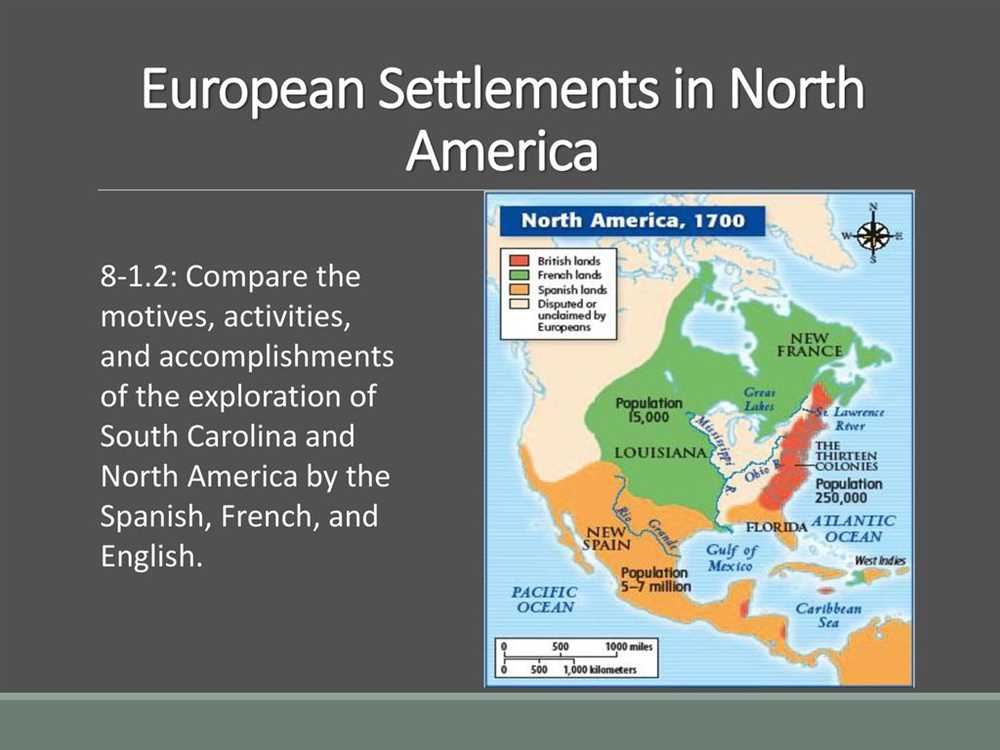
European exploration and settlement in the New World during the 15th and 16th centuries had a profound impact on the course of history. This period of exploration was characterized by the quest for new trade routes, the discovery of new lands, and the establishment of colonies. The answer key to understanding this era lies in examining the motivations behind European exploration, the key players involved, and the consequences of their actions.
One of the primary motivations for European exploration was the desire to find new trade routes to Asia. For centuries, European merchants had relied on overland trade routes, which were long and perilous. They sought to find a direct sea route that would allow them to bypass these treacherous routes and establish lucrative trade connections with the wealthy markets of the East. This desire for wealth and trade played a significant role in spurring European explorers to set sail and discover new lands.
The key players in European exploration and settlement were the European monarchies and their sponsored explorers. In the 15th and 16th centuries, countries such as Spain, Portugal, England, and France sponsored voyages of exploration in search of new lands and trade routes. Explorers like Christopher Columbus, Vasco da Gama, and Ferdinand Magellan were instrumental in opening up new territories and establishing European control over them. These explorers were often driven by a combination of personal ambition, the promise of wealth and prestige, and the desire to spread Christianity.
The consequences of European exploration and settlement were far-reaching. For the indigenous peoples of the New World, the arrival of Europeans meant the loss of their land, resources, and sovereignty. European diseases, warfare, and forced labor had devastating effects on the indigenous populations, leading to the decimation of entire civilizations. On the other hand, European exploration and settlement also brought about the exchange of ideas, goods, and technologies between the Old World and the New World, forever shaping the course of human history.
European Exploration and Settlement Answer Key
The European exploration and settlement of the Americas brought significant changes to the continent. Here is the answer key to some of the key questions related to this topic.
1. Why did Europeans explore and settle in the Americas?
Europeans explored and settled in the Americas for various reasons. One of the main motivations was to find new trade routes to Asia and establish colonies to gain economic benefits. They also aimed to spread Christianity and convert the indigenous peoples. Additionally, European rulers sought to increase their power and prestige by expanding their territories overseas.
