If you are currently studying energy and its various forms, you may have been assigned a worksheet exploring the concept of an energy curve. This worksheet helps students understand how energy is transformed and transferred within a system, and how it can be represented graphically. In this article, we will provide an answer key for the energy curve worksheet, which will help you check your answers and deepen your understanding of this important topic.
The energy curve worksheet typically consists of a series of graphs or diagrams representing different scenarios. Each graph displays the energy levels of the system over time, and students are required to analyze and interpret the transformations and transfers of energy represented in the graph. By understanding these energy curves, students can gain insights into concepts such as conservation of energy, potential energy, and kinetic energy.
In our answer key, we will walk you through each question on the energy curve worksheet, explaining the reasoning behind the correct answers and providing additional insights to enhance your comprehension. We will also highlight common misconceptions or pitfalls that students may encounter while working on this assignment. By thoroughly reviewing the energy curve worksheet and its accompanying answer key, you will be better equipped to handle similar problems and deepen your understanding of energy and its transformations.
What is an energy curve worksheet?
An energy curve worksheet is a tool used in physics or chemistry education to graphically represent the changes in energy during a particular process or reaction. It allows students to visualize and analyze the energy changes that occur as reactants are converted into products.
The energy curve worksheet typically includes an x-axis representing the progress of the reaction or process and a y-axis representing the energy level. The worksheet may include multiple curves or lines to represent different energy components, such as potential energy, kinetic energy, or total energy. The curves may be labeled or color-coded for clarity.
Students are usually provided with data or information about the reaction or process, such as the initial and final energy states, and they are required to plot the energy curve accordingly. This requires understanding the concepts of energy conservation, potential energy, and kinetic energy. By constructing the energy curve and analyzing it, students can gain insights into the energy changes that occur during the reaction or process.
Energy curve worksheets are important tools in understanding and visualizing the principles of energy conservation and transformation. They help students develop critical thinking skills and deepen their conceptual understanding of energy in various scientific phenomena.
How to use an energy curve worksheet
Using an energy curve worksheet can be a helpful tool for analyzing and understanding the flow of energy in a system. Whether you are studying physics, engineering, or any other science related to energy, this worksheet can provide valuable insights. Here are some steps to effectively use an energy curve worksheet:
- Identify the system: Start by clearly defining the system you want to analyze. This could be a mechanical system, an electrical circuit, or any other system where energy is involved.
- Identify the different forms of energy: List down all the different forms of energy that are present in the system. This could include kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, or any other form that is relevant.
- Plot the energy curve: Using the gathered information, plot an energy curve on the worksheet. The x-axis represents time, while the y-axis represents the amount of energy in the system. Use different colors or patterns to differentiate between the different forms of energy.
- Analyze the curve: Once the energy curve is plotted, carefully analyze the shape and changes in the curve. Look for patterns, trends, and any abrupt changes that might indicate energy conversions or transfers.
- Calculate energy transfer: Use mathematical equations and formulas to calculate the amount of energy transferred between different forms at different points in time. This can help in understanding the efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
By following these steps and utilizing an energy curve worksheet, you can gain a deeper understanding of how energy flows and changes in a system. This visual representation can enhance your learning experience and make complex energy concepts more accessible.
Understanding the components of an energy curve worksheet
In order to better understand the concept of an energy curve worksheet, it is important to break down its components and understand their purpose. The energy curve worksheet is designed to help individuals visualize and analyze energy usage over a period of time. It consists of various components that provide valuable insights into energy consumption patterns and trends.
