting of one or two letters. For example, oxygen is represented by the symbol “O”, and carbon is represented by the symbol “C”. These symbols are derived from either the English or Latin names of the elements. In addition to the symbol, elements are assigned an atomic number and atomic mass, which provide further information about their properties.
Compounds: Compounds are substances made up of two or more different elements chemically bonded together. The formula for a compound represents the ratios and types of atoms present. For example, water is a compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, so its formula is H2O. The formula of a compound is determined by the valence (combining) ratios of the elements involved.
In terms of naming conventions, compounds are named using a system based on the elements present. Generally, the element with the lower electronegativity (ability to attract electrons) is named first, followed by the element with the higher electronegativity. The second element is then modified by changing the end of the name to “-ide”. For example, sodium chloride consists of sodium and chlorine, so it is named as such. Another example is carbon dioxide, which consists of carbon and oxygen. The first element, carbon, is named first, while the second element, oxygen, is modified to become “oxide”.
In conclusion, understanding the formulas and naming conventions for elements, compounds, and mixtures is essential in chemistry. It allows scientists to accurately represent and communicate the composition of substances, which is crucial for further research and analysis.