2. How did the Europeans navigate and explore the Americas?
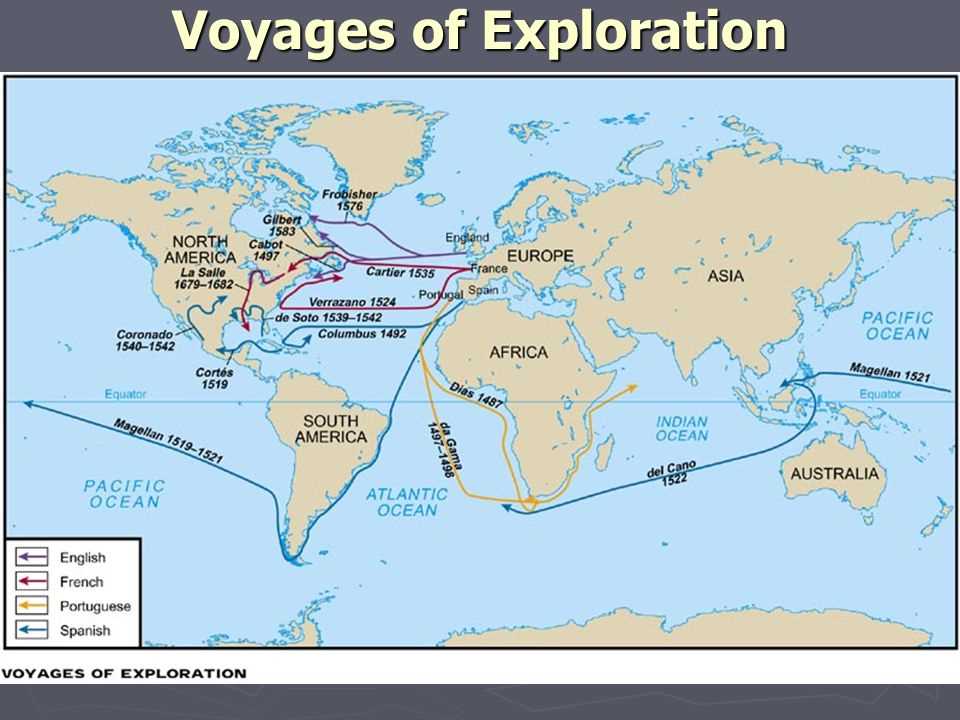
The Europeans used various navigation techniques to explore the Americas. They relied on the astrolabe and compass to determine their position and direction. They also used maps and charts, which were constantly improved and updated as new discoveries were made. The Europeans often followed the coastlines and used natural landmarks to navigate. They also relied on the knowledge and skills of Native American guides and interpreters to explore the unfamiliar territories.
3. What were the consequences of European exploration and settlement?
The consequences of European exploration and settlement were both positive and negative. On one hand, the European presence led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and technology between the Old World and the New World. This exchange, known as the Columbian Exchange, had a significant impact on the global economy and the development of both regions. On the other hand, the exploration and settlement resulted in the displacement and mistreatment of indigenous populations, the introduction of new diseases that decimated native communities, and the establishment of a system of colonization and exploitation. It also laid the foundation for the transatlantic slave trade, which had devastating consequences for African communities.
4. What were some of the major European explorers and their contributions?
Some of the major European explorers and their contributions include Christopher Columbus, who is credited with the discovery of the Americas; John Cabot, who explored the North American coast; Hernán Cortés, who conquered the Aztec Empire in Mexico; and Ferdinand Magellan, who led the first expedition to circumnavigate the globe. These explorers opened up new areas for European colonization and contributed to the expansion of European influence and power.
