In order to understand and improve the efficiency of energy storage and transfer, scientists and engineers often create models and conduct experiments to test their hypotheses and predictions. These models allow researchers to simulate various scenarios and study the behavior and characteristics of different energy storage and transfer systems.
One common type of model used in energy storage and transfer research is the mathematical model. This model involves using equations and mathematical principles to describe the behavior of energy storage and transfer systems. By inputting different variables and parameters into the model, researchers can simulate the performance of various energy storage and transfer technologies and analyze their efficiency and effectiveness.
Another type of model used in energy storage and transfer research is the physical model. This model involves building physical replicas of energy storage and transfer systems in order to study their behavior and performance. These physical models often include scaled-down versions of energy storage devices such as batteries or capacitors, and researchers can manipulate and measure various parameters to analyze how the system responds to different conditions.
By using these models, researchers can gain valuable insights into the behavior and efficiency of energy storage and transfer systems. They can identify potential issues or weaknesses and develop strategies to optimize the performance and reliability of these systems. Ultimately, the goal is to improve the sustainability and reliability of energy storage and transfer technologies, leading to a more efficient and environmentally friendly energy infrastructure.
Energy Storage and Transfer Model Test
Energy storage and transfer is a crucial aspect of modern-day technology and infrastructure. It is essential for ensuring a reliable and continuous supply of energy to meet the demands of various industries and individuals. To evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of energy storage and transfer models, rigorous testing is necessary.
One of the key parameters that need to be tested is the storage capacity of the energy storage system. This involves measuring the amount of energy that can be stored and retrieved from the system under different operating conditions. The testing procedure typically involves charging the system with a known amount of energy and then measuring the energy discharged over a specific period of time. This helps determine the storage capacity and efficiency of the system.
Another important aspect of testing energy storage and transfer models is evaluating their ability to handle peak power demands. This involves subjecting the system to high power loads to assess its performance under stressful conditions. The testing procedure may involve simulating real-world scenarios or using simulated loads to replicate peak power demands. The system’s ability to deliver energy without experiencing significant performance degradation or failures is crucial for its successful deployment.
In addition to storage capacity and peak power handling, the testing of energy storage and transfer models also includes assessing their efficiency and reliability. The efficiency of the system refers to the amount of energy that is lost during the storage and transfer process. Testing can involve measuring the energy losses at different stages of the system, such as during charging, discharging, and transmission. Reliability testing, on the other hand, focuses on evaluating the system’s ability to operate consistently and predictably over an extended period of time.
In summary, energy storage and transfer model testing is a critical step in ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of these systems. By evaluating parameters such as storage capacity, peak power handling, efficiency, and reliability, researchers and engineers can identify the strengths and weaknesses of different models and make informed decisions regarding their deployment in various applications.
Importance of Model Testing in Energy Storage and Transfer
Model testing plays a crucial role in the development and optimization of energy storage and transfer systems. It provides a cost-effective and efficient way to evaluate the performance, safety, and reliability of these systems before their implementation in real-world applications. By simulating different scenarios and conditions, model testing allows engineers to identify potential issues, assess the system’s behavior, and make necessary modifications to improve its performance.
One of the key advantages of model testing is its ability to predict the behavior of energy storage and transfer systems under various operating conditions. This is particularly important in renewable energy systems, where the availability and variability of energy sources can significantly impact system performance. By using models, engineers can evaluate the system’s response to different energy inputs, storage capacities, and transfer mechanisms, allowing them to optimize system design and operation.
- Performance Evaluation: Model testing enables engineers to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of energy storage and transfer systems. This includes evaluating parameters such as energy conversion efficiency, power output, and charging/discharging rates. Through model testing, engineers can identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies and make design improvements to enhance system performance.
- Safety Assessment: Model testing also helps in evaluating the safety aspects of energy storage and transfer systems. By simulating different operating conditions and failure scenarios, engineers can assess the risks associated with these systems and develop appropriate safety measures to mitigate them. This ensures the implementation of reliable and safe energy storage and transfer systems.
- Optimization and Cost Reduction: Model testing allows engineers to explore different design configurations, materials, and operating strategies without the need for expensive and time-consuming real-world experiments. By optimizing system parameters through model testing, engineers can reduce development costs, achieve better system performance, and advance the overall efficiency of energy storage and transfer technologies.
Overall, model testing is a vital tool in the development and optimization of energy storage and transfer systems. It enables engineers to evaluate performance, assess safety, and optimize system design, ultimately advancing the deployment of efficient and reliable energy storage and transfer technologies.