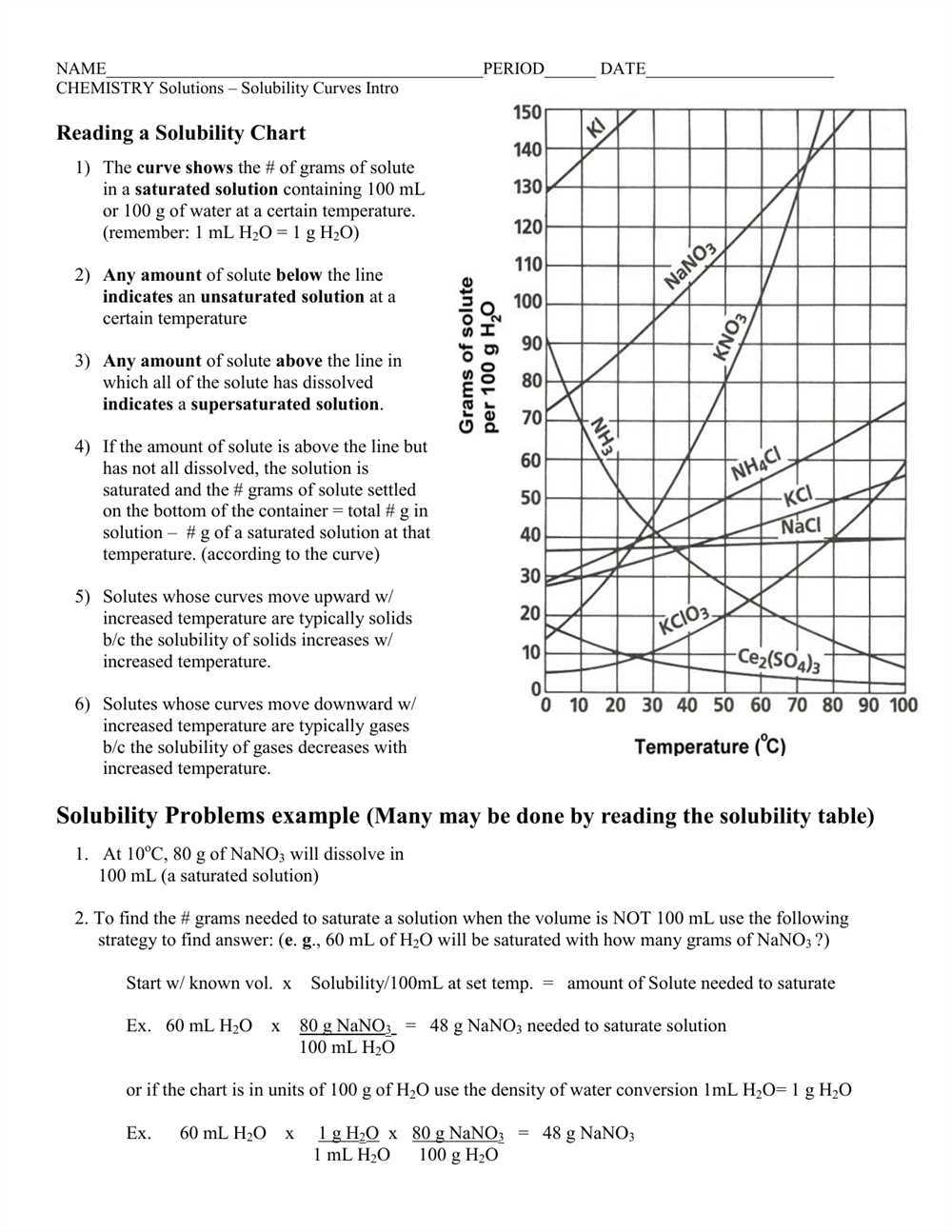
1. Time interval: The time interval is an essential component of an energy curve worksheet as it determines the duration over which the energy data is collected and analyzed. This could be hourly, daily, monthly, or any other specified timeframe.
2. Energy data: The energy data is the primary information collected and plotted on the energy curve worksheet. It represents the energy consumption or generation values for each time interval. This data can be obtained from various sources such as utility bills, energy meters, or sensors.
3. X-axis: The X-axis of an energy curve worksheet represents the time intervals in a chronological order. It allows for easy identification and comparison of energy usage patterns over time, enabling users to identify peak demand periods or any recurring trends.
4. Y-axis: The Y-axis represents the energy consumption or generation values. It provides a quantitative measure of the energy consumed or generated during each time interval. The Y-axis scale can be adjusted to accommodate the magnitude of the energy values being plotted.
5. Energy curve: The energy curve is the graphical representation of the energy data over the specified time interval. It allows users to visualize the fluctuations and trends in energy consumption or generation. By examining the shape and slope of the curve, users can identify energy-saving opportunities or detect abnormal energy usage patterns.