Christopher Columbus and the Age of Exploration
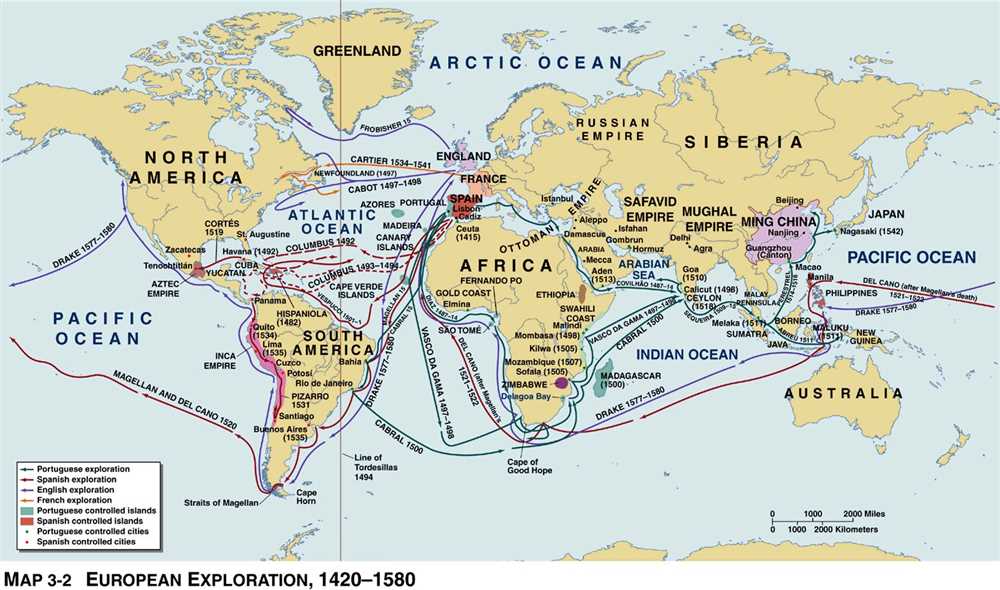
The Age of Exploration, also known as the Age of Discovery, was a period of time in the late 15th century and early 16th century when European explorers embarked on expeditions to discover new trade routes, riches, and land. One of the most well-known figures from this era is Christopher Columbus, an Italian explorer who is credited with leading the first European expedition to the Americas.
Columbus was born in Genoa, Italy, and began his career as a sailor and navigator at a young age. Inspired by the writings of Marco Polo and other explorers, he became convinced that it was possible to reach Asia by sailing west across the Atlantic Ocean. In 1492, Columbus secured funding from the Spanish monarchs, Queen Isabella and King Ferdinand, and set sail on his first voyage.
Columbus’s first voyage – Columbus’s first voyage took him to the Caribbean islands of the Bahamas, Cuba, and Hispaniola. Although he believed that he had reached Asia, he had actually arrived in the Americas, thus beginning a new era of exploration and colonization.
Impact of Columbus – Columbus’s voyages had a profound impact on world history. They opened up new trade routes and led to the colonization and exploitation of the Americas by European powers. However, they also led to the displacement and mistreatment of indigenous peoples, as well as the spread of diseases that had devastating effects on native populations.
- Exploration and colonization – Columbus’s voyages paved the way for European powers to establish colonies in the Americas. These colonies became important hubs of trade and helped to fuel European expansion and dominance in the world.
- Cultural exchange – Columbus’s voyages also led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the Old World and the New World. This exchange had lasting effects on both sides, shaping the development of art, literature, and society.
- Controversy and criticism – Columbus’s legacy is not without controversy. His treatment of indigenous peoples and his role in the transatlantic slave trade have been widely criticized, and there have been calls to reconsider the celebration of Columbus Day as a national holiday.
In conclusion, Christopher Columbus and the Age of Exploration were pivotal in shaping the modern world. While Columbus’s expeditions opened up new trade routes and expanded European influence, they also had significant negative consequences. It is important to study and understand this era of history in order to fully grasp the complexities and impact of European exploration and settlement.
The Motives for European Exploration
European exploration of the world was driven by a variety of motives, including economic, religious, political, and technological factors. The desire for wealth and resources, such as gold, spices, and precious metals, was a major driving force behind European expansion. The discovery of new trade routes to the East, specifically to India and China, was seen as a way to bypass the Middle Eastern and Mediterranean middlemen who controlled the lucrative spice trade.
Religion also played a significant role in European exploration. Many European explorers were motivated by a desire to spread Christianity to new lands and convert indigenous populations to their faith. This was particularly true for Spanish and Portuguese explorers, who were influenced by the religious fervor of the Catholic Church during the time of the Spanish Inquisition and the Reconquista.
In addition to economic and religious motives, political factors also played a role in European exploration. The quest for power and prestige drove many European monarchs to sponsor exploratory voyages. They hoped to establish colonies and expand their empires, which would increase their wealth and influence on the world stage.
Lastly, technological advancements in navigation and shipbuilding during the Renaissance period enabled European explorers to undertake longer and more dangerous voyages. The invention of the compass, improvements in mapmaking, and the development of more seaworthy ships, such as the caravel, allowed European sailors to venture further into uncharted waters.