Overview of Energy Storage and Transfer Models
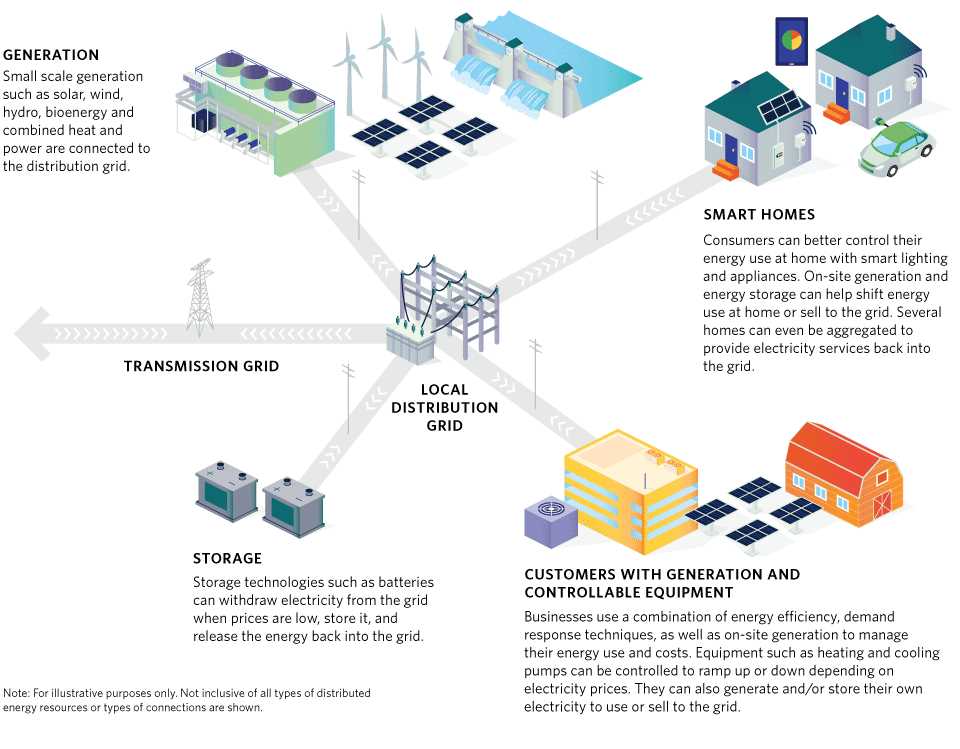
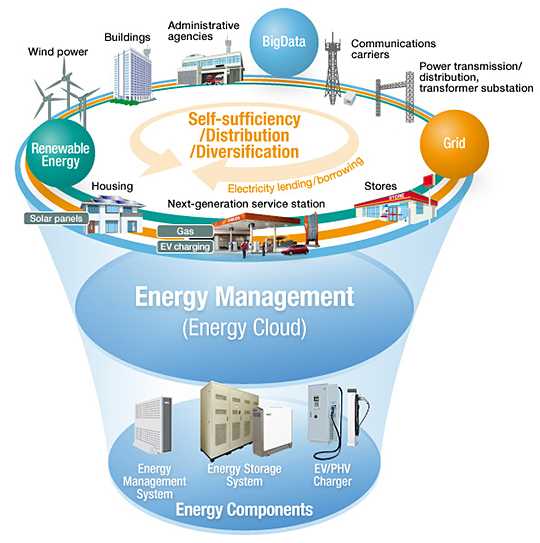
Energy storage and transfer play a crucial role in various industries and technological advancements. Understanding the different models and methods used for energy storage and transfer is essential for optimizing efficiency, reducing waste, and ensuring sustainable energy practices.
One common energy storage model is the use of batteries. Batteries store electrical energy through chemical reactions and can be utilized in various applications such as electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems. They provide a reliable and portable source of energy and have become increasingly advanced and efficient over time.
Another key model for energy storage and transfer is pumped hydro storage. This method involves pumping water from a lower reservoir to a higher one during periods of low energy demand, and then releasing it through turbines to generate electricity during peak demand. Pumped hydro storage systems offer a large-scale and long-lasting solution for storing excess energy and can be integrated with renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
Thermal energy storage is another important model utilized in industries such as manufacturing and district heating. This method involves storing thermal energy in various forms such as molten salt or phase change materials, which can later be used to generate steam or heat. Thermal energy storage provides a way to efficiently utilize waste heat, optimize energy consumption, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, power-to-gas technology is gaining attention as a valuable energy storage and transfer model. This technique converts excess electrical energy into chemical energy by using electrolysis to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen produced can then be stored and utilized as a fuel source or feedstock for various industrial processes, offering a way to store renewable energy and enable its use in sectors that currently rely on fossil fuels.