6. Annotated data points: Some energy curve worksheets may include annotated data points, which provide additional information about specific data points on the curve. This could include labels or tooltips that display the exact energy consumption or generation values for a particular time interval.
Overall, an energy curve worksheet is a valuable tool for understanding energy consumption patterns and making informed decisions to reduce energy waste and improve efficiency. By analyzing the components of the worksheet, users can gain insights into their energy usage and identify areas for improvement.
Step-by-step guide to filling out an energy curve worksheet
Completing an energy curve worksheet can be an important step in understanding the energy usage and efficiency of a system or process. Whether you are a student learning about energy conservation or a professional analyzing energy data, this guide will provide you with a step-by-step approach to filling out an energy curve worksheet effectively.
1. Gather the necessary data
The first step in filling out an energy curve worksheet is to gather all the necessary data about the energy usage. This may include information such as the time period for data collection, the type of energy being measured (electricity, gas, etc.), and any specific variables that need to be considered.
2. Identify the energy sources
Next, identify the different energy sources that are being used in the system. This could include electricity from the grid, renewable energy sources, or fuel sources such as gas or oil. It is important to have a clear understanding of all the energy sources involved in order to accurately analyze the energy curve.
3. Record the energy usage
Using the gathered data, record the energy usage at regular intervals throughout the designated time period. This could be done hourly, daily, weekly, or any other suitable time interval. Be sure to include any fluctuations or anomalies in the energy usage that may have occurred during the data collection period.
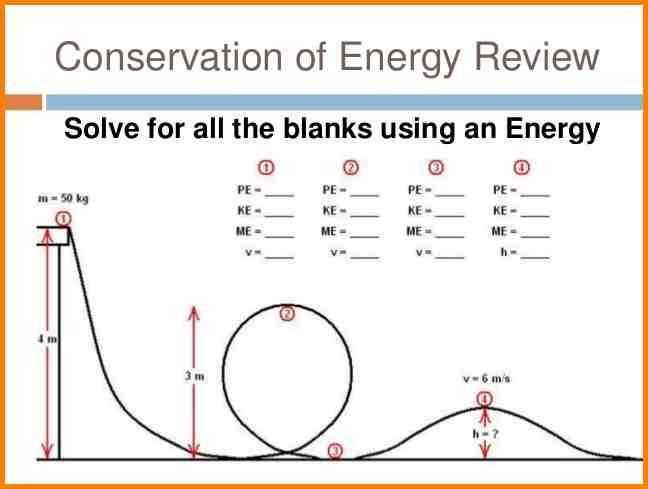
4. Plot the energy curve
Once the energy usage data has been recorded, plot the energy curve on a graph. Use the time period as the x-axis and the energy usage as the y-axis. This will visually represent how the energy usage fluctuates over time.
5. Analyze the energy curve
Analyze the energy curve to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in the energy usage. Look for any spikes or dips in the curve that may indicate inefficiencies or areas for improvement. Consider any external factors that may have influenced the energy usage during the recorded time period.
6. Make recommendations and set goals
Based on the analysis of the energy curve, make recommendations for energy conservation and efficiency improvements. Set specific goals for reducing energy usage or increasing efficiency and develop an action plan to achieve these goals.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively fill out an energy curve worksheet and gain valuable insights into energy usage and efficiency.
Common mistakes to avoid when completing an energy curve worksheet
Completing an energy curve worksheet can be a challenging task, as it requires a thorough understanding of the concepts and principles involved. However, there are some common mistakes that students often make when attempting to complete these worksheets. By identifying and avoiding these mistakes, students can ensure they accurately represent the energy changes and transitions depicted in the curve.
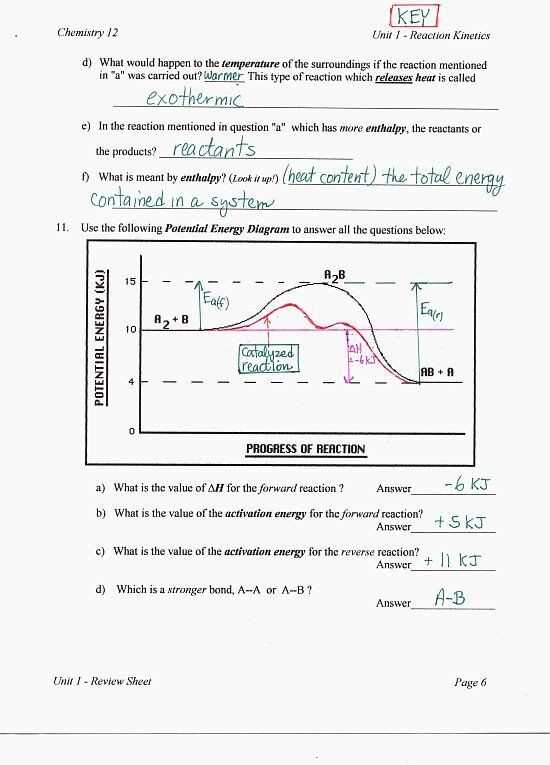
1. Misinterpretation of the axes: One of the most common mistakes is misinterpreting the axes of the energy curve. The x-axis represents the progress of the reaction or process, while the y-axis represents the energy. Students should be careful to correctly label and interpret these axes to accurately depict the energy changes.
2. Incorrect labeling of energy states: Another common mistake is incorrectly labeling the energy states on the curve. It is important to accurately identify the reactants, products, and transition states, as well as any other energy states that may be present. Students should carefully analyze the curve and use their knowledge of the specific reaction or process to correctly label these states.
3. Inaccurate depiction of energy changes: Students may also make mistakes in accurately depicting the energy changes on the curve. It is crucial to correctly represent the energy differences between the different states and transitions. This includes correctly depicting the energy of activation and any potential energy barriers or intermediate energy states.
4. Failure to consider conservation of energy: A common mistake is failing to consider the principle of conservation of energy. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. Therefore, the total energy of the system should remain constant throughout the reaction or process. Students should ensure that their energy curve reflects this principle and accurately represents the energy changes in accordance with conservation of energy.
5. Neglecting significant factors: Finally, students may overlook certain significant factors that can affect the energy curve. These factors may include catalysts, temperature changes, or changes in pressure. It is important to consider these factors and their influence on the energy changes depicted in the curve.
In conclusion, completing an energy curve worksheet requires careful attention to detail and a solid understanding of the underlying concepts. By avoiding common mistakes such as misinterpreting the axes, incorrectly labeling energy states, inaccurately depicting energy changes, neglecting conservation of energy, and overlooking significant factors, students can ensure they accurately represent the energy transitions and changes in the curve.
Tips and tricks for accurately analyzing energy curve data

When it comes to analyzing energy curve data, accuracy is key. Making mistakes or misinterpreting the data can lead to incorrect conclusions and decisions. To ensure an accurate analysis, here are a few tips and tricks:
1. Understand the variables and units:
Before diving into the data, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the variables being measured and the units they are expressed in. This will help in correctly interpreting the data and conducting calculations accurately. Take time to familiarize yourself with the energy units and any conversions that may be necessary.
2. Use proper visualization techniques:
Visualizing the energy curve data can provide valuable insights and make it easier to identify trends and patterns. Utilize graphs and charts to represent the data in a clear and concise manner. Line plots, scatter plots, or histograms are commonly used to analyze continuous data, while bar graphs are suitable for categorical data.
3. Check for outliers:
Outliers in the data can significantly affect the analysis. These extreme values may be errors or represent unusual occurrences. It’s important to identify and address outliers to prevent them from skewing the results. One approach is to use statistical measures like the z-score or interquartile range to identify and remove outliers.
4. Consider the context:
When analyzing energy curve data, it’s crucial to consider the context in which the data was collected. Understand the purpose of the study or experiment and how the variables were measured. Any external factors or conditions that may have influenced the data should be taken into account to avoid drawing incorrect conclusions.
5. Validate and cross-reference:
Double-checking your analysis by cross-referencing with other sources of information or conducting validations can help ensure the accuracy of your conclusions. This can involve comparing your results with previous studies or consulting with experts in the field to verify your findings.
By following these tips and tricks, you can improve the accuracy of your analysis when working with energy curve data. Ensuring an accurate analysis will provide more reliable insights and support better decision-making in various energy-related contexts.