In conclusion, the motives for European exploration were multi-faceted, encompassing economic, religious, political, and technological factors. The pursuit of wealth, the spread of Christianity, the desire for power and prestige, and advancements in navigation all played a significant role in driving European expansion and the discovery of new lands.
The Conquest of the Americas
The conquest of the Americas by European explorers and settlers in the late 15th and early 16th centuries had a profound impact on the indigenous peoples of the region. The arrival of the Europeans, particularly the Spanish and Portuguese, brought about significant changes in the social, political, economic, and cultural landscape of the Americas. The conquest resulted in the establishment of European colonies, the introduction of new diseases, the displacement and enslavement of indigenous populations, and the exploitation of the continent’s natural resources.
One of the key factors that facilitated the conquest of the Americas was the technological and military superiority of the European explorers. The Europeans possessed advanced weapons, such as firearms and cannons, which gave them a significant advantage over the indigenous peoples who mainly used traditional weapons like bows and arrows. Additionally, the Europeans had superior ships and navigational skills, enabling them to travel long distances and explore new territories.
The conquest of the Americas was also driven by economic motives. The Europeans were searching for new trade routes to Asia and hoped to find wealth and resources in the Americas. They sought to establish colonies to exploit the vast reserves of gold, silver, and other valuable resources that they discovered. The Europeans also introduced new agricultural practices and crops to the Americas, transforming the landscape and creating new economic opportunities.
However, the conquest of the Americas had devastating consequences for the indigenous peoples. The introduction of new diseases, such as smallpox, to which the indigenous populations had no immunity, resulted in widespread death and population decline. The Europeans also engaged in violent conflicts with the indigenous peoples, often leading to the destruction of their communities and the enslavement of survivors. The cultural and social fabric of the Americas was forever changed as indigenous languages, customs, and traditions were suppressed or lost.
In conclusion, the conquest of the Americas by European explorers and settlers had far-reaching effects on both the indigenous populations and the European colonizers. While it resulted in the establishment of European colonies and the exploitation of the region’s resources, it also brought about the tragic loss of lives, cultural assimilation, and the lasting impact of European dominance in the Americas.
The Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the New World and the Old World that occurred after Christopher Columbus’s arrival in the Americas in 1492. This exchange had a profound and lasting impact on both regions, shaping the course of history and influencing the development of societies on both sides of the Atlantic.
One of the most significant aspects of the Columbian Exchange was the transfer of crops and agricultural practices. Europeans introduced crops such as wheat, rice, and barley to the Americas, while indigenous people shared their knowledge of maize, potatoes, and tomatoes. This exchange of crops revolutionized agriculture in both regions, leading to increased food production and population growth.
Another major impact of the Columbian Exchange was the introduction of new animals to the Americas. Europeans brought livestock such as horses, cows, and pigs, which dramatically transformed the way of life for indigenous people. Horses, in particular, revolutionized transportation and warfare, allowing for the rapid expansion of European colonies and the destruction of indigenous civilizations.
However, along with these beneficial exchanges came the spread of diseases. Europeans unintentionally brought diseases such as smallpox, measles, and influenza to the Americas, diseases to which indigenous populations had no immunity. The result was devastating: millions of indigenous people died from these diseases, leading to the collapse of entire societies and the decimation of indigenous cultures.
In summary, the Columbian Exchange was a complex network of interactions between the Old World and the New World that brought about significant changes to both regions. While it led to the exchange of valuable resources and knowledge, it also had devastating consequences, particularly for the indigenous populations of the Americas. The legacy of the Columbian Exchange can still be felt today in the cultural, economic, and environmental transformations that took place as a result of this historic event.
Impact on Native American Societies
The arrival of European explorers and settlers had a profound impact on Native American societies in North America. These societies had developed complex cultures and thriving economies long before the Europeans arrived, but their way of life was fundamentally altered by the arrival of these new settlers.
One of the most significant impacts of European exploration and settlement on Native American societies was the introduction of foreign diseases. Diseases such as smallpox, measles, and influenza, for which Native Americans had no immunity, decimated their populations. This led to the collapse of many Native American societies, as entire communities were wiped out by these diseases. The loss of so many people had devastating effects on their social structures, economies, and cultural practices.
The arrival of Europeans also led to the displacement and forced relocation of Native American tribes. As the Europeans expanded their colonies, Native Americans were often pushed off their ancestral lands and forced to move to unfamiliar territories. This created conflict and tension between Native American tribes, as they were often forced to compete for limited resources in new areas. The disruption caused by forced relocation also had profound effects on their social structures and traditional ways of life.