Overall, these various energy storage and transfer models offer diverse solutions to address the challenges of energy management, grid stability, and sustainability. By exploring and developing these models further, we can enhance the integration of renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Methodology for Conducting Energy Storage and Transfer Model Test
Developing an accurate and reliable energy storage and transfer model is crucial for assessing the performance of various energy systems and optimizing their efficiency. The methodology for conducting a model test involves a series of steps to ensure the accuracy and validity of the results obtained.
Step 1: Define the objectives: Prior to conducting the model test, it is important to clearly define the objectives of the study. This involves identifying the specific energy system being analyzed and determining the key parameters and variables that need to be considered.
Step 2: Gather data: The next step involves gathering the necessary data to build the energy storage and transfer model. This includes information on the energy sources, the energy storage technologies used, and any relevant environmental factors. Accurate and reliable data collection is crucial for the accuracy of the model test.
Step 3: Design the model: Using the gathered data, the energy storage and transfer model is designed. This involves developing mathematical equations and algorithms that represent the energy system and its components. The model should accurately reflect the behavior and characteristics of the system being studied.
Step 4: Validate the model: The developed model is validated by comparing its predictions with real-world data or existing experimental results. This helps ensure that the model accurately represents the system being studied. If discrepancies are found, adjustments and refinements are made to improve the model’s accuracy.
Step 5: Perform the model test: Once the model is validated, the actual test is conducted using the model to simulate different scenarios and conditions. This may involve analyzing the performance of the energy storage technologies, evaluating the efficiency of energy transfer processes, or assessing the impact of external factors on the system.
Step 6: Analyze and interpret the results: After the model test is completed, the results obtained are analyzed and interpreted to draw meaningful conclusions. This involves identifying trends, patterns, and relationships between different variables, and assessing the overall performance of the energy system.
Step 7: Optimize and refine the model: Based on the results and conclusions obtained from the model test, the energy storage and transfer model can be further optimized and refined. This may involve making adjustments to the model parameters or incorporating additional data and variables to improve its accuracy and predictive capabilities.
In conclusion, the methodology for conducting an energy storage and transfer model test involves defining objectives, gathering data, designing the model, validating it, performing the test, analyzing the results, and optimizing the model. This systematic approach ensures that the model accurately represents the energy system being studied and helps in making informed decisions regarding the design and operation of energy systems.
Challenges in Energy Storage and Transfer Model Testing
Energy storage and transfer models are crucial for understanding and predicting the performance of various energy storage technologies and systems. These models help engineers and researchers design and optimize energy storage systems, ensure their reliability and efficiency, and make informed decisions regarding their deployment and integration into the grid. However, testing these models poses several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Complexity of the system: Energy storage and transfer models often involve complex systems that include multiple components, such as batteries, capacitors, inverters, and converters. These components interact with each other and with other elements of the system, making it challenging to accurately model their behavior and interactions. Testing these models requires a thorough understanding of the individual components and their interactions, as well as the ability to accurately represent these interactions in the model.
Data availability and quality: Testing energy storage and transfer models requires access to accurate and reliable data for the various components and their performance characteristics. However, obtaining such data can be challenging, especially for emerging technologies or when real-world data is limited. In addition, the quality of the available data can vary, leading to uncertainties in the model predictions. Ensuring data accuracy and relevance is crucial for validating and refining the models.
Verification and validation: Validating energy storage and transfer models is essential to ensure that they accurately represent the behavior of the real-world systems. However, verification and validation can be challenging due to the lack of standardized testing protocols and metrics. Developing robust verification and validation methods and benchmarks is necessary to establish the credibility and reliability of the models.
Model scalability and adaptability: Energy storage and transfer models need to be scalable and adaptable to different system sizes, configurations, and operating conditions. However, developing models that can accurately represent a wide range of system scales and operating conditions can be challenging. Testing the scalability and adaptability of these models requires access to diverse test data and the ability to accurately capture the behavior of the system under different scenarios.
Addressing these challenges in energy storage and transfer model testing is crucial for advancing the development and deployment of energy storage technologies and systems. Overcoming these challenges will help researchers and engineers develop more accurate and reliable models, leading to improved design, optimization, and integration of energy storage systems into the